Secure SAP with SAPRouter – Ultimate Setup Guide 2025
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital age, safeguarding your sensitive business data is of paramount importance. With the relentless onslaught of cyber threats, securing communication channels has assumed even greater significance, particularly when it comes to safeguarding sensitive business data.
To ensure that SAP customers can receive secure remote support and service delivery, they must establish a reliable channel. This is precisely where SAPRouter comes into play, guaranteeing that your data remains shielded and accessible solely to authorized users. SAPRouter serves as a fortified conduit, enabling secure communication with your SAP systems and effectively shielding your confidential information from potential threats.
As we embark on this blog journey, let’s delve into the intricacies of SAPRouter. We’ll explore its fundamental architecture, elucidate the installation procedures, and shed light on its robust security features. Furthermore, we will elucidate the best practices for its implementation and maintenance, ultimately uncovering the myriad benefits that result from deploying SAPRouter to fortify the security measures of your SAP system.
Understanding SAProuter
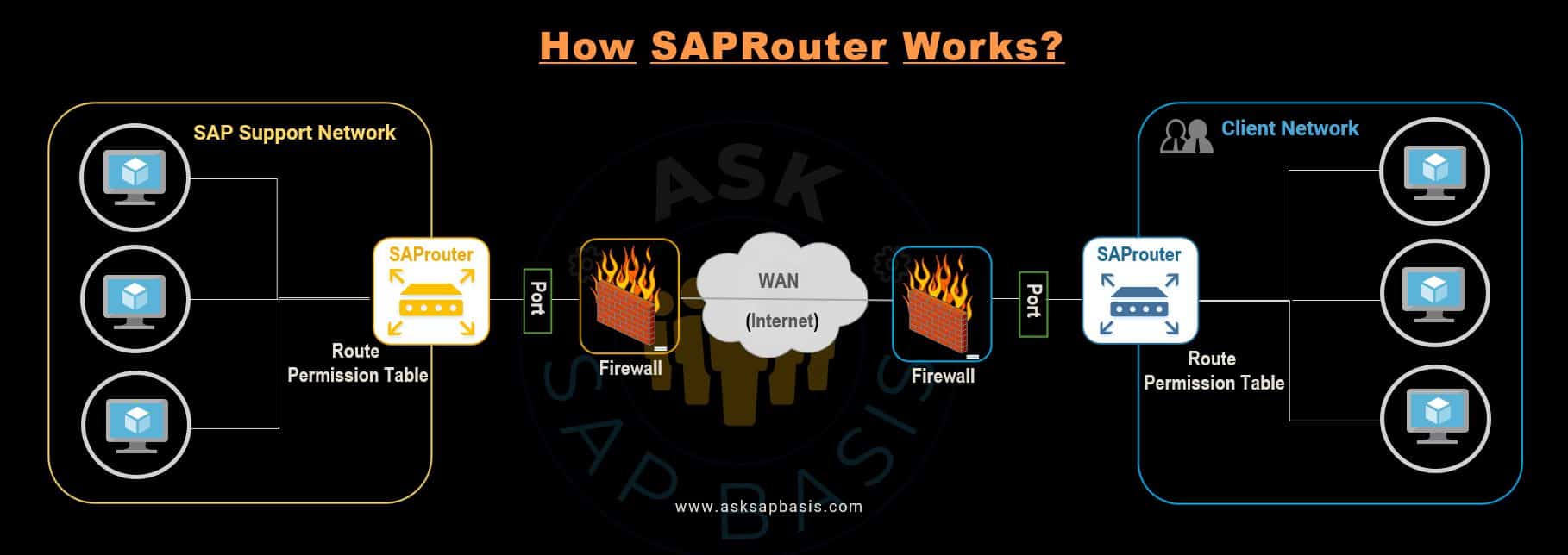
SAPRouter is a software application that serves as a secure communication channel to provide remote connection between your customer network and SAP.
- acts as a proxy server between SAP systems and external networks. It controls access to your network at the application level & is a useful enhancement to an existing firewall system (port filter).
- acts as an extra firewall to the existing firewall (port filter). It’s installed directly on the firewall host.
- enhances network security by blocking unauthorized access and providing secure communication channels. Just specify the connections you want to allow in a route permission table.
Benefits
Here are some benefits of using SAPRouter:
- Improved security: SAP Router adds an extra level of security to SAP systems by encrypting and decrypting network traffic between them. It also restricts unauthorized access to SAP systems by filtering incoming and outgoing network traffic.
- Network flexibility: SAProuter enables the communication between SAP systems that are not in the same network zone. This is particularly useful for organizations that have distributed SAP landscapes.
- Reduced network latency: By enabling communication between SAP systems through a direct and secure connection, SAP Router can reduce network latency and improve performance.
- Simple setup and maintenance: SAP Router is easy to configure and maintain, and can be integrated with various third-party tools for monitoring and management.
- Access Management Control: SAPRouter allows administrators to control access to SAP systems by configuring access control lists (ACLs) to specify which IP addresses are allowed to connect. This feature ensures that only trusted systems are allowed to connect to the SAP system, preventing unauthorized access.
- Scalability: SAP Router can be easily scaled to accommodate additional SAP systems or network zones, making it a suitable solution for organizations that are rapidly expanding their SAP landscapes.
Overall, SAP Router is a powerful tool that enhances the security, flexibility, and performance of SAP system communication across different network zones.
Why is SAProuter important?
An integral part of SAProuter’s functionality is preventing hackers from gaining access to SAP systems. When not protected by SAProuter, SAP systems are left wide open to internet-borne threats. SAProuter acts as a firewall to block malicious traffic and protect data from hackers.
The reduced amount of traffic that must be transmitted over the internet is just one way in which SAProuter helps to improve the performance of SAP systems. SAProuter’s ability to filter unwanted connections helps the SAP system by reducing the amount of traffic it must process, which in turn speeds up the network and reduce latency
How does SAProuter work?
Authenticating Clients
Once a client requests to connect, SAProuter checks their credentials to verify that they are authorized to access the target system. It facilitates authentication using methods such as digital certificates, user IDs, and passwords and access control list (ACL) limit access based on specific criteria, such as IP addresses.
After verifying the client, SAProuter connects to the target SAP system on its behalf, using a protocol called SAProuter Protocol that is designed specifically for SAP systems. The hostname of the target system tells SAProuter which SAP system to forward the connection to, and this information is stored in a routtab file.
Securing Communication
SAProuter encrypts all communication between the client and the target SAP system to ensure data confidentiality and integrity. To ensure confidentiality and integrity of the communication between SAProuter and the target SAP system, a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption algorithms like AES and RSA are used. This encryption ensures that the communication remains private and secure.
SAProuter also offers additional security features, such as using VPN devices to make secure connections over the public network. It can also limit IP addresses or require two-factor authentication to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
Monitoring and Auditing
SAProuter generates logs that can be used to monitor and audit network traffic, allowing users to spot any suspicious activity. This is a crucial feature in maintaining the security of the SAP landscape.
Components of SAProuter
SAProuter is an essential tool that allows secure communication between SAP systems and the Internet. It acts as a firewall, proxy, and router between the SAP system and external networks. The components of SAProuter are as follows:
SAProuter Executables
The main component of SAProuter is the SAProuter executable, which provides the functionality to intercept and route traffic between SAP systems and external networks. The executable runs on the operating system of the machine on which SAProuter is installed.
Machine or Device
SAProuter is a software application that needs to be installed and run on a machine or device. The machine or device must meet the hardware and software requirements specified by SAP for SAProuter installation. The machine must have a network interface card with an IP address that is accessible from the SAP system and the external network.
Configuration File
The configuration file commonly referred to as “routtab” file. It contains all the configuration settings and parameters that determine its behavior.
The configuration file specifies the IP addresses of SAP system, access control rules, network interfaces, external networks that SAProuter should allow or block and other parameters related to the operation of SAProuter. It is an essential component of SAProuter and is used to define the network topology and security policies for SAP systems.
Certificates
These cryptographic certificate file is a vital component of SAProuter that ensures the connection between the SAP system and external clients is secure and trustworthy. It contains key information like the public key and certificate holder’s name that authenticate the connection and keep transmitted data confidential. Along with the “routtab” configuration file, SAProuter maintains the security and smooth operation of the SAP system, providing a reliable and safe data transmission.
Log File
The log file is an essential component of SAProuter that acts like a virtual traffic cop, recording all network traffic passing through it. This includes details like the source and destination IP addresses, traffic type (HTTP or HTTPS), and any errors or warnings.
The log file in SAProuter is your go-to tool for troubleshooting network issues and monitoring network activity. It gives you a comprehensive view of your SAP system’s performance by capturing important details like traffic types, source and destination IP addresses, and any errors or warnings. With this valuable insight, you can quickly identify and resolve network issues and ensure that your SAP system is running smoothly and securely.
Remote Connectivity Options
Remote connectivity plays a crucial role in any SAP system architecture, as it allows users to access SAP systems and applications from remote locations. Additionally, it facilitates secure communication between SAP systems and external networks.
In order to accomplish this, SAP systems provide two remote connectivity options to configure router:
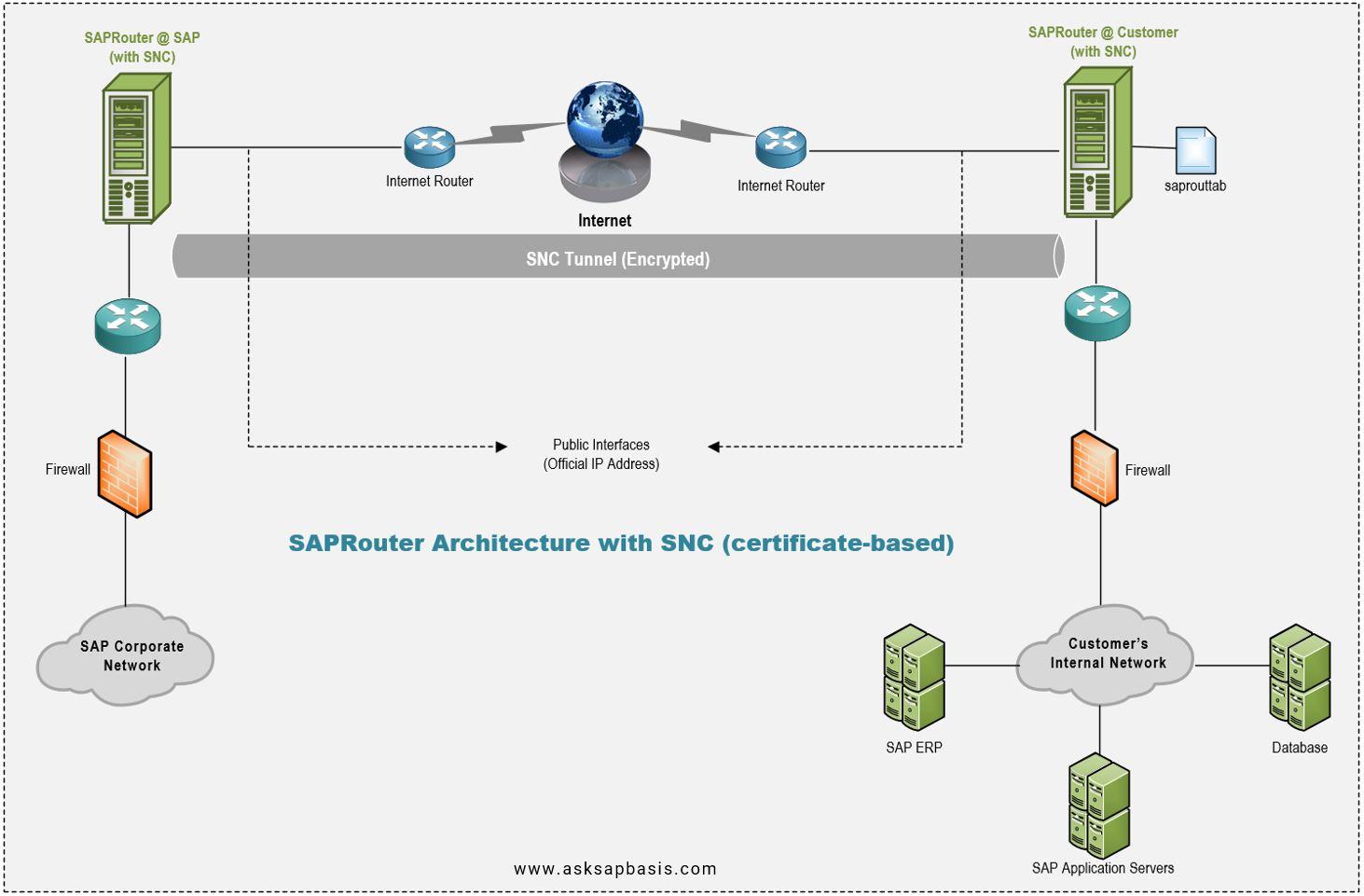
- Secure Network Communication (SNC)
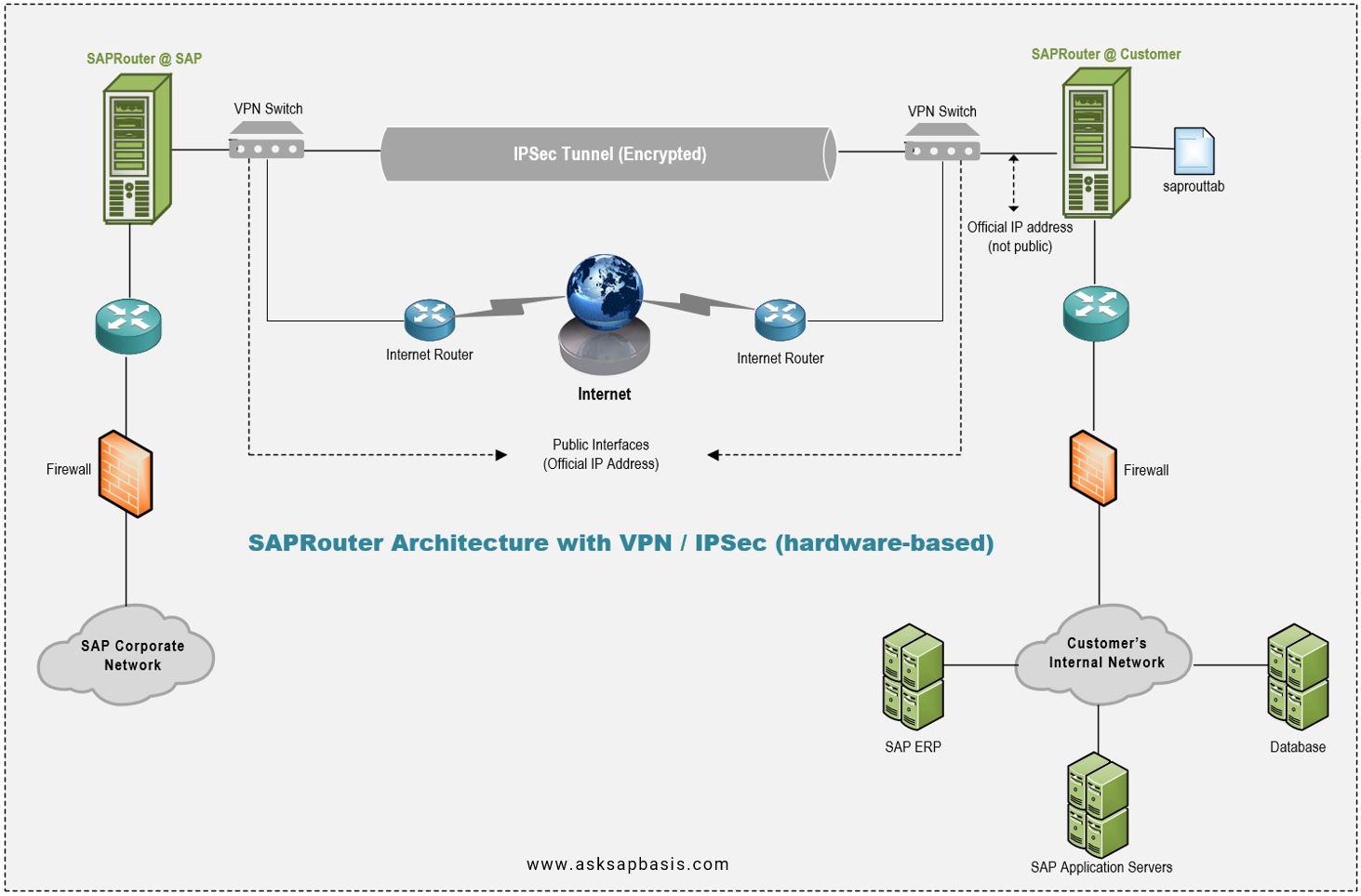
- Virtual Private Network (VPN)
| Option | SNC (via Internet) | VPN |
| Deployment | Certificate-based | Hardware-based |
| Hardware Requirement | Firewall + SAProuter host in DMZ | VPN switch + firewall + SAProuter host (VPN and firewall may be the same box) |
| Network Address | 1 Official static IP address for SAProuter | 1 Official static IP address for VPN switch + 1 official static IP address for customer SAProuter host. |
| Configuration | 1) Setup of saprouttab necessary for security. 2) SAProuttab influences security strongly as access is controlled via saprouttab and firewall | 1) Setup of routing configuration in VPN switch necessary for security. 2) SAProuttab influences security less strongly as access is controlled via VPN switch, SAProuter software and firewall |
| Encryption | By Software | By Hardware |
| Encrypted Data | TCP packets; Only data stream between SAPRouter is encrypted; Encryption handled at Application layer. | IPsec (IP packets) Encryption is handled on IP |
| Internet Bandwidth | 64 kbit/s but may work also with 32 kbit/s | 64 kbit/s |
| Key Management | Digital certificates being requested via Service Marketplace Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) | Pre-shared keys provided by SAP, later Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) |
| Key Storage | In File System | In VPN Switch |
| Technical Requirements | Clients must install SAProuter with a static IP address (DHCP address will not work) and secure inbound and outbound connections to SAP at their end of demilitarized zone (DMZ) | Customers must also install a SAProuter with an official IP address at their end of the connection, in addition to the VPN devices (also known as a VPN switch or VPN gateway). |
| The required cryptographic certificates area available on SAP Service marketplace. | Access to a VPN is also available through a telecommunications provider. The provider will then be connected to SAP's VPN switch and will be able to offer Internet connectivity to consumers. SAP will establish a directory of VPN service providers. | |
| SAPRouter machine required. Internet Connection – recommended minimum bandwidth = 64 kbps. | SAPRouter machine required. Internet Connection – recommended minimum bandwidth = 64 kbps. | |
| Since the host running the SAProuter software is a full computer with operating system, the security at the operating system level must be hardened. | SAP uses CISCO VPN equipment. Customers may also try to connect using other IPSec compliant VPN equipment. The equipment must support certain IPSec features that are mandatory to establish communication with SAP’s VPN equipment. | |
| Other networking equipment (routers and hubs) needed to form the network at the customer’s premises. | Other networking equipment (routers and hubs) needed to form the network at the customer’s premises. |
Secured Network Connection (SNC)
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Setting Up SAProuter
System Requirements
This sections lists the hardware and software requirements for setting up SAProuter.
Hardware Requirements
If you’re using an SAProuter that connects 2500-3000 SAP GUIs with application servers, and you’re transferring a typical amount of data with only a few file downloads and uploads (about 8kB of data transferred in each direction every 10 seconds for each connection), Following recommendation is suggested:
- Network Interface Card (NIC) that supports TCP/IP communication.
- 2 hyper-threading (HTT) CPUs with 2GHz tact frequency.
- at least 2 GB RAM.
- 50 MB disk space (for SAProuter, configuration & log files).
Software Requirements
- Operating system: SAProuter can be installed on various operating systems, including Windows, Linux, Unix and macOS. The specific OS version and operating system will depend on the SAProuter version and hardware configuration.
- SAProuter Installation package: You can download the it from SAP support portal.
- SAP Cryptographic library: It is required to encrypt and decrypt data transmitted through the SAProuter. This library is included with the SAProuter distribution and will be installed during SAProuter installation.
New Connection Requirements
- Prior to logging a ticket for SAP router network configuration, you must have or be able to provide a contact who has a sound understanding of the operating system.
- You will not require deep network experience but should have an individual contact that can be called upon to support, should it become necessary.
- In order to establish your VPN, you must log in to the SAProuter host, which may require intervention from your IPSEC administrator.
- You must have two public IPs available for IPSEC connection.
- You need to complete SAP Note 28976 to register your new SAProuter installation.
SAProuter SNC Installation & Configuration (Windows)
To install and configure SNC SAProuter step-by-step, click here
SAProuter Security Overview
SAProuter is a critical component of SAP security infrastructure that provides an additional layer of security by filtering and redirecting network traffic between SAP systems and the Internet.
However, like any other network device, SAProuter can be susceptible to security threats that can compromise the security of the entire SAP landscape. Therefore, it is essential to understand the common security threats and the security features that SAProuter provides to mitigate these threats.
Common Security Threats
- Denial of Service (DoS) attacks: Hackers can take over SAProuter by flooding it with network traffic, which makes it stop functioning.
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks: Hackers can listen in on, change, or steal sensitive information by intercepting network traffic between SAP systems and the Internet.
- Brute force attacks: Attackers can try to guess the SAProuter password by using automated tools that use a combination of characters.
- Exploitation of vulnerabilities: Hackers can use known or unknown flaws in SAProuter software to get unauthorized access to SAP systems.
Security Features
- Encryption: SAProuter uses encryption to protect the confidentiality and integrity of network traffic between SAP systems and the Internet. SAProuter supports various encryption protocols, such as SSL/TLS, SNC, and VPN.
- Access control: SAProuter provides access control mechanisms to restrict network traffic between SAP systems and the Internet. SAProuter uses the saprouttab file to define access rules that specify which SAP systems are allowed to communicate with which external networks.
- Authentication: SAProuter uses a password-based authentication mechanism to control access to SAP systems. SAProuter passwords are stored in a secure password file and are encrypted. This ensure remote users can access SAP only until they have been authenticated.
- Logging and auditing: SAProuter provides logging and auditing features that allow organizations to monitor and track network traffic between SAP systems and the Internet. SAProuter logs contain detailed information about network traffic, including source and destination IP addresses, ports, and protocol types. This can help detect and investigate security breaches.
- Firewall: SAProuter can be configured to act as a firewall by blocking or allowing specific types of traffic based on predefined rules. This can help prevent unauthorized access to SAP systems.
- Protocol Validation: In order to prevent attacks that exploit protocol vulnerabilities, SAProuter scrutinizes incoming traffic to verify that it adheres to the expected protocol. This measure ensures that potential security breaches are detected and thwarted before they can do any damage.
In summary, SAProuter provides several security features to ensure the secure operation of the SAP landscape. Organizations should configure SAProuter correctly and follow the SAProuter security best practices to ensure that SAProuter is protected against common security threats.
SAProuter Maintenance Tasks
There are some maintenance task that you should perform to ensure the smooth functioning of SAProuter. These tasks include:
- Checking and updating SAProuter software: Regularly check for new SAProuter software updates and patches to ensure that you are running the latest version. You can download the latest version from the SAP support portal.
- Monitoring SAProuter logs: SAProuter generates various logs that contain information about its activities. Regularly monitor these logs to detect any problems or errors and take necessary measures to resolve them.
- Verifying SAProuter connectivity: Verify that SAProuter is properly connected to your SAP system and that it is routing traffic correctly. You can use the “ping” command to test connectivity.
- Cleaning up SAProuter logs: Over time, SAProuter logs can accumulate and consume a significant amount of disk space. Regularly delete old logs to free up disk space.
- Configuring firewall rules: If you are using a firewall, ensure that the necessary ports and protocols are open for SAProuter to communicate with your SAP system.
Performing these regular maintenance tasks can help prevent issues with SAProuter and ensure that it continues to function properly.
Best Practices for Using SAPRouter
To maximize the benefits of SAProuter, organizations should follow these best practices for configuration and ongoing management:
1) Regular Audits
- Conduct Security Audits: Schedule regular audits of SAProuter configurations to ensure compliance with security policies and identify any unauthorized changes.
- Review Access Logs: Periodically analyze access logs to track who accessed the system, when, and from where, to detect any unusual activity.
2) Keep Software Updated
- Install Updates Promptly: Regularly check for and install updates to the SAProuter software to ensure it includes the latest security patches and enhancements.
- Version Compatibility: Verify that the version of SAProuter is compatible with the connected SAP systems to avoid performance issues.
3) Secure Configuration
- Limit Access: Configure the
saprouttabfile to limit access to known and trusted IP addresses only. Avoid using wildcard entries. - Utilize Encryption: Always enable Secure Network Communication (SNC) to encrypt data transmitted through SAProuter, protecting sensitive information from eavesdropping.
4) Personnel Training
- Train Staff: Provide training for IT personnel on SAProuter configuration, management, and troubleshooting. Ensure they understand best practices for maintaining security and efficiency.
- Documentation: Maintain thorough documentation of all configurations, changes, and procedures related to SAProuter for reference and training purposes.
5) Monitor Performance
- Implement Monitoring Tools: Use network monitoring tools to track the performance of SAProuter and detect any bottlenecks or issues proactively.
- Alerting Systems: Set up alerts for unusual activity, such as a spike in connection attempts or failed login attempts, allowing for timely intervention.
Troubleshooting Tips For Common Issues
Here are some common issues users may encounter with SAProuter and steps to resolve them:
1) Connection Problems
- Issue: SAProuter is not establishing a connection to the SAP system.
- Solution: Check the saprouttab file for correct entries. Ensure that the IP address and port numbers are accurate. Verify that the SAP system is up and running.
2) Authentication Failures
- Issue: Users are unable to authenticate when trying to connect through SAProuter.
- Solution: Ensure that the user credentials are correct and that the user has the necessary authorizations. Check if SNC is enabled and configured properly if used.
3) Authentication Failures
- Issue: Slow response times when using SAP applications via SAProuter.
- Solution: Monitor network bandwidth and performance metrics. Identify any bottlenecks in the network path and address them. Review the routing configuration to ensure optimal performance.
4) Unauthorized Access Attempts
- Issue: Increased unauthorized access attempts reported in logs.
- Solution: Review the saprouttab file to restrict access to specific, trusted IP addresses. Consider implementing IP whitelisting or firewall rules to block unwanted traffic.
5) Configuration Errors
- Issue: Changes made to the SAProuter configuration are not taking effect.
- Solution: After making changes to the saprouttab or other configuration files, restart the SAProuter service to apply the updates. Check for any syntax errors in configuration files.
6) Encryption Issues
- Issue: Users cannot establish a secure connection.
- Solution: Verify that all necessary encryption settings are correctly configured. Ensure that the SSL certificates are valid and not expired. Check that all endpoints support the required encryption protocols.
By following these best practices and utilizing the troubleshooting guide, organizations can ensure that their SAProuter implementation remains secure, efficient, and effective, ultimately enhancing their overall SAP system performance.
References
- SAProuter: Step-by-Step SNC Configuration on Windows
- SAP Note 1628296 – SAProuter Installation Process
- SAP Note 1921693 – How to update SAProuter
- SAP Note 2910668 – Useful information on configuring the SAPRouter
- SAP Note 30289 – SAProuter documentation
- 41054 – Installation of SAProuter as Windows Service