SAP Software Logistics Tools: A Complete Guide 2025
Introduction
SAP Software Logistics tools (SLT) stands as an indispensable component within the realm of software development processes. It assumes responsibility for the meticulous planning, seamless coordination, and flawless execution of activities entailing the development, deployment, and sustained maintenance of software applications.
At the core of this endeavor lies the Software Logistics Toolset, a suite of purpose-built tools meticulously crafted by SAP. The primary objective? To elevate the management of these critical activities to new heights of efficiency and effectiveness. In the following article, we’ll embark on an in-depth exploration of the SL Toolset, uncovering its rich array of features and the substantial benefits it brings to the table.
Overview of Software Logistic Tool
Definition
Software logistics tools comprise a collection of software applications meticulously crafted to oversee the intricate processes of software development, deployment, and maintenance. These tools play a pivotal role in automating the software development lifecycle (SDLC) and establish a standardized framework for the management of software changes and updates within an IT landscape.
SAP’s software logistics (SL) tools are purpose-built to cater to the complex demands of enterprise-level software development and deployment. Their core mission is to significantly reduce the time and effort required for managing software logistics.
Concept
The essence of SAP Software Logistics (SL) tools lies in delivering a standardized set of procedures that comprehensively oversee the SAP development lifecycle from inception to deployment. This encompassing approach includes tasks such as managing dependencies between software components, facilitating the smooth movement of software components across different systems, handling releases, versioning, branching of code, quality management and testing, and robust documentation and reporting.
SAP’s SL tools are seamlessly integrated with other SAP solutions, providing developers and IT teams with a cohesive and consistent experience that simplifies the entire software logistics process.
Benefits
Here are some of the key benefits of using SAP software logistic tools:
- Streamlined Process: SAP’s software logistics tools assists businesses streamline their software development processes. These tools automate manual tasks and provide tools for software development, reducing the time and effort required for development and deployment.
- Improved Software Quality: Utilizing SAP’s software logistics tools enhances software quality. They offer testing and release management tools that enable businesses to identify and resolve issues before they impact users.
- Reduced Development Costs: Streamlining software development and improving quality through these tools can significantly reduce development costs. Faster development with fewer errors reduces the need for costly rework.
- Increased Efficiency: SAP’s software logistics tools boost efficiency by offering automation features and process optimizations, enabling businesses to work more efficiently.
- Enhanced Collaboration: These tools facilitate collaboration among team members by providing task management and change tracking capabilities, enabling teams to work together more effectively.
- Consistent User Experience: SAP’s software logistics tools include features for designing user-friendly and consistent interfaces. With tools like SAP Fiori, businesses can create seamless and intuitive user experiences for their software applications. This, in turn, can increase user adoption rates, lower training costs, and improve overall user satisfaction.
Types of SAP Software Logistic Tools
When it comes to managing SAP systems and landscapes, having the right set of tools is crucial. SAP Software Logistics Tools provides a diverse range of tools and methodologies for managing SAP systems and landscapes, each with its own unique features and benefits.
- System Provisioning Manager (SWPM)
- System Maintenance
- System Management
- Change & Transport Management (CTS)
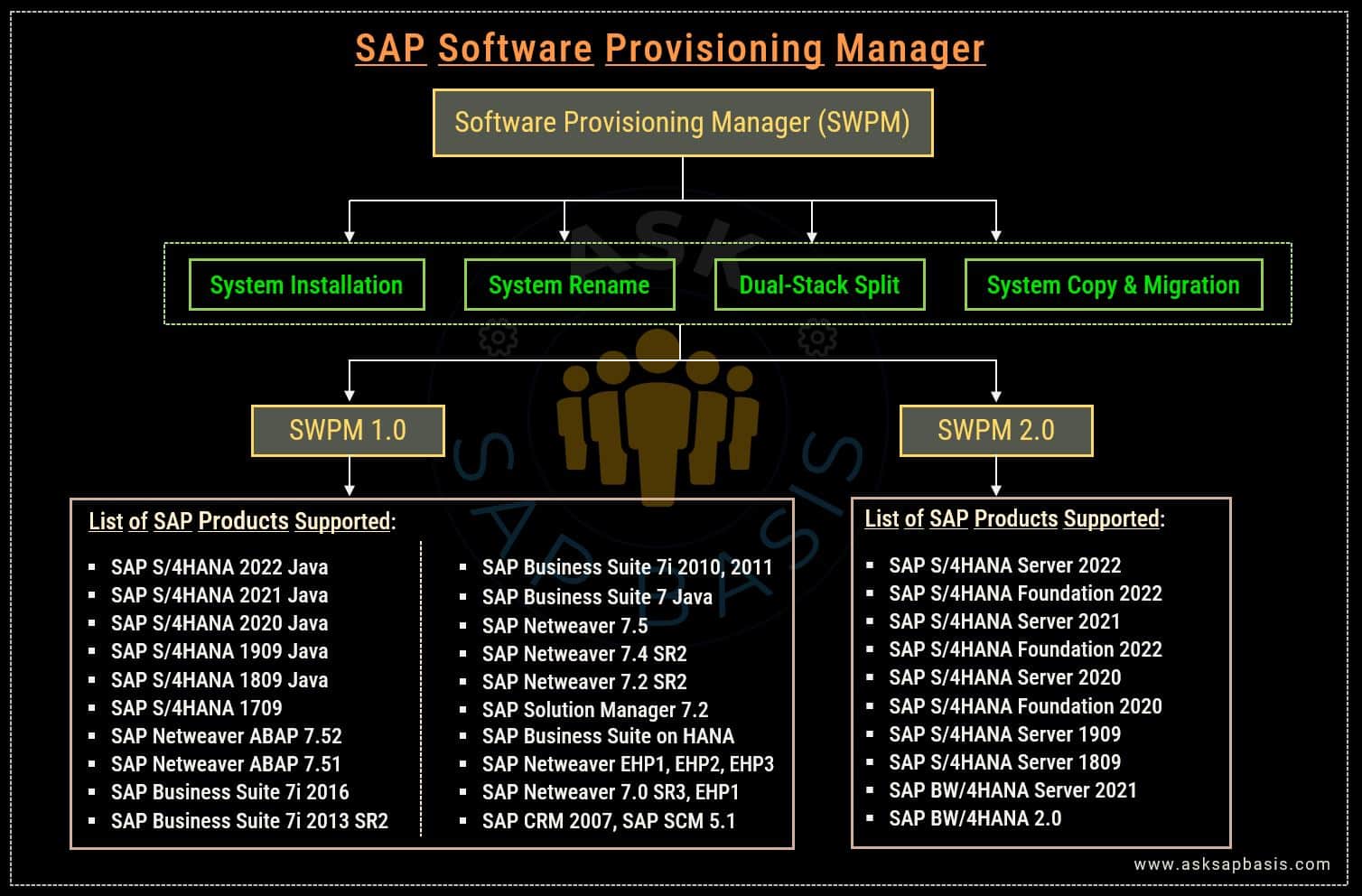
System Provisioning Manager (SWPM)
The Software Provisioning Manager is a robust tool that facilitates the execution of a vast array of system provisioning tasks across different platforms and products. This tool is adaptable and dependable, ensuring a seamless experience on all supported platforms. It is characterized by a consistent look-and-feel and behavior, making it effortless to utilize irrespective of the task at hand.
Use Cases
It has the capability to perform various tasks. Some of the use cases are:
- SAP System Installation
- System Copy and Migration
- System Rename
- Dual-Stack Split
Offering
The software provisioning manager is an advanced tool, that replaced the conventional delivery of provisional tools that were specific to product and releases. This cutting-edge software offers the latest version of SAPinst, that enables provisioning processes for several products and releases across all supported platforms.
Releases
Starting from SL toolset SPS 23, there are two versions of Software provisioning manager. To select the appropriate version, it is necessary to determine which SAP software you intend to provision:
1) Software Provisioning Manager 1.0
- SWPM 1.0 version supports provision scenarios for SAP system based on SAP NetWeaver and S/4HANA.
- Below are some of the scenarios:
- Installation of new systems, instances, and standalone engines.
- System copy of existing systems.
- System transformation such as via system rename and dual-stack split.
- Deletion of systems, instances, and standalone engines.
- To access the detailed product list of all SAP products supported by SWPM 1.0, click here.
2) Software Provisioning Manager 2.0
- SWPM 2.0 version supports provision scenarios for SAP system based on SAP NetWeaver ABAP and SAP HANA.
- Below are some of the scenarios:
- Installation of new ABAP systems using a HANA backup.
- System copy of existing systems with HANA DB method.
- Transformation of systems such as via system rename.
- Deletion of systems and instances.
- SWPM 2.0 has the capability to support SAP S/4HANA 2020 or higher and SAP BW/4HANA 2.0 or higher. To access a detailed product list, click here.
System Maintenance
System maintenance plays a pivotal role in software logistics for several compelling reasons. First and foremost, it serves as a critical component in ensuring the successful delivery and installation of software.
Primarily, system maintenance is instrumental in upholding the optimal performance of SAP servers and networks. By conducting routine checks and updates, it becomes possible to pinpoint and resolve potential issues before they escalate into system failures or costly downtimes. This level of proactive maintenance is of paramount importance, especially for businesses heavily reliant on their computer systems and networks to sustain their operations.
Furthermore, system maintenance assumes a critical role in bolstering security. Regularly scheduled security updates and patches serve as a robust defense mechanism against threats like malware and viruses. In today’s digital landscape, marked by an increasing prevalence of cyberattacks, this aspect of system maintenance gains even greater significance.
Use Cases
Below are the uses cases of system maintenance (SM):
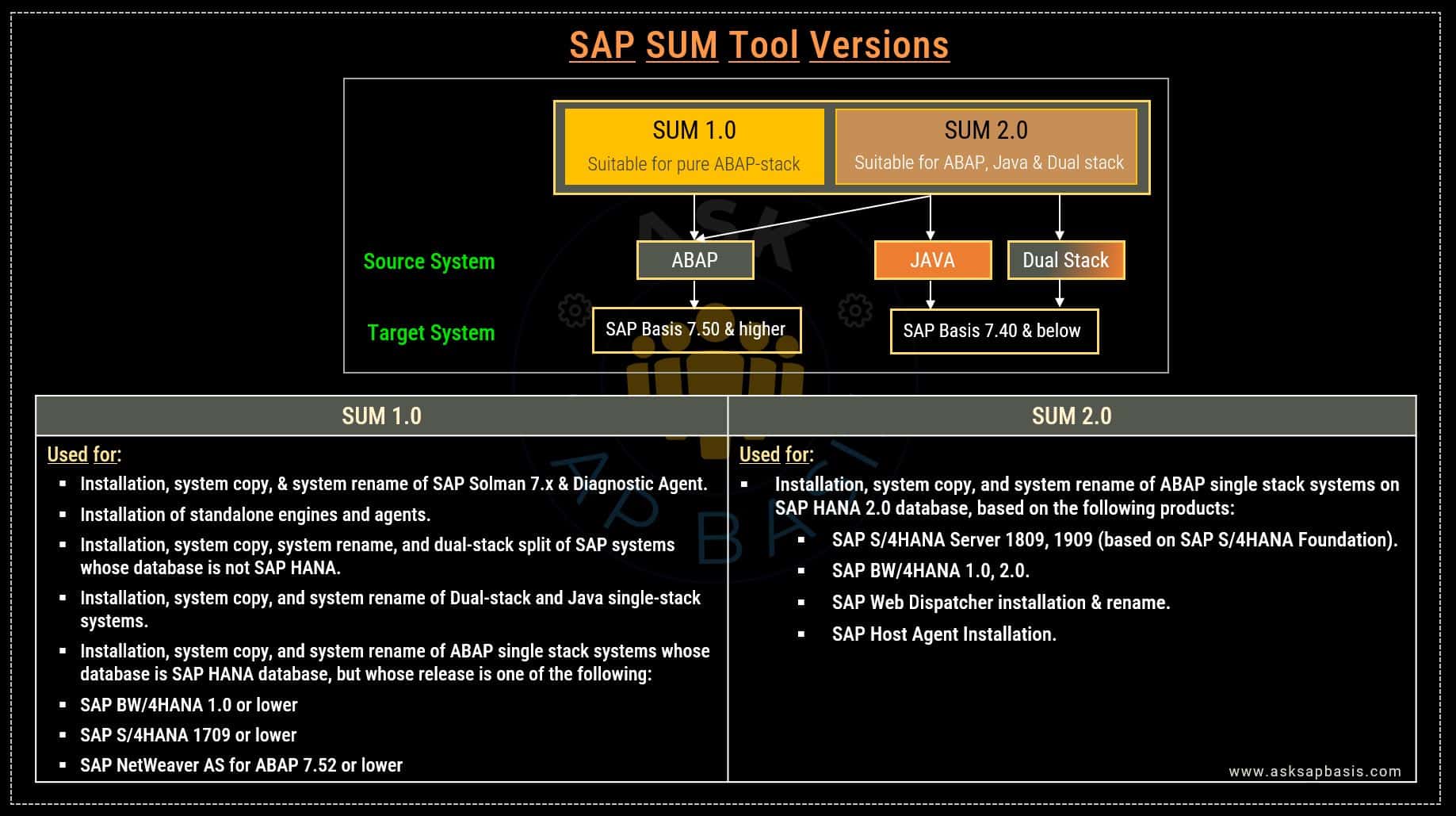
Software Update Manager (SUM)
SUM is a multi-purpose tool that is used for system upgrades and updates in both ABAP and JAVA-based SAP systems.
Software Update Manager (SUM) is a crucial tool in the SAP ecosystem, enabling seamless system upgrades and updates. It serves as a multi-purpose tool used for system upgrades and updates in both ABAP and JAVA-based SAP systems.
Key Benefits:
- Streamlined planning, execution, and tracking of system updates.
- Support for release upgrades, database migrations, EHP installations, support pack & stack updates, and system conversion to S/4HANA.
- Automatic system analysis and planning, including prerequisite and dependency checks, system requirements, preparation, compatibility, and backup procedures.
- Support for parallel processing, minimizing system downtime during updates.
- Regular updates by SAP to provide new features and improvements.
Choosing the Right SUM Version:
Post release of SL toolset SPS 23, SUM is offered in two releases – 1.0 and 2.0. Based on the relevant software version, choose the right SUM version.
- SUM 1.0: Designed for java stack, dual stack & ABAP stack (with target versions below 7.50).
- SUM 2.0: Recommended for pure ABAP stack & target versions based on 7.5 and above. It’s the ideal choice for system conversions and transitions from SAP ERP to SAP S/4HANA.
Note: If you use the “Maintenance Planner,” it automatically calculates the right SUM version based on your software version provisioning.
In practice, SUM plays a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth transition and maintenance of SAP systems, making it a valuable asset for businesses in their software management journey.
Scenarios:
SUM serves various use cases or scenarios, including:
a) Software Maintenance
This involves managing and updating the software components of an SAP system like:
- SAP Release Upgrade (major release change).
- EHP Install / Upgrade.
- Applying Support packages / stacks, for bug fixing and adding new functionality.
- Applying Java patches.
- Correcting installed software information.
- Merging updating, and migrating to SAP HANA (Database Migration Option ie DMO).
- System conversion from SAP ERP to SAP HANA.
b) Database Maintenance
This process entails converting an SAP system from one database type to another, primarily facilitated by SUM’s functionality called Database Migration Option (DMO). Its a combine technology for both update and migration.
Initially, DMO was designed to migrate to SAP HANA database only, but now can be used to convert to other database types too. DMO offers two options:
- DMO without system change: A pure migration without software-level alterations.
- DMO with system move: Migrating both the application server and database host. In cases where the target software level is lower than SAP BASIS 7.50. DMO can include technical Unicode conversion.
c) System Conversion
System Conversion transforms an SAP ERP system into an SAP S/4HANA system. Highlighted below are some important points to note:
- If the source system is not running on an SAP HANA database, SUM will perform the migration using DMO.
- In all cases, SUM is responsible for the software update, including applying new software components and updating existing ones.
- SUM also partially triggers the data conversion process. This involves transferring table content from the old data model to SAP S/4HANA’s simplified model.
- It’s important to note that SAP S/4HANA releases are all based on SAP BASIS 7.50 or higher. Therefore, a system conversion should be performed using SUM version 2.0.
Near Zero Downtime Maintenance (nZDM) for NW Java
nZDM technology minimizes downtime while applying software updates, enhancements, and maintenance to various SAP systems, including SAP Enterprise Portal, SAP Business Process Management, SAP Process Orchestration, and SAP Manufacturing Integration and Intelligence (MIII).
The nZDM Java tool supports the following database platforms:
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
- SAP HANA 1.0 SP10 and higher
- IBM DB2 for Linux, Unix and Windows (DB6)
- IBM DB2 for z/OS (DB2)
- SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (ASE)
- SAP MaxDB
You can find nZDM Java on SAP Service Marketplace at http://support.sap.com/sltoolset -> System Maintenance -> near-Zero Downtime Maintenance (nZDM) for Java 1.0 SP22 -> Download nZDM for Java.
SPAM / SAINT
SPAM (Support Package Manager) and SAINT (Software Application Integrated) are tools used in SAP systems to manage updates and enhancements. SPAM installs support packages and add-ons, while SAINT applies enhancement packages.
These tools enables SAP system administrators to handle updates and enhancements systematically and automatically. They offer a user-friendly interface for package downloads and installations, as well as package installation status tracking. Moreover, these tools ensure consistent updates and enhancements across all SAP systems in an organization.
SAP regularly updates these tools to introduce new features and improvements. The latest version of SPAM/SAINT, as of this article, is 7.57, providing enhanced performance and stability. Updating from version 7.00 to 7.57 involves several steps, including checking prerequisites, downloading the software, and installing the update.
Keeping SPAM/SAINT up-to-date is essential for maintaining optimal system performance and security. SAP offers comprehensive documentation and support for effective SPAM/SAINT use, including troubleshooting guides and best practices.
Keeping SPAM/SAINT up-to-date is essential for maintaining optimal system performance and security. SAP offers comprehensive documentation and support for using SPAM/SAINT, including troubleshooting guides and best practices.
System Management
In today’s digital age, managing a complex landscape of software applications and systems can be overwhelming. To simplify this process, many organizations turn to software tools and solutions. SAP offers a suite of landscape management tools that can help organizations streamline their processes, reduce downtime, and improve overall performance.
Let’s delve into a high-level understanding of the tools and software provided by SAP for landscape management and explore how they can benefit your organization.
SAP Landscape Management (LaMa)
The IT landscape is a critical component of businesses, comprising systems, servers, and software products. In the case of SAP-centric solutions, such as SAP S/4HANA and SAP BW/4HANA, the landscape’s deployment models can be on-premise, cloud-based, or a hybrid of both.
There are three states of the IT landscape: the current version, the next version in detailed planning, and the future vision for long-term planning. Landscape management helps you run and evolve your IT landscape by providing information on its current state, ways to change it (such as installations, updates, upgrades, and conversion to SAP S/4HANA and SAP BW/4HANA), and the integration of subscribed software.
The landscape evolution process involves planning and implementing changes to adapt to emerging business opportunities and new technologies. This process occurs in cycles, with each cycle starting by analyzing the current status quo to find the required changes to reach the next level. The process includes natural changes, such as the introduction of support packages, as well as more fundamental changes, such as the deployment model used.
Effective management of the SAP-centric IT landscape is essential to keep pace with changing business needs and technology advancements. By using the landscape management process, businesses can run and evolve their IT landscape efficiently, ensuring they remain competitive and innovative.
SAP Maintenance Planner
SAP Maintenance Planner is a web-based tool that helps customers plan and manage their SAP software updates and upgrades. It provides a streamlined and simplified approach to software maintenance planning and is integrated with the SAP Support Portal.
Key Features
- Plan and schedule maintenance activities.
- Create and edit maintenance plans.
- Track the progress of maintenance activities.
- Generate upgrade and installation guides.
- Plan downtime and minimize disruption to business operations.
- Manage dependencies between software components.
- Support both SAP Solution Manager and non-SAP systems.
- Provide access to the latest software updates and patches.
Benefits
- Provides a single point of access for all maintenance activities.
- Simplifies the software update and upgrade process.
- Enables detailed maintenance planning.
- Ensures systems are always up-to-date and secure.
Availability
- The maintenance planner tool is available for free to all SAP customers with an active support agreement.
Tools for Landscape Management
- SAP Landscape Transformation: A tool used to redesign SAP system landscapes by consolidating, splitting, or migrating systems.
- SAP Cloud ALM (CALM): An application lifecycle management tool designed for cloud-based SAP solutions.
- SAP Enterprise Architecture Designer: A collaborative tool used for designing, analyzing, and sharing enterprise architectures.
- SAP Focused Build: A project and portfolio management tool used for managing large-scale SAP projects.
- SAP Test Suite: A testing tool used for managing and executing automated tests in SAP applications.
- SAP IT Infrastructure Management: A tool used to manage and monitor IT infrastructure components in SAP systems.
- Solution Manager: An end-to-end application lifecycle management platform that provides a comprehensive set of tools for landscape management.
- SAP Solution Manager Process Management: Provides a framework for defining, executing, and monitoring business processes.
- SAP Solution Manager Test Management: Provides tools for planning, executing, and evaluating tests in SAP systems.
- SAP Solution Manager Custom Code Management: Provides insights into custom code usage in SAP systems.
By leveraging these tools, organizations can streamline their SAP operations, reduce costs, and improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of their SAP landscapes from application lifecycle management and testing to enterprise architecture design and IT infrastructure management.
Change & Transport Management (CTS)
SAP change and transport management (CTS) is a tool used for managing and transporting changes between different systems. It facilitates the movement of changes from development to testing and production environments. These changes are collected in transport requests, which can contain one or more modifications. CTS supports both ABAP & Java software components, including SAP HANA objects.
Key Features
- Transport Request Management (TMS): CTS provides various features to manage transport requests including locking, releasing requests, checking dependencies, and setting transport routes and layers.
- Transport Types: The tools supports different types of transports such as customizing, workbench and correction transports. Transport requests can be created manually or automatically, and can be grouped together into change documents for easier tracking.
- Logging and Monitoring: The tool provides detailed logging and monitoring capabilities to track the status of transports and troubleshoot any issues that arise.
- Integration: SAP Change and Transport System integrate with other SAP tools, such as SAP NetWeaver and SAP S/4HANA.
Benefits
- Improved Change Management: The tool allows for efficient management of changes, ensuring they are transported to the correct system in a controlled and organized manner. Developers can easily track the status of transport requests and ensure proper testing before being moving changes to production.
- Reduced Risk of Errors: CTS helps reduce the risk of errors that can occur when transporting changes between different systems. The system checks for dependencies and ensures that all necessary changes are transported together.
- Greater Control and Visibility: The tool provides greater control and visibility over the transport landscape, enabling administrators to manage transport routes, monitor transport status, and troubleshoot issues more frequently. This allows for faster and more efficient problem resolution.
Integrations
a) Git-Enabled CTS (gCTS)
- gCTS allows you to store all versions of ABAP development and customizing objects in Git repository (either on on-premise git sever or cloud-based git server). This feature is available in SAP S/4HANA 1909 and onwards.
- The key concept involves moving objects to a Git repository and deploying them to any environment such as test, production or another development. Notably, a shared transport directory is no longer required when using gCTS.
- As a pre-requisite for using gCTS, you first need to define the ABAP packages managed by the gCTS repository and assign a gCTS-specific transport layer to those packages.
b) HTA for HDI
- With SAP HANA Transport for ABAP (HTA) for SAP HANA Deployment Infrastructure (HDI), allows you to create content for ABAP for SAP HANA applications encompassing both HDI and ABAP objects. This content can then be transported efficiently using CTS of AS ABAP.
- HTA is successor to previous tool SAP HANA repository and is available from SAP Netweaver 7.5 Enhancement Package 2, Support Package 02 onwards.
c) Central CTS (cCTS)
- cCTS introduces functions that enhance the classic CTS, enabling centralized control of transports in complex heterogeneous system landscapes.
- cCTS introduces two new entities: Clusters and Collections. Clusters are used to group systems together, while collections are used to bundle transport requests from different systems. This allows you to group multiple systems from your transport landscape into system clusters.
- Its important to note, that cCTS is designed to be used within ChaRM and Quality Gate Management (QGM) and cannot be used outside of these application.
- You can control the transports into the managed systems, from the cCTS server.
Enhanced Change & Transport Management (CTS+)
The CTS+ empowers you to transport non-ABAP objects, such as Java objects and objects of SAP-related non-ABAP applications, across your system landscape, alongside ABAP objects.
Starting with SAP Netweaver 7.0 SP12, CTS+ is available with option of integration of applications through close coupling. The objective is to create a single transport tool that supports all development workbenches and applications, while keeping the tools for creating applications and content unchanged.
Key Features
- Compatibility
- CTS+ is compatible with both on-premise and cloud-based SAP systems.
- Transport Management System
- CTS+ supports multiple transport routes, enabling users to transport changes from the development environment to production in a flexible manner.
- Transport requests can be released independently of each other, allowing for greater agility in the development process.
- A graphical user interface (GUI) is provided to manage transports and monitor their status.
- Error Handling & History Tracking
- CTS+ uses the Quality of Service Management (QoSM) framework to automate error handling during the transport process and also keeps a track a transport history.
- The tool is designed to transport non-ABAP objects, allowing for more diverse changes to be transported across the systems.
- Customization
- CTS+ is highly customizable, allowing users to configure transport paths and routes to meet specific business needs.
- The tool supports different types of transport routes, including sequential, parallel, and round-trip routes.
- The tool supports both manual and automated transport workflows, and it can integrate with third-party automation tools.
- The tool supports the creation of custom transport requests for transporting specific changes across the systems.
- Integration
- CTS+ integrates with SAP Solution Manager to provide end-to-end change management for SAP systems.
- CTS+ also integrates with other SAP tools, such as SAP BTP, SAP PI, SAP BusinessObjects etc to provide a comprehensive change management solution.
- The tool can be integrated with third-party automation tools, such as Jenkins or Git, to automate the transport process.
Benefits
- Improved Change Management
- CTS+ provides greater flexibility and control over the transport process.
- The tool supports the independent release of transport requests, allowing for agile development.
- The tool can transport non-ABAP objects, enabling the transportation of more diverse changes.
- Increased Efficiency
- CTS+ supports multiple transport routes, enabling changes to be transported to multiple systems simultaneously or sequentially.
- Advanced features like automated error handling and transport history tracking streamline the transport process.
- Greater Flexibility
- CTS+ is highly customizable, allowing users to configure transport paths and routes to meet specific business needs.
- The tool supports both manual and automated transport workflows and can integrate with third-party automation tools.
Useful Resources
- SAP Software Provisioning Manager (SWPM)
- SAP Note 1680045: Release Note for Software Provisioning Manager 1.0
- SAP Note 2568783: Release Note for Software Provisioning Manager 2.0
- SAP Note 1738258: System Copy for Systems Based on SAP NetWeaver (SWPM 1.0)
- SAP Note 1619720: System Rename for SAP Systems based on SAP NetWeaver (SWPM 1.0)
- SAP Note 1797362: Dual-Stack Split for Systems Based on SAP NetWeaver (SWPM 1.0)
- nZDM (Near Zero Downtime Management) for NW Java