SAP Landscape Transformation SLT Server: Beginners Guide 2025
Background
The SLT (SAP Landscape Transformation) replication server is an essential tool for organizations using SAP HANA as their primary reporting database. For these enterprises, fast and efficient data replication is crucial to support timely decision-making. Data can come from a variety of sources, including both SAP and non-SAP systems. Balancing the need for up-to-date data while minimizing the load on the original source is key.
The SLT Replication Server addresses this need effectively, offering a reliable solution for HANA users who require real-time or scheduled data replication from both SAP and non-SAP sources, whether their systems are on-premise or in the cloud. With SLT, accessing the latest information is straightforward, ensuring timely and accurate data availability.
Evolution of SLT Replication Server
The journey of SLT replication server originally began in 2010 as a real-time replication tool for SAP HANA, formerly known as DMIS – Data Migration Server. Since its inception, SLT has undergone significant developments, evolving into a robust middleware solution capable of supporting change data capture and real-time replication scenarios for various SAP products.
Introduction
The SAP Landscape Transformation (SLT) Replication Server is a robust solution designed for real-time or scheduled data replication to SAP HANA databases. It connects to both SAP and non-SAP systems, facilitating the transfer of data while ensuring minimal disruption to source systems. This capability is crucial for organizations that rely on timely and accurate data for their business operations. The SLT Replication Server is an integral component of the SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP), enabling real-time data loading and replication. This capability equips businesses with the tools to operate applications efficiently and conduct swift analysis of data.
By facilitating seamless, real-time data transfer across diverse systems within the same network, wide-area network (WAN), and the cloud, the SAP LT replication server ensures that precise information is promptly accessible exactly when and where it is needed. It seamlessly integrates with various software’s such as SAP HANA, SAP S/4HANA for central finance foundation, and SAP BW/4HANA.
Trigger-based Approach
The SAP LT replication server adopts a trigger-based replication approach for transferring data from the source system to the target system. Furthermore, users have the flexibility to establish transformation rules, allowing for selective data replication during the data replication process. This empowers users to exert granular control over the data replication process, ensuring that only relevant data is transferred based on specific requirements.
Features
- SLT utilizes a trigger-based approach for data transfer, recording inserts, updates, and deletes for specific chosen tables, all while minimizing impact on the source system’s performance.
- Additionally, it provides a user-friendly interface for easy configuration, monitoring, and reporting.
- Supports both real-time and scheduled data transfer, aligning with multiple use cases.
- Ensures data consistency and integrity between source and target system(s).
- Provides built-in error handling and logging mechanism for easy issue resolution.
- Supports and configures multiple system connections, including both 1:N and N:1.
- Offers data transformation, conversion, and filtering capabilities.
- Facilitates parallel processing to optimize data transfer performance.
- Supports pool, cluster, and INDX-like tables, a feature that other technologies may struggle to support.
- Enables manipulation of data before loading into a SAP HANA database.
- Actively supports non-Unicode and Unicode conversion during data replication.
- Integrates with SAP HANA studio.
- Offers data monitoring through SAP Solution manager.
Key Benefits
The SAP LT replication server offers several significant benefits that make it valuable data replication tools for organizations:
- Real-Time Data Access: SLT provides real-time or scheduled data replication, ensuring that the most current information is always available. This is vital for effective decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Seamless Integration: SLT integrates smoothly with both SAP and non-SAP data sources. Whether your systems are on-premise or in the cloud, SLT ensures efficient data transfer with minimal impact on source systems.
- High Availability: By maintaining a standby database, SLT helps ensure business continuity. In the event of system failures or disasters, SLT’s replication capabilities support uninterrupted operations.
- Reduce Data Volume: It minimizes data volume transfers to delta technology using SAP solutions like SAP BW/4HANA, resulting in significantly decreased data loads. SLT uses trigger based approach to extract and replicate only selective or relevant and modified data changes, rather than transferring entire data sets.
- Facilitates Efficient Data Migration: It serves as an effective tools for data migration projects, enabling businesses to seamlessly transfer data from legacy systems or non-SAP systems to newer SAP systems or databases in real-time. This ensures smooth and continuous flow of data, minimizing downtime and disruptions to business operations.
- Flexible Data Replication: SLT supports various data replication methods, including initial data loads and delta updates, allowing businesses to tailor the replication process to their specific needs.
In summary, the SLT replication server actively delivers various advantages. It empowers organizations to efficiently manage their data integration needs and leverage the benefits of real-time data for better decision-making and business insights.
Use Cases
SAP Landscape Transformation (SLT) Replication Server offers various benefits for managing data across your organization. Here are some key use cases:
- Automated Data Loading and Replication: SLT streamlines data replication across large and distributed systems, supporting both non-Unicode and Unicode conversions. This automation ensures efficient and accurate data transfer.
- Simplified Data Transformation: It translates complex SAP application structures into clear and straightforward table formats, making data transformation easier and more transparent.
- Real-Time Data for Analytics: SLT provides real-time data provisioning, ensuring that the latest and most accurate data is available for reporting and analysis.
- Enhanced Performance for Large Transactions: It accelerates the processing of large-volume transactions in SAP HANA, leading to improved performance and faster data handling.
- Active Synchronization Between SAP ERP Systems: SLT enables smooth data exchange and synchronization between multiple SAP ERP systems, facilitating efficient business operations.
- Replacement of Current Data Transfer Solutions: Consider upgrading to real-time data replication to enhance your current data transfer methods. SLT offers automated data loading, replication, and conversion processes.
- Transaction Integrity and Recovery: SLT ensures reliable data replication with transaction integrity, point-in-time recovery, and extensive logging capabilities for added reliability.
These use cases highlight how SLT can improve data management, enhance performance, and ensure reliability across your SAP systems.
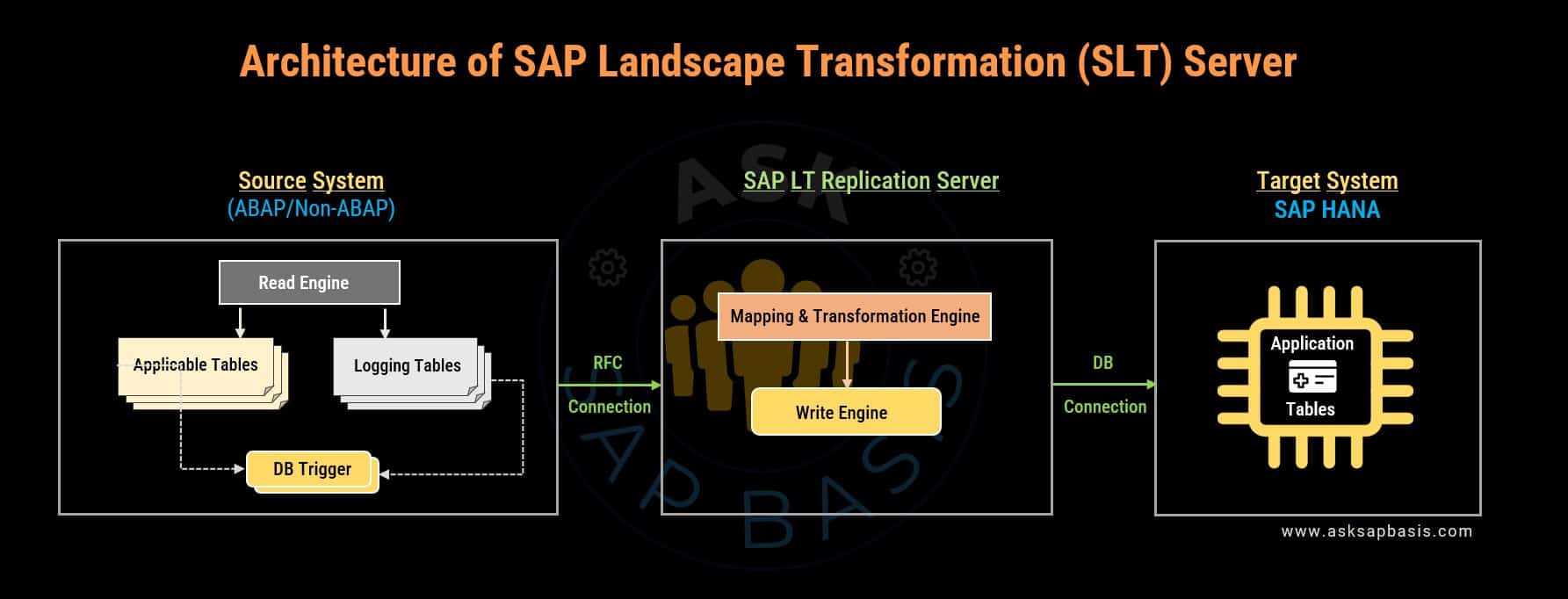
SLT Architecture
The technical system landscape comprises the following components:
SAP Source System (ABAP Based)
- The source system utilizes database triggers to track database changes and records information about those changes in logging tables.
- Read engine, situated on the ABAP source system, transfer the data from the source system to the SAP LT replication server. The read modules extract the relevant data from the application tables.
- For source systems, the data is extracted by means of remote function calls (RFC) and pushed to HANA by means of direct SQL calls (via DB connection).
Non-ABAP Based Source System
- The non-ABAP source system actively tracks database changes using database triggers and captures information about those changes in logging tables.
- Read modules, situated at the SAP LT Replication Server, transfer the data from the non-ABAP source system to the SAP LT Replication Server. The read modules extract the relevant data from the application tables.
SAP Landscape Transformation Replication Server
- It is an SAP server that is based on replication technology that enable the replication of data from one or more source systems to one or more target systems. The source system can be SAP or non-SAP system.
- It manages the database triggers that are set up on the source tables to capture data changes. The mapping engine facilitates the mapping of data from source to target data structures.
- The transformation engine enables the transformation of data during the replication process. It applies data manipulation rules, such as filtering, aggregating, and splitting, to ensure data is adapted to the structure of target system.
SAP HANA System
- The target system is SAP HANA which contains the SAP HANA database, used to store the replicated data.
- The SAP LT Replication Server communicates with SAP HANA via database connection.
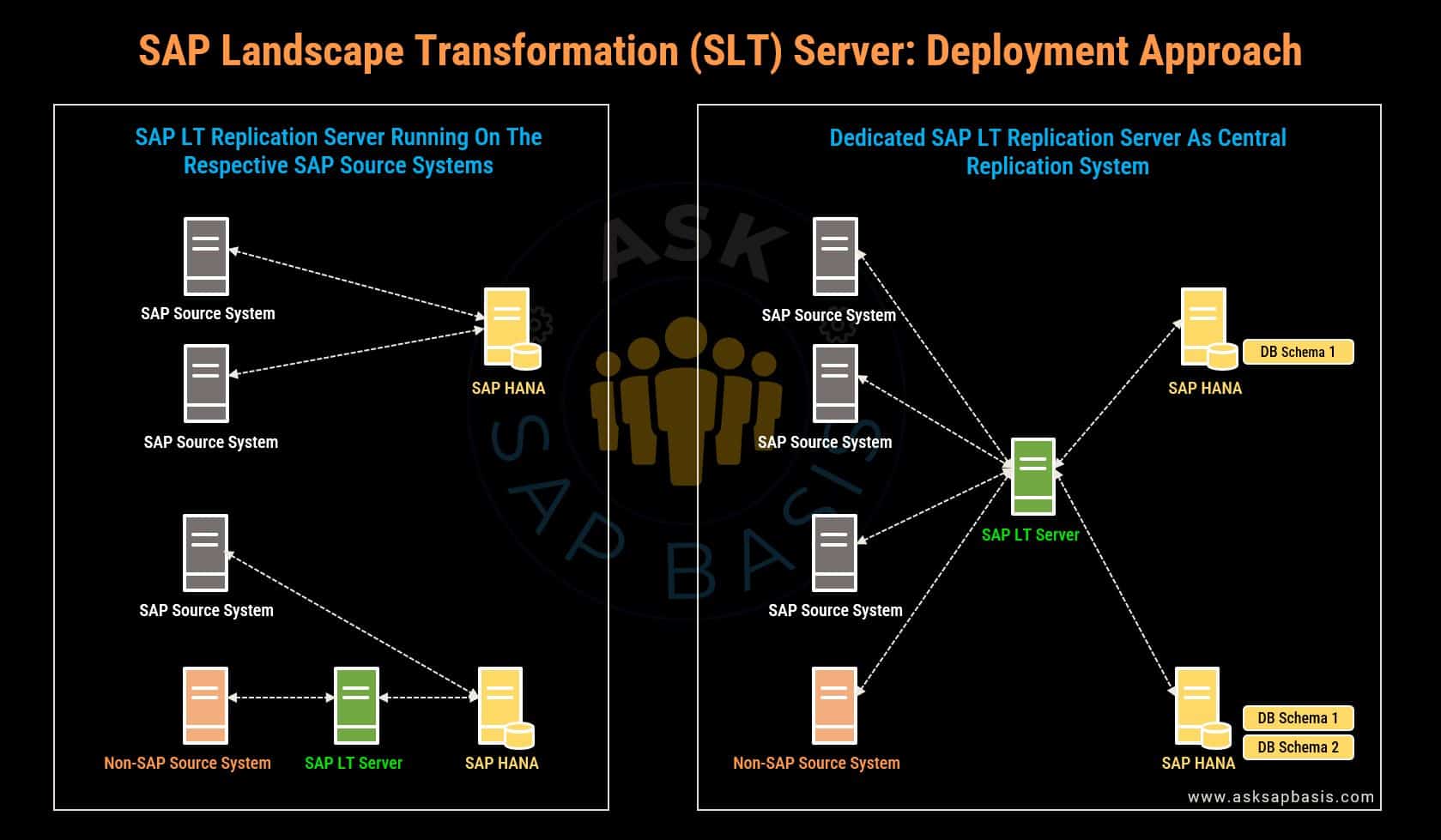
SLT Deployment Approach
First and foremost, SAP LT is a technology that is deployed exclusively on-premise.
SAP offers additional technologies, like like SDI (Smart Data Integration) and SDA (Smart Data Access), to seamlessly support data replication, integration and access. For more details, you can refer to SAP HANA cloud documentation.
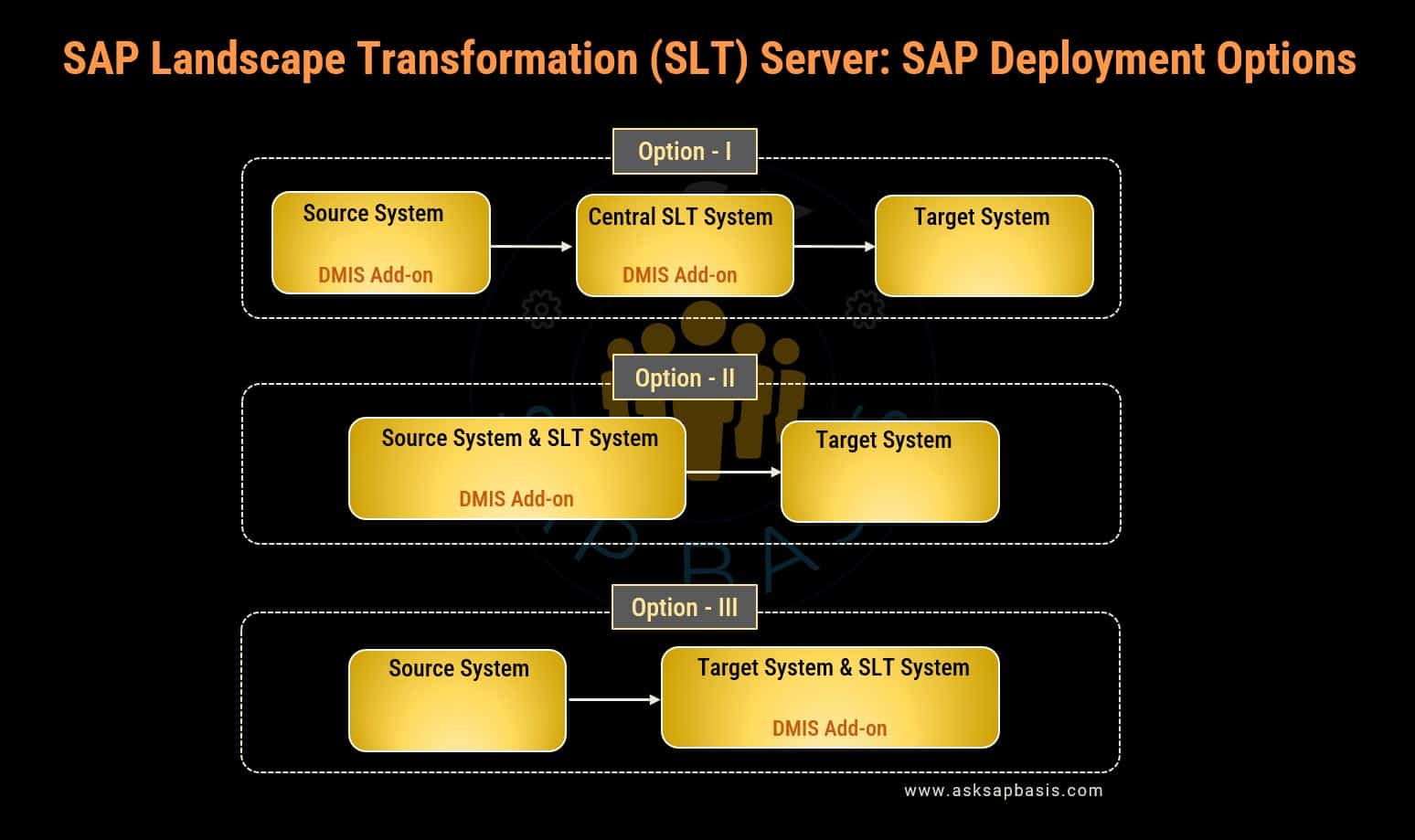
The deployment approach for the SAP LT Replication server offers a high degree of flexibility. It can be installed as:
1) An add-on (DMIS) on any SAP source system or on separate host.
- In case of S/4HANA system (onPremise), SLT is included.
- However, it should be noted that S/4HANA as central SLT system is only released for distinct scenarios, such as replication to various SAP systems (like S/4HANA, SAP Business Suite, SAP Central Finance, SAP Data Intelligence etc).
- In case of any other ABAP-based system, SLT can be installed via DMIS add-on.
2) An central component which serves multiple source and multiple target systems. (Recommended approach)
- If deployed as a central component, you have two options:
- to connect source systems to either the same HANA system and schema.
- to connect source systems to separate HANA schemas on the same HANA system.
Various deployment options for SAP based systems are available, based on specific scenarios and the involved systems.
Key Deployment Factors
The critical performance influencing factors for the SAP LT replication server deployment include:
1) SAP LT replication server and SAP HANA Version compatibility
To achieve optimal performance of SAP LT replication server, you must apply all relevant SAP Notes and recommendations outlined in the installation guide and central SAP note (Note#1605140) for SAP LT replication server to your system.
2) Network Connectivity
Achieving high performance with the SAP LT Replication Server solution relies on a low-latency network and accurately calculated bandwidth. In environments with frequent network failures, the replication process repeats until successful completion, resulting in increased resource consumption and longer execution time.
3) Data Reading Options
The following reading types are supported by SAP LT Replication Server:
| Read Options | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Type 1 - Access Plan Calculation | 1) Enables fast data loading, if index exists. 2) Allows parallel data loading | 1) May necessitate an additional index. 2) Needs a key field that is adequately selective. 3) Demands calculation prior to loading. |
| Type 3 (default) - DB_SETGET | 1) Eliminates the need for separate index. 2) Permits parallel data loading with lastest DMIS add-on. | 1) Results in additional consumption of the database buffer. |
| Type 4 & 5 - Index Cluster | 1) Achieves very rapid data loading once data is extracted into the table DMC_INDXCL. 2) Uses the database buffer minimally. | 1) Temporarily requires additional tablespace in the source system. |
4) Balancing Workloads and Resources
There is a direct and crucial correlation between the number of replication jobs in the SAP LT replication server system and the count of background work processes in the SAP ERP source system.
In the source system, its vital to synchronize the count of reserved dialog work processes for replication with the active data transfer jobs in the SAP LT replication server. This synchronization guarantees a harmonious workflow.
Therefore, to ensure optimal performance and effective hardware utilization, it is essential for both systems to maintain sufficient number of dialog and background work processes.
5) Data Volume
When the table accumulates over 2 billion records, it becomes necessary to employ table splitting using available partitioning features. For more guidance on this, please refer to “SAP Note 2209687 – SLT HANA target table Source Table Has More Than 2 Billion Records“.
Table partitioning in SAP HANA is a data organization technique that involves dividing a large table into smaller, more manageable segments called partitions. Each partition contains a subset of the table’s data. This approach offers several benefits, including performance optimization, improved data management and enhanced query processing.
In summary, SAP LT replication server provides a wide range of advantages in terms of data management, performance enhancement and seamless integration. As organizations venture into the realm of data replication, the SAP LT replication server stands as a reliable companion, ensuring precision, efficiency, and real-time insights to empower informed decision-making.
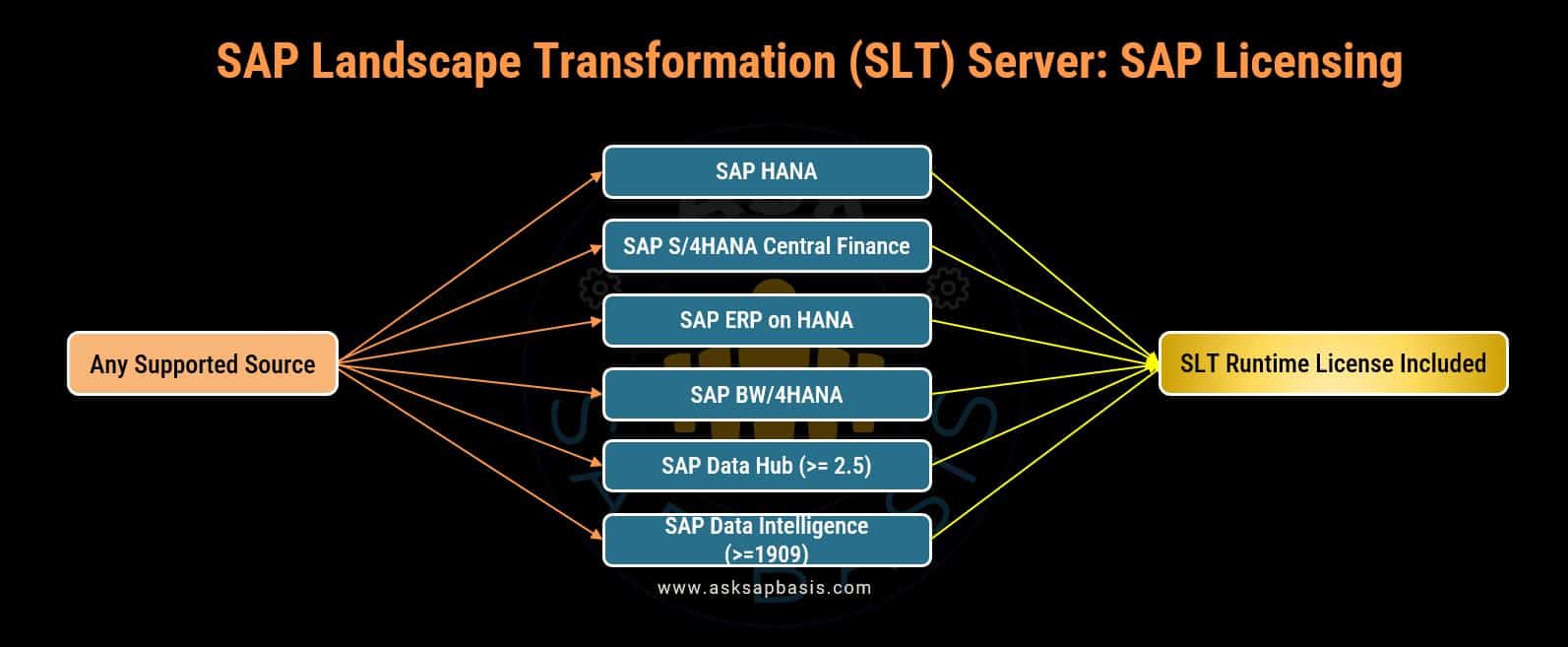
SLT Licensing
The licensing of SLT replication server depends on the specific scenario, with a particular emphasis on the target system for data replication. If the license for the target system already covers the SLT utilization, then there is no need to procure a separate runtime license. Otherwise, a full SLT license is required.
- A runtime license, offers a limited subset of SLT functionalities and capabilities. Typically, tailored for specific use cases, it often focuses on basic data replication tasks. This type of license may impose specific restrictions or limitations when compared to full license.
- The following SAP HANA and SAP Data Hub licenses include a runtime SLT license, enabling unlimited replication from source systems:
- SAP HANA Enterprise Edition
- SAP HANA Enterprise Edition,
- SAP HANA Edge Edition, advanced version
- Standalone Use of HANA Enterprise Edition
- Standalone Use of SAP HANA, Edge edition, advanced version
- SAP HANA, Realtime Replication Option
- SAP HANA, Runtime Edition for Applications and SAP BW
- SAP Data Hub, up to 10 units: 7019382
- SAP Data Hub, 11 to 25 units: 7019383
- SAP Data Hub, 26 to 50 units: 7019384
- SAP Data Hub, 51 to 100 units: 7019385
- SAP Data Hub, above 100 units: 7019386
- Cloud SAP Data Hub: 8005511
- ……
- A full SLT license provides unrestricted access to all SLT functionalities and capabilities. It allows users to leverage SLT for a wide range of data replication scenarios, data transformation, real-time monitoring and other advanced features.
- The following licenses cover a SLT full use license:
- SAP Data Integrator, premium edition: 7020027
- SAP Data Services, enterprise edition: 7020026
- The following licenses cover a SLT full use license:
In both cases, the pricing is subject to CPU cores used by the SLT instance. In order to determine the suitable sizing, refer to the SLT sizing guide.
It’s crucial to thoroughly examine the terms and conditions associated with each license type to ensure the chosen option aligns with your organization’s requirement and intended utilization of SLT.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Address Common Issues: Expand on how to resolve typical problems like latency, large data volume handling, or system crashes.
- Performance Optimization: Offer recommendations on tuning SLT for better throughput (e.g., using parallel processing, optimizing network bandwidth).
- Replication Failures: Use transaction LTRO to check log details for replication issues like table structure mismatches or connectivity problems.
- Handling Data Load Errors: Restart the initial load if there’s a failure, and check for table-level errors in SLT logs.
- SLT Authorization Issues: Ensure appropriate user roles and authorizations (SLT Admin, SLT Config) are set up in both source and target systems.
Best Practices
- Regular System Checks: Periodically review SLT configurations to prevent bottlenecks.
- Archiving: Use data archiving to manage the volume of historical data.
- Disaster Recovery: Implement high-availability setups or disaster recovery plans for critical data replication.
Real-Time Use Cases
- Manufacturing Industry: Companies replicate data from SAP ERP to HANA for real-time production monitoring and predictive analytics.
- Retail Sector: Retailers use SLT to sync inventory and sales data from multiple branches to a central data warehouse for consolidated reporting.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: During corporate mergers, SLT is used to migrate and merge critical data from different SAP systems into one unified database.
- Finance Industry: Financial institutions use SLT to replicate transactional data from SAP ERP systems to HANA for real-time fraud detection and risk management.
- Supply Chain Management: Companies with complex supply chains leverage SLT to sync data between multiple SAP systems, ensuring real-time inventory management and order processing.
- Data Migration Projects: SLT is vital during system migrations, allowing businesses to move data from legacy systems to SAP S/4HANA with minimal downtime.
- Data Harmonization: Large corporations use SLT to harmonize data across multiple subsidiaries or regions by replicating and standardizing data for consolidated reporting.