SAP S/4HANA Transition Framework: A Roadmap Guide
Introduction
Is your enterprise grappling with technical debt, siloed data, and the limitations of an aging ERP system? Still running on ECC? Then your ERP is holding you back. In today’s hyper-competitive landscape, merely keeping the lights on with your legacy SAP ECC environment is no longer enough. The imperative to innovate, operate in real-time, and leverage cutting-edge technologies like AI and machine learning demands a fundamental shift. This is where SAP S/4HANA comes in – not just as an upgrade, but as the strategic foundation for your future.
Why the Urgency? Why the Shift?
The move to S/4HANA isn’t optional — it’s business critical and its driven by a combination of strategic, technical, and time-sensitive factors. Here’s why:
- 2027 Mainstream Maintenance Deadline: SAP support for ECC ends in 2027 (extended from 2025), creating a hard stop for businesses relying on legacy systems.
- Real-Time Business Demands: S/4HANA’s in-memory architecture enables instant reporting and agile decision-making—critical in today’s dynamic market landscape.
- Cloud-Readiness & Innovation: Whether you’re planning a full cloud migration or adopting a hybrid model, S/4HANA offers the flexibility, scalability, and native integration needed to embrace modern architectures and innovations like AI, ML, and RPA.
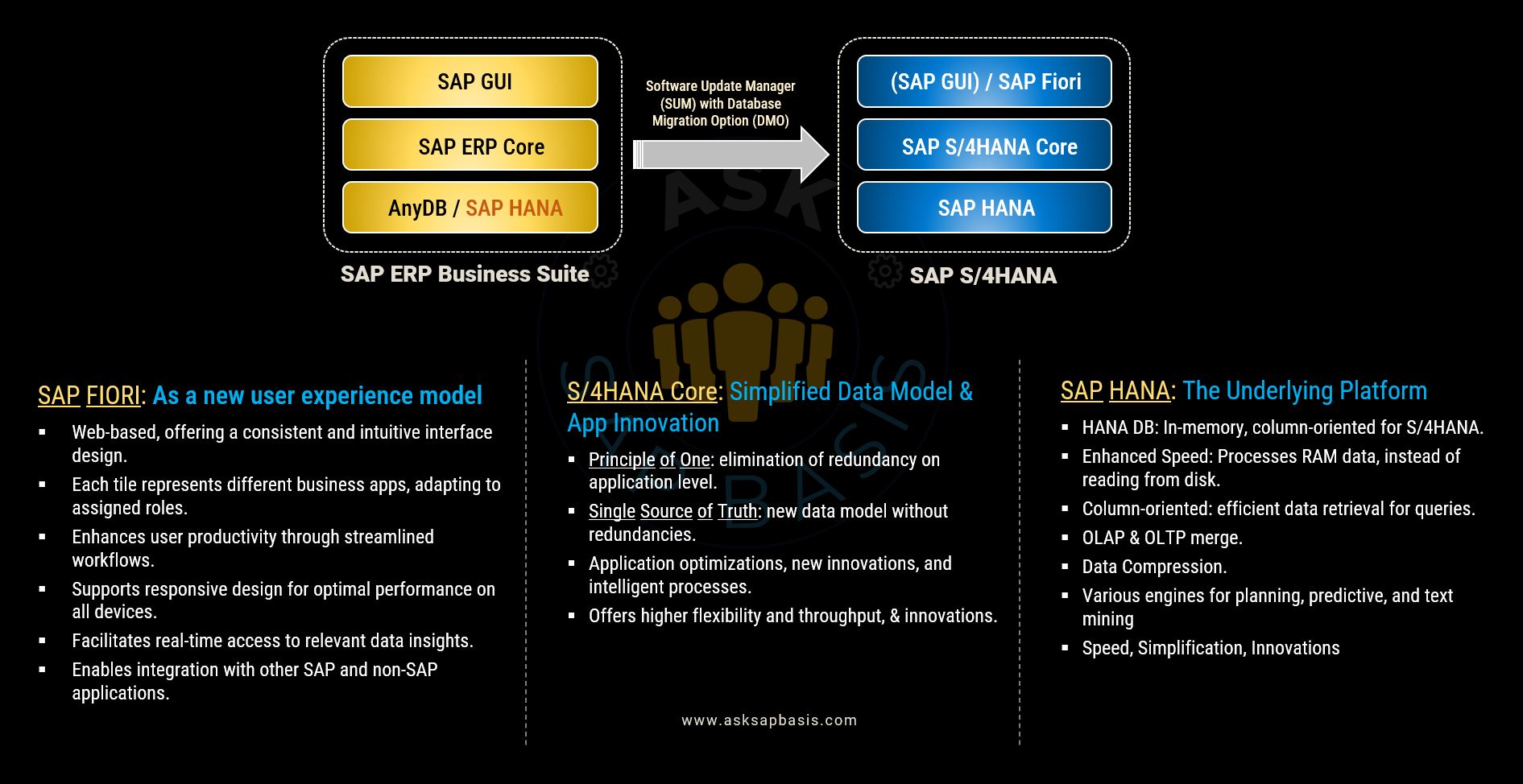
ECC vs S/4HANA: What’s Changing?
This transition journey to SAP S/4HANA, is not just a technical upgrade; its a strategic and transformative shift that prepares your organization for the future in how businesses run ERP. This transition will help you drive business growth, streamline operations and leverage advance SAP software capabilities, reduce technical debt. Hence SAP S/4HANA transition becomes an intrinsic step.
ECC, built on a traditional relational database, relies heavily on batch processing and complex data models. In contrast, S/4HANA runs on the revolutionary in-memory SAP HANA database, delivering lightning-fast analytics, simplified data structures, and a modern user experience through Fiori. Key differences include:
- Data Model Simplification: Reduced tables and no more index aggregates.
- Real-Time Processing: Elimination of delays caused by batch jobs.
- UX Upgrade: Fiori replaces the classic SAP GUI, bringing consumer-grade experiences to enterprise users.
These drivers highlight that transitioning isn’t just about compliance—it’s about future-proofing operations and unlocking next-gen capabilities. When initiating your SAP S/4HANA transition, focus on your company’s vision and adaptability, as these factors outweigh technological considerations. Regardless of the transition approach, the success of your transition depends on how well your project is managed and structured.
This comprehensive guide takes you through every step of a successful transition, ensuring you’re fully prepared for the change. Discover the essential steps, benefits, and strategies needed to make your transition smooth and successful.
Understanding SAP S/4HANA
SAP S/4HANA: Powering the Intelligent Enterprise
SAP S/4HANA represents the next generation of the SAP business suite software serving as the digital core of your organization, designed to power an Intelligent Enterprise. It offers seamless integration and provides a range of capabilities within the applications, allowing you to easily create extensions and customizations tailored to your specific needs.
Unlike the previous SAP Business Suite ERP system, S/4HANA is not just a successor release; it constitutes an entirely new product line. Transitioning from an SAP Business Suite ERP system to an SAP S/4HANA system involves specific incompatible changes:
- It is built exclusively on SAPs innovative in-memory database, SAP HANA.
- It introduces a new application architecture and simplifies the data model.
- You can now leverage the new UI technology, SAP Fiori.
One of the key principles guiding the development of SAP S/4HANA was to deliver an ‘upgrade-like’ experience to customers transitioning their existing SAP ERP system into the digital era. To foster innovation and ensure a seamless transition, SAP used a copy of the SAP ERP as the foundation for SAP S/4HANA. This served as the basis for the modernization, simplification, and extension of the existing solutions.
Planning Your Transition
Planning is crucial for a successful SAP S/4HANA transition. Start by assessing your current system landscape and defining your business requirements. Key steps include:
- Assessment: Evaluate your existing SAP environment and identify what needs to be changed or upgraded.
- Strategy Development: Create a comprehensive transition and deployment strategy, including timelines, resource allocation, and risk management.
- Budgeting: Prepare a budget that covers all aspects of the transition, including licensing, training, and consulting services.
Executing The Transition
With a solid plan in place, you can begin the execution phase. This includes:
- System Configuration: Set up and configure SAP S/4HANA to meet your organization’s requirements.
- Data Migration: Transfer data from your old system to SAP S/4HANA, ensuring data integrity and accuracy.
- Testing: Conduct thorough testing to identify and resolve any issues before going live.
Post-Implementation and Optimization
After the transition, focus on optimizing your new SAP S/4HANA system. Key activities include:
- Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitor system performance to ensure it meets your business needs.
- User Training: Provide training for users to help them adapt to the new system and maximize its capabilities.
- Support: Establish a support system to address any issues and ensure ongoing success.
Pre-Migraton Assessment
Before any technical work begins on your SAP S/4HANA transition, a comprehensive pre-migration assessment is the foundational step. This crucial phase involves a detailed analysis of your existing SAP ECC landscape, business processes, and data to identify potential challenges, define the project scope, and set realistic expectations. It’s about gaining a clear picture of your starting point and the path ahead.
Key areas covered during this assessment include:
- Business Process Impact Analysis: Understanding how your current business processes (e.g., finance, logistics, procurement) are mapped in ECC and how they will be affected by S/4HANA’s simplifications and innovations. This helps identify areas for re-engineering or adopting SAP Best Practices.
- Custom Code Analysis: A critical step to determine the volume, complexity, and impact of custom ABAP code on the S/4HANA target system. This analysis identifies code that needs to be adapted, remediated, or even retired due to changes in S/4HANA’s data model or functionalities. Tools like the Custom Code Migration App and ABAP Test Cockpit (ATC) are indispensable here.
- Data Volume and Quality Assessment: Evaluating the size and growth of your database, identifying data archiving opportunities, and assessing data quality. Poor data quality can significantly hinder the transition and impact the new S/4HANA system’s performance and reporting accuracy.
- Interface and Integration Review: Cataloging all existing interfaces with other SAP and non-SAP systems. This assesses their compatibility with S/4HANA and identifies where adaptations or re-implementations are needed.
- Add-on and Third-Party Product Compatibility: Checking the compatibility of all installed SAP add-ons and third-party solutions with S/4HANA. Some might require upgrades, replacements, or might not be compatible at all.
- Organizational Change Management (OCM) Assessment: Understanding the readiness of your users and organization for the changes S/4HANA brings, especially with the new Fiori user experience. This assessment informs training needs and communication strategies.
- Licensing Review: A preliminary review of your current SAP licenses and how they will align with S/4HANA licensing models, which can impact costs.
The output of a thorough pre-migration assessment is a detailed report that outlines the scope, effort, potential risks, and a preliminary roadmap for your S/4HANA transition. It provides the necessary insights for informed decision-making and project planning.
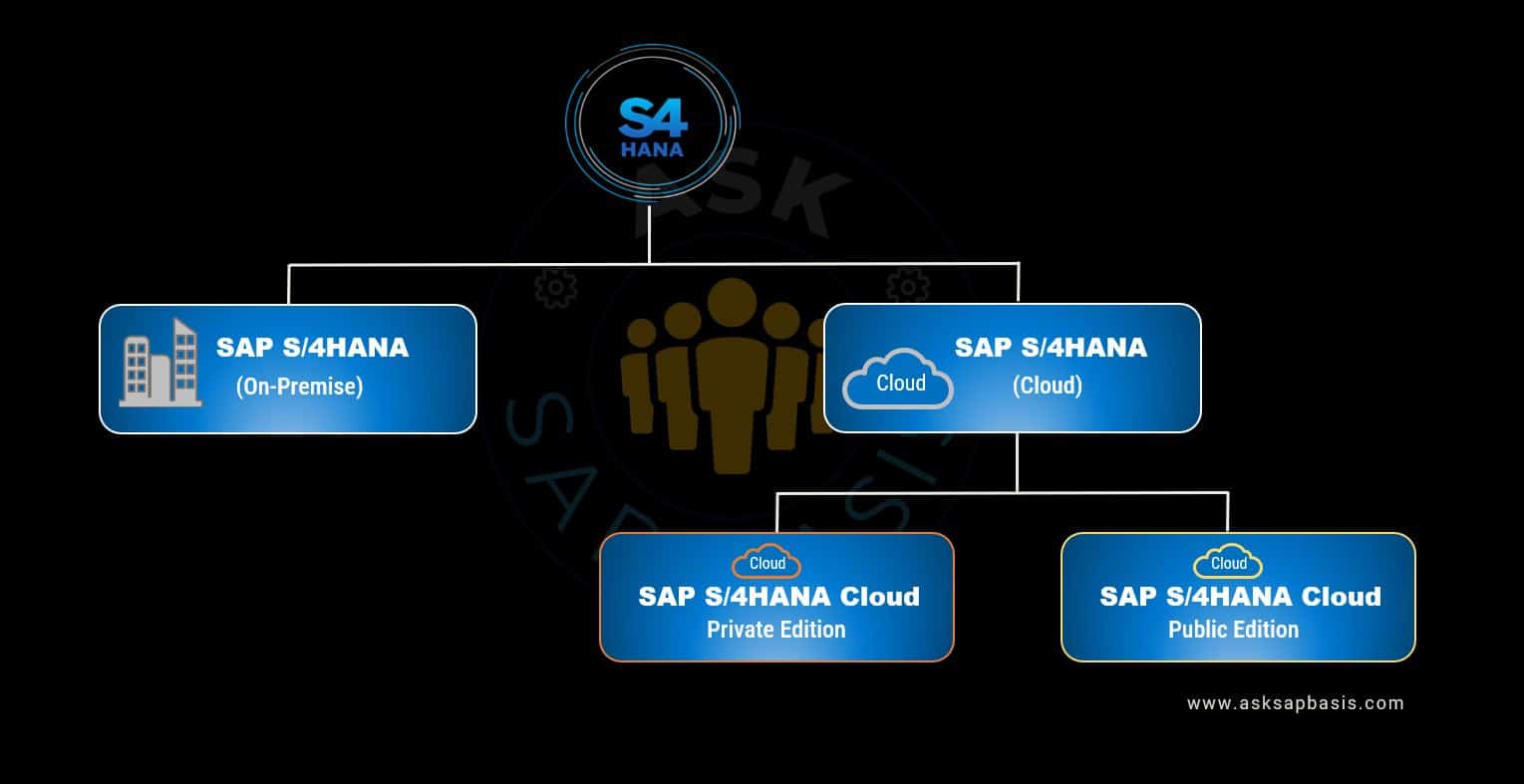
S/4HANA: Deployment Options
You have the option to choose between two deployment models: On-Premise and Cloud (with both private and public cloud versions available)
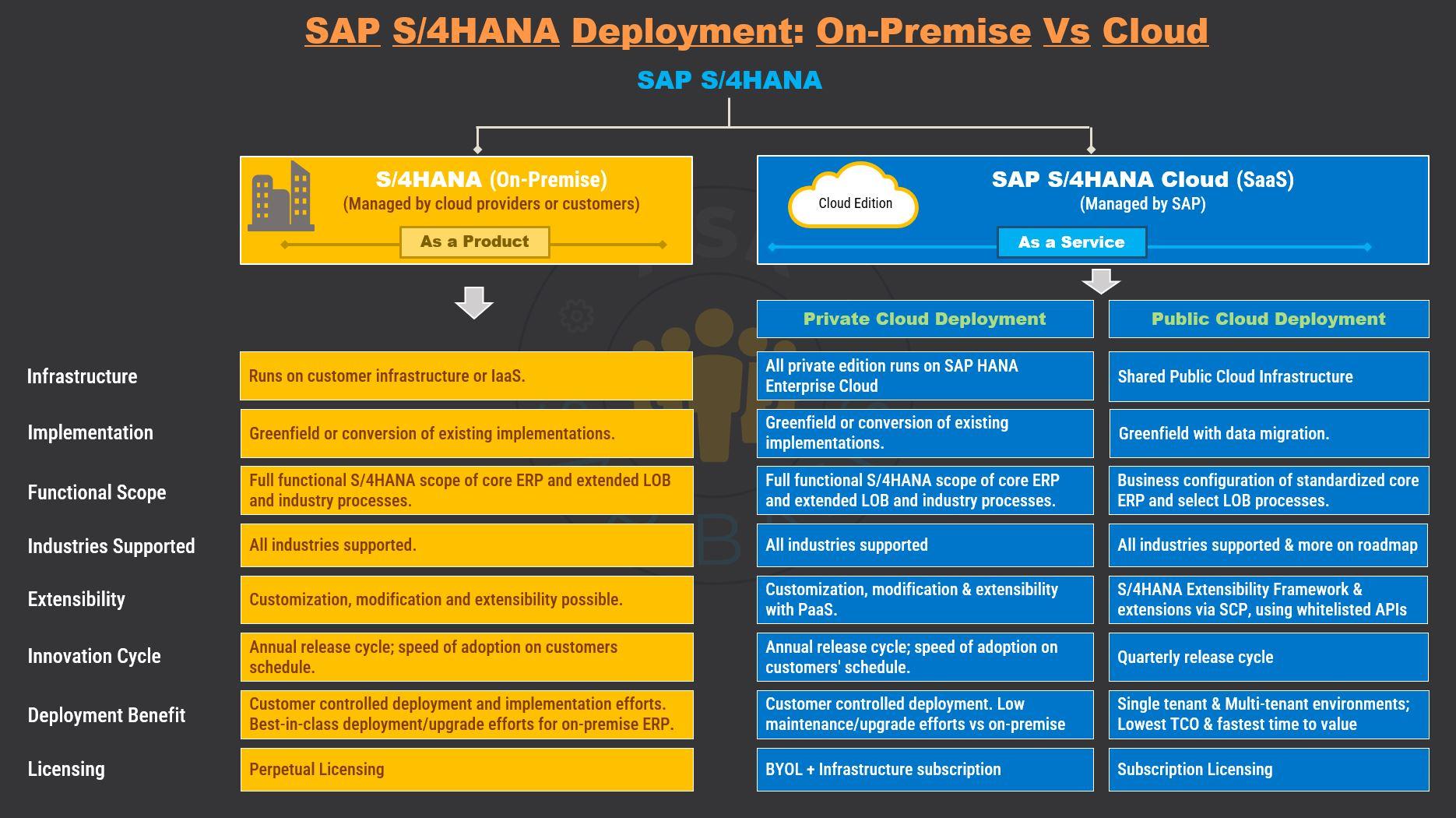
On-Premise Deployment
SAP S/4HANA On-Premise: Empowering Your Business
The S/4HANA On-premise product version utilizes SAP’s standard licensing model, offering you ownership of the software and a reduction in the current maintenance fees.
- This version involves deploying the product internally on company’s infrastructure, which your business and/or IT partners self-manage and maintain.
- It’s the ideal choice for businesses seeking a comprehensive set of features seamlessly integrated with highly flexible customization options. This makes it particularly well-suited for large companies with established and proven business processes.
- By choosing this version, your organization takes on the responsibility of planning, installing, testing, controlling, upgrading and updating changes within the system. This dynamic nature of S/4HANA emphasizes the need for proactive maintenance and adaptation within your organization.
- This ERP version grants you full control over the hardware, software and maintenance schedules. Its preferred choice for businesses seeking extensive process flexibility and seamless third-party integration.
The on-premise SAP S/4HANA version hold particular value for large manufacturing enterprises, especially those with well-established, unchanged internal processes.
Cloud Deployment
Embrace Efficiency and Innovation
Choosing the cloud deployment option for SAP S/4HANA grants you access to most of its on-premise features while eliminating the need for specialized hardware, database investments, and IT specialists for maintenance. Additionally, it allows you to leverage the advantages of SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) and SAP Business Network.
- This option is perfect if:
- Your functional scope is sufficient.
- You prioritize standardization.
- You seek faster delivery of innovation.
- You aim to lower your operational costs.
- Mid-sized companies looking to scale effortlessly can opt for this on-cloud edition, which provides high-performance solution aligned with their core business strategies. Furthermore, it offers increased agility, flexibility, scalability and a faster quarterly cycle for rapid advancements.
- This version comes with built-in intelligent technologies, including AI, machine learning and advanced analytics. SAP position’s it as “next generation intelligent ERP”, enabling companies to achieve digital transformation.
- The SAP S/4HANA Cloud implementation offers a choice between two options:
- S/4HANA Private Cloud Edition: Ideal for those who require a dedicated cloud environment tailored to their unique needs and preferences.
- S/4HANA Public Cloud Edition: Designed for those who value the convenience of a shared cloud infrastructure with benefits of scalability and cost-efficiency.
1) SAP S/4HANA Cloud, Private Edition
The SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud is an on-premise implementation situated within a dedicated, highly secure private cloud environment, expertly managed by leading hyperscalers.
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, is a customized ERP solution designed to dynamically adapts to your organization’s unique transformation needs. This exclusive offering is available through a RISE subscription contract.
- With private cloud edition, you receive:
- Full S/4HANA functionality.
- The highest level of flexibility and extensibility options.
- A customer-influenced innovation cycle.
- A lower total cost of ownership (TCO).
- In this private cloud edition, SAP serves as your trusted cloud service provider, responsible for managing both infrastructure and software. However, all update schedules require approval from customer.
- This implementation empowers you to safeguard your existing SAP ERP investment while gaining enhanced flexibility. Additionally, it grants you innovation flexibility through a five-year upgrade cycle, yearly releases, and support packs.
- Furthermore, you can rely on a robust 99.7% Service Level Agreement (SLA) for your mission-critical systems. Alongside this assurance, the subscription-based model and transition from capital expenditure (CapEx) to operational expenditure (Opex), reduce total cost of ownership (TCO).
2) SAP S/4HANA Cloud, Public Edition
SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud, a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solution, delivers the industry-specific capabilities that companies require. It seamlessly merges these capabilities with cloud attributes and simplifies solution lifecycle management, meeting customers expectations.
- The public edition of SAP S/4HANA Cloud, stands as an embodiment of a cloud-native ERP solution, providing the latest industry best practices and a constant stream of innovation.
- This cloud edition of S/4HANA adopts a subscription-based licensing model (available under RISE with SAP) and resides within a shared public cloud environment, expertly managed and maintained by SAP.
- This edition serves as the ideal choice for new implementations (often referred to as greenfield implementations), offering the best foundation for a digital future by delivering:
- The lowest total cost of ownership (TCO).
- The fastest time-to-value.
- The shortest innovation cycle.
- SAP takes full responsibility for overseeing SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud, including mandatory system updates. While customer schedules are not negotiated, this approach ensures the continuous adoption of the latest best practices and uninterrupted innovation.
- Unlike SAP S/4HANA Private Cloud, this version operates within a unified system and does not allow users to modify system settings. As a result, it streamlines the implementation process, leading to shorter project timelines when compared to other deployment scenarios.
- Additionally, this edition offers more cost-effective solution compared to private cloud edition.
S/4HANA: On-Premise Vs Cloud
S/4HANA: Deployment Tier
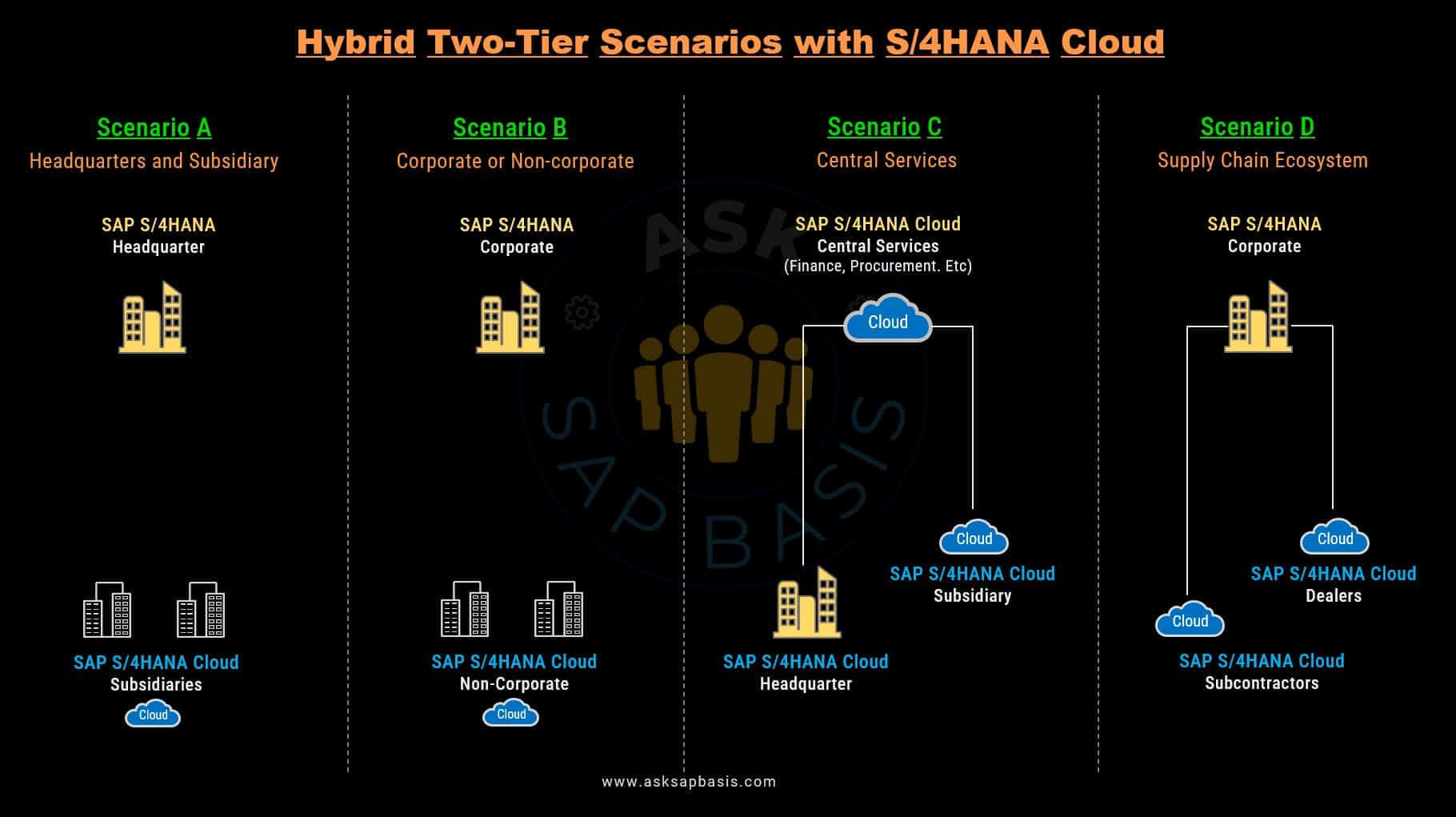
Hybrid Two-Tier Deployment
SAP S/4HANA and SAP S/4HANA Cloud actively collaborate, sharing a common code line, data entities, and analytical structures. This collaborative approach, combined with default integration scenarios, unlocks the potential to establish a robust and sustainable hybrid two-tier architecture.
A two-tier deployment is an IT strategic architecture approach that employs two distinct levels or tiers of systems within an organization’s technology landscape. This dynamic strategy involves maintaining a combination of both on-premises and cloud-based SAP systems.
In this configuration, the headquarters or main office serves as the custodian of the on-premises SAP system, acting as the central hub for critical data and processes. Meanwhile, subsidiary offices, remote locations, or smaller entities utilize a cloud-based SAP system for localized operations. This setup not only streamlines central management but also harnesses the inherent scalability and flexibility of the cloud for peripheral functions.
Case Study: Streamlining Operations with Hybrid Two-Tiers
Background
Company XYZ, a global manufacturing firm, grappled with complex IT systems across its subsidiaries. The headquarters used an on-premise SAP system, while subsidiaries operated with disparate legacy systems. This led to data silos, inefficiencies, and lack of scalability.
Solution
Company XYZ adopted a hybrid two-tier deployment, implementing SAP S/4HANA cloud in select subsidiaries, while maintaining the on-premises system at the headquarters. This allowed central data management while providing subsidiaries with cloud-based solutions.
Results
- Efficient Data Integration: Real-time data synchronization reduced errors.
- Scalability: Subsidiaries easily scaled operations as needed.
- Cost Savings: Reduced IT infrastructure costs.
- Standardization: Streamlined processes and ensured compliance.
- Innovation: Access to the latest industry practices.
- Maintenance: SAP managed cloud updates, simplifying operations.
Conclusion
Company XYZ’s hybrid deployment improved efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness while standardizing processes and accelerating innovation. This case study illustrates the practical benefits of such an approach for organizations seeking operational enhancements.
Traditional ERP Approach Vs Hybrid Two-Tier Deployment
| Traditional ERP Template Approach | Hybrid Two-Tier Architecture | ||
| Deployment Structure | Single centralized ERP instance with customization for all subsidiaries or divisions. | Hybrid Two tiers: Central ERP (Tier 1) for core processes, and local ERPs (Tier 2) for subsidiaries or divisions. | |
| Centralization / Localization | Centralized processes and data, often requiring extensive customization to meet local needs. | Central ERP handles core processes, while local ERPs can be configured for specific regional requirements. | |
| Master Data Harmonization | Typically, organizations use SAP Master Data Governance or develop their in-house solution for this task. | Built-in replication framework for master data replication, while options include SAP Master Data Governance or more advanced tools. | |
| Intercompany Processes | Within the same system, using intercompany transactions (ie between the headquarters company code and subsidiary company code). This necessitates complex integration for federated ERP landscapes. | Smooth sales-order-to-purchaseorder automation and billingto- supplier invoice automation delivered by SAP | |
| Scalability | Limited scalability as the single instance must accommodate growing subsidiaries. | More scalable, as local ERPs can be added or adjusted based on the growth of individual subsidiaries. | |
| Complexity | High complexity due to a single instance serving various diverse business units. | Reduced complexity in the central ERP as it focuses on core functions, while local ERPs handle local complexities. | |
| Risk Management | High risk, as issues in customization or upgrades can impact all subsidiaries. | Lower risk, as issues are contained within local ERPs and critical processes are managed centrally. | |
| Data Volume and Performance | Increased data volume and potential performance issues as all subsidiaries share the same instance. | Improved performance as local ERPs manage their data, while central ERP manages critical data. | |
| SAP-to-SAP Integration | The headquarters' team has to establish and handle this. | SAP manages the pre-built integration scenarios by default. | |
| SAP-To-Third-Party Integration | The headquarters' team must build, establish and manage this | ||
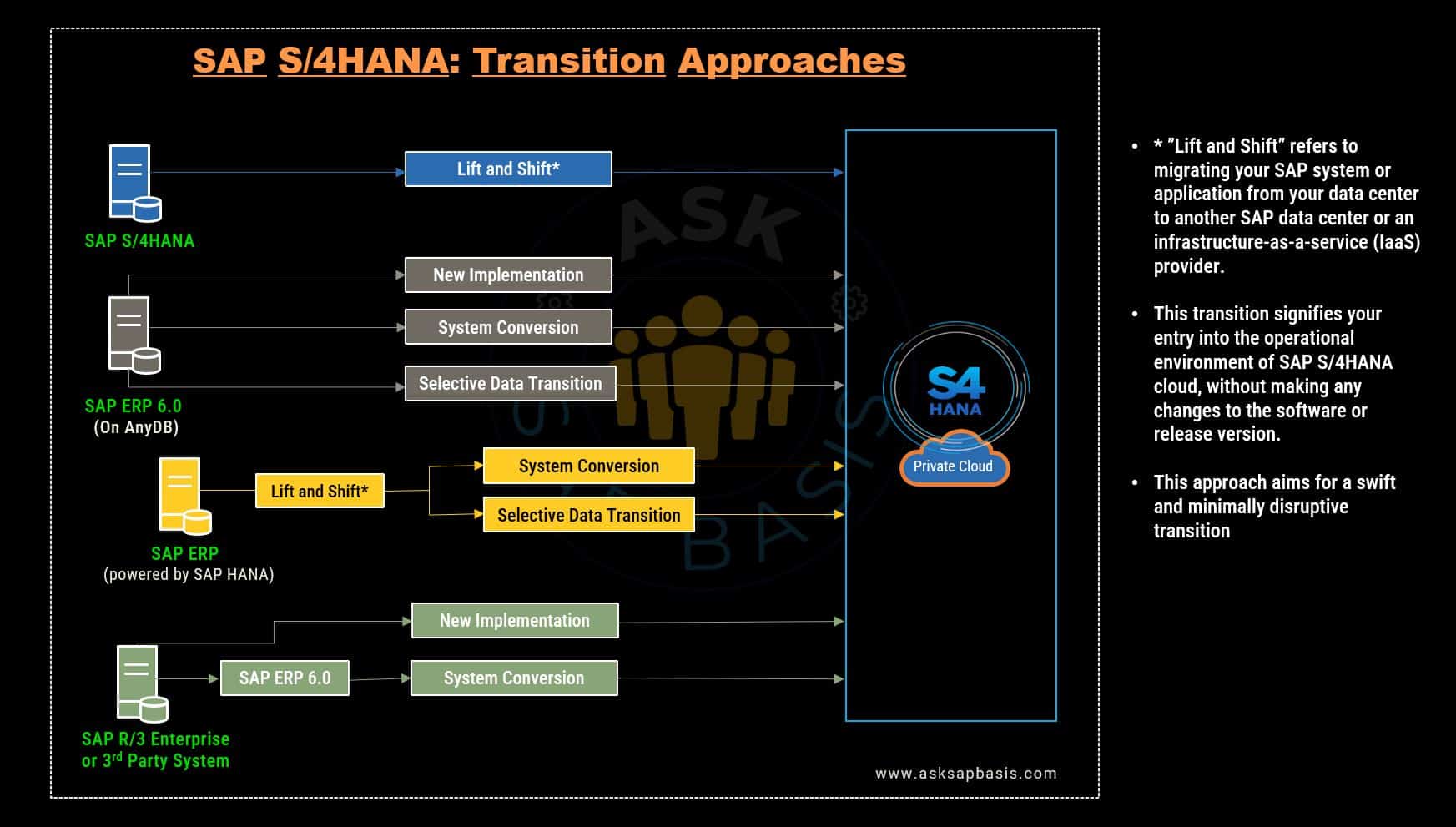
S/4HANA: Transition Options
In the dynamic landscape of digital transformation, SAP S/4HANA emerges as a beacon of opportunity, offering organizations transformative upgrades that unlocks a multitude of new capabilities and efficiencies. Within this realm, the transition to S/4HANA unfolds diverse pathways, each meticulously tailored to address an organization’s unique needs and ambitions.
Whether embarking on greenfield implementations or orchestrating seamless system conversion, businesses embark on a journey that promises heightened agility and innovation in their quest for the future.
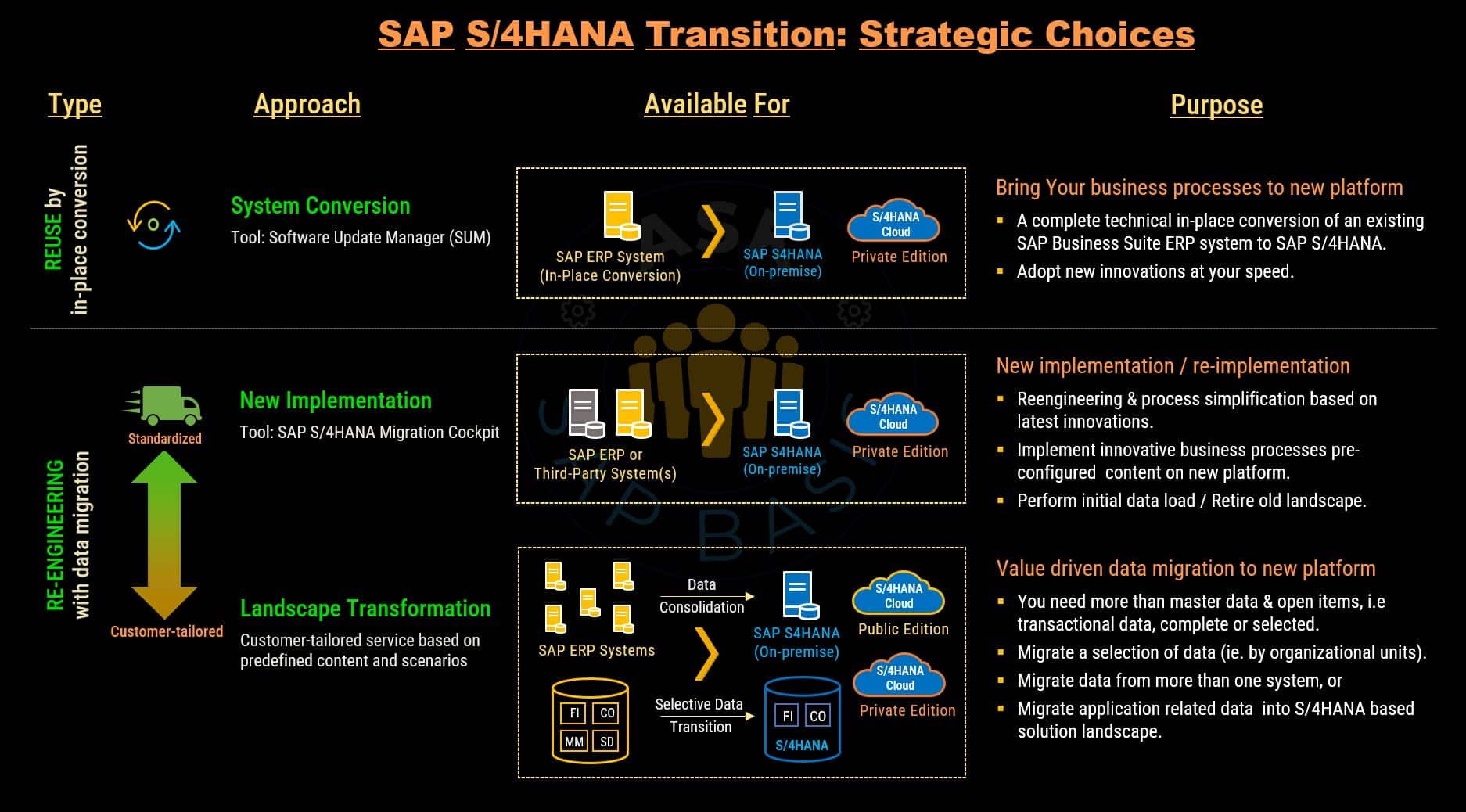
System Conversion
The system conversion, often referred to as the ‘brownfield approach,’ involves transforming your existing SAP ERP system into a newer version of S/4HANA, while safeguarding your critical data, processes, and customizations.
System conversion is executed in a one-step seamless procedure, minimizing downtime while implementing the following changes:
- Migrating your any database from SAP ERP to the S/4HANA database.
- Adapting the data model from SAP ERP to align with the one used in SAP S/4HANA.
- Upgrading the software by substituting the application code of SAP ERP with code designed specifically for SAP S/4HANA.
This transition option aims to strike a balance between harnessing the benefits of S/4HANA and minimizing disruptions. It also ensures data continuity and reduces the need for extensive re-training. Essentially, it represents a gradual, risk-mitigating strategy for modernizing technology while capitalizing on existing investments.
Factors to Consider When Choosing this Transition Option
- Select this option if your primary objective is to transition your existing business processes to the new platform and/or retain your investment in custom code.
- Consider adopting this approach to mitigate risks and investments associated with a substantial conversion project.
- Streamline the transition by focusing on a technical conversion project, which minimizes operational disruptions and ensures uninterrupted business continuity.
- This strategic approach significantly reduces the overall risk associated with a major overhaul, offering enhanced control over the implementation process.
- Choose this option, if you want to prefer a phased approach. The step-by-step adoption of new innovations aligns seamlessly with a gradual transformation strategy, reducing the likelihood of encountering unexpected challenges.
New Implementation
A new implementation, often referred to as the ‘greenfield approach,’ empowers organizations to embark on a journey with a clean slate. It offers unique opportunity for organizations to assess and redesign their business processes, configurations, and data models.
With this approach, you create a brand new SAP S/4HANA system. Following this, you can choose to either execute a cutover to the new system (referred to as the ‘big bang’ approach) or gradually migrate individual business units from your legacy SAP ERP application to the new system (termed a ‘phased rollout’).
Factors to Consider When Choosing this Transition Option
- This new implementation option is the ideal choice, if your primary focus is on reengineering and simplifying process using the latest innovations. It is particularly suitable for customers who are contemplating migration:
- from a non-SAP system or third-party legacy system.
- from an older SAP release and/or that has undergone extensive customization and/or modification.
- when existing system does not meet the requirements for a technical system conversion.
- By choosing this option, the customer benefits from:
- re-engineering and streamlined processes based on pre-configured best practice content.
- access to predefined migration objects and best practices, eliminating the need for intensive migration logic programming.
- rapid adoption of new innovations in a standardized manner.
- avoiding the burden of carrying legacy issues (unlike system conversion), empowering organizations with modern technology to optimize processes, streamline data, and tailor the system to their needs.
- Morever, the adaptable nature of this approach equips your organization to navigate future changes and innovations beyond the initial transition, ensuring sustained preparedness.
- This option strategically addresses the challenges that may arise during a transition, including potential process disruptions and concerns about data integrity.
Landscape Transformation
Landscape transformation refers to the process of selectively migrating a subset of data or specific entities from the current SAP ERP system to the new S/4HANA system. This approach is instrumental when companies aim to streamline their data and avoid migrating unnecessary or outdated information to the new system.
Consequently, landscape transformation offers several strategies or sub-scenarios to choose from:
- Selective data transition based on legal entities (such as clients or company codes).
- The consolidation of your current SAP Business Suite landscape, involving multiple systems or specific clients from various system, into a unified SAP S/4HANA global system.
- Implementing the SAP Central Finance scenario.
Factors to Consider When Choosing this Transition Option
- This transition option focuses on value-centric, selective data migration to a new S/4HANA platform. Instead of transferring an entire system, the emphasis is on choosing specific legal entities (such a clients or company codes) for extraction and migration to the SAP S/4HANA platform.
- This option is also ideal for businesses seeking to consolidate or streamline their landscapes or strategically transform data for integration into an SAP S/4HANA system.
- This selective data transition option offers several benefits:
- Value-Centric Migration: By adopting a phased strategy, it strategically prioritizes the initial SAP S/4HANA migration for segments of the business with the highest ROI (Return On Investment) and lowest TCI (Total Cost of Implementation). This strategic alignment significantly amplifies the migration’s overall value.
- Agile Transition: While maintaining current business processes, the gradual movement to SAP S/4HANA innovations is facilitated. This ensures flexibility and lets your move at your own pace.
- Lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Achieved through the consolidation of systems and landscapes, as well as the harmonization and simplification of processes, along with unified master data. This comprehensive approach results in a notable reduction in operational costs.
In conclusion, landscape transformation stands as a strategic approach that not only reduces the cost of transition but also sets the stage for a more agile and efficient future. By selectively migrating data and embracing modern innovations, businesses can navigate change with confidence, ensuring sustained success and preparedness for what lies ahead.
S/4HANA: Transition Approaches
Transitioning to SAP S/4HANA involves migrating from your current SAP system to S/4HANA platform. The transition approaches vary based on various factors such as your current SAP landscape, business requirements and available resources.
S/4HANA: Transition Tools and Methodologies
Successfully navigating the SAP S/4HANA transition requires a robust set of tools and a clear methodology. These indispensable resources empower your project team, particularly the Basis professionals, to manage complexities, automate tasks, and ensure a smooth journey to the intelligent enterprise.
Here are the essential tools and methodologies you’ll leverage:
- Software Update Manager (SUM) with Database Migration Option (DMO): This is the cornerstone technical tool for System Conversion (Brownfield) projects. SUM orchestrates the entire upgrade and conversion process, while its DMO capability allows for the concurrent migration of your existing database to SAP HANA as part of the same technical step. This significantly reduces downtime and simplifies the overall transition process.
- Simplification Item Catalog: A crucial reference point that details all functional and technical changes between your current ECC version and SAP S/4HANA. Understanding and addressing the relevant Simplification Items is a key activity, as they often impact custom code, standard functionalities, and business processes.
- Custom Code Migration Tools:
- Custom Code Migration App: A Fiori-based application that analyzes your custom ABAP code against S/4HANA compatibility rules. It helps identify code that needs to be adapted, remediated, or retired due to changes in S/4HANA’s data model or functionalities.
- ABAP Test Cockpit (ATC): Used to perform static and dynamic code checks, ensuring your custom developments comply with S/4HANA standards and highlighting required remediations for optimal performance and compatibility.
- Data Migration Tools (for Greenfield):
- SAP S/4HANA Migration Cockpit (LTMC): This is the recommended tool for New Implementation (Greenfield) scenarios. It offers pre-configured content and guided procedures for migrating master and transactional data from various legacy sources into your new S/4HANA system.
- Legacy System Migration Workbench (LSMW): While still available, it’s a more traditional tool for structured data migration, often used for smaller, less complex data sets in Greenfield projects.
- SAP Solution Manager: A comprehensive application lifecycle management (ALM) platform that is invaluable for your S/4HANA transition. It supports various aspects, including project planning and documentation, process modeling, automated testing management, change control, and crucial post-go-live monitoring and operations.
- SAP Activate Methodology: This is SAP’s recommended framework that guides S/4HANA implementations and conversions. It combines SAP Best Practices, guided configuration, and a structured methodology across various phases (Discover, Prepare, Explore, Realize, Deploy, Run) to accelerate adoption, reduce costs, and ensure consistent project execution.
The output of a thorough pre-migration assessment is a detailed report that outlines the scope, effort, potential risks, and a preliminary roadmap for your S/4HANA transition. It provides the necessary insights for informed decision-making and project planning.
S/4HANA: Decision Matrix
| Consider System Conversion path if... | Consider new implementation or landscape transformation path if... | |
| Readiness For Future | Your current system fulfills your requirements for master data and organization structures for both today and the future. | You are striving to entirely redesign your master data and organizational structures. |
| Viewpoint of Current System | Critical Asset | Development or Innovation Bottleneck |
| Assumed Data Integrity | Good | Bad |
| Customized Code | Properly maintained | Obsolete |
| Release Version | At ERP 6.0 or higher | Below SAP ERP 6.0 |
| Historical Data | Mandatory to preserve historical data | No obligation to preserve historical data |
S/4HANA: High-Level Transition Roadmap
- Begin by delving into the available transition options.
- Build a high-level comprehensive strategy and plan for the initial discovery phase.
- Assess both SAP’s technical intricacies and business process assessment.
- Explore SAP’s industry best practices templates, for their potential as a foundation for new implementation.
- Dive into meticulous analyses of both master and transactional data to extract insights.
- Scrutinize how adaptable your financial processes and data are to upcoming transformative changes.
- Evaluate the readiness of integration of critical partner systems and supplementary system add-ons.
- Execute the SAP readiness check, covering intricate simplification items and custom code assessment.
- Comprehend the available deployment options for transitioning and their associated impacts.
- Conduct an in-depth business and IT discovery sessions to gain detailed insights.
- Assess the potential of data archiving to optimize your data for demands of an in-memory environment.
- Organize all conducted analyses and assess the pros and cons associated with each transition approach.
- Select the strategy that aligns most effectively with the specific requirements of your company.
- Develop a tangible proof-of-concept to show the practicality of the conversion process.
- Prioritize thorough testing and validation procedures to preemptively identify and address potential issues.
- Develop a comprehensive business case and program charter, tailored to the chosen trajectory.
- Develop a change management strategy, covering training, communication and stakeholder management.
- Prioritize data security and privacy throughout the transition process.
- Gather and compile estimates that provide a realistic outlook on achieving your chosen transition strategy.
- Outline a post-transition support strategy, to ensure a smooth and stable operational phase.
- Collaborate with a suitable partner who can provide comprehensive support throughout the journey.