SAP Sizing on Cloud: A Foundational Guide 2025
Overview
Sizing your SAP systems in the cloud isn’t just a technical checkbox—it’s the foundation of your performance, cost, and scalability strategy. Unlike traditional on-prem sizing, the cloud brings elasticity, dynamic scaling, and platform-specific nuances that can either elevate or hinder your SAP environment. SAP sizing on cloud is a critical process that involves determining the appropriate size and configuration of the cloud infrastructure to support SAP workloads efficiently.
In this guide, we break down the tools, techniques, and key considerations for getting cloud sizing right—whether you’re running SAP HANA, ECC, or S/4HANA across AWS, Azure, or GCP. Let’s demystify the cloud sizing journey and help you avoid costly mistakes.
Purpose
The goal of this article is to provide a comprehensive guide to size public cloud infrastructure for hosting SAP. It should cover the basics of virtual machine (VM) sizing to specific considerations for SAP workloads on cloud. This article is for those who already have experience in sizing on-premises systems.
Benefits of SAP on Cloud
In recent times, the corporate landscape has witnessed a significant shift as companies increasingly migrate their SAP systems from on-premises environments to the cloud. This migration trend is driven by a compelling array of advantages.
SAP, as a cornerstone Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, plays a pivotal role in how businesses manage their operations. Meanwhile, cloud computing platforms featuring behemoths like Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud offer a wealth of opportunities for scalability, agility, and efficiency. By seamlessly integrating SAP with the cloud, organizations can harness the synergistic power of these two technological juggernauts.
Here are some key benefits of hosting SAP on the cloud, compared to traditional on-premises systems, to help you make an informed decision for your deployment:
1) Cost Effectiveness
- Pay-as-You-Go Model: Cloud services often operate on a pay-as-you-go or subscription basis, wherein you pay only for the exact resources you utilize. This eliminates the need for substantial upfront capital investment, making it more cost-effective for businesses of various sizes to access and maintain SAP systems.
- Resource Optimization: Cloud providers offer cost optimization tools and recommendations, helping you identify opportunities to reduce expenditure without sacrificing performance.
2) Flexibility in Resource Allocation
- Granular Control: SAP on the cloud provides organizations with an exceptional degree of granularity in managing their resources. This level of detail allows for the meticulous allocation of resources, aligning them perfectly with specific requirements. By doing so, it not only eliminates resource wastage but also orchestrates a finely tuned, cost-effective SAP environment.
- Preventing Waste, Optimizing Costs: The cloud’s adaptability is a financial boon. It empowers organizations to shelve the concept of over-provisioning and, instead, cultivate an environment where resources are allocated with surgical precision. This prevents excess spending while maximizing the value of every resource invested.
- Smooth, Efficient, and Cost-Effective Operation: As a result of this granular control, SAP environments on the cloud operate with exceptional smoothness, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Resource allocation aligns harmoniously with operational demands, eliminating bottlenecks and ensuring peak performance.
3) Scalability and Agility
- Effortless Scalability: With traditional sizing, it can be difficult to accurately estimate the resources needed for a particular workload. Cloud platforms offer the ability to effortlessly scale up or down based on demand. This eliminates over-provisioning scenarios, ensuring you never pay for unused resources. Cost savings accrue as your SAP environment aligns precisely with your needs.
- Rapid Adaptation: Cloud platforms are inherently agile, capable of swiftly adapting to changing organizational needs. This agility is especially valuable in a dynamic business landscape where market shifts, customer demands, and internal changes necessitate quick resource adjustments. SAP on the cloud ensures that your environment remains agile and efficient.
4) Enhanced Performance and Efficiency
- High Availability: With SAP on Cloud, organizations can benefit from improved efficiency and performance of their SAP environment. The cloud platform offers optimized resources, ensuring that the SAP system runs smoothly, without any performance issues. They are designed with redundancy and failover capabilities, ensuring your organization’s SAP environment is always accessible, reducing any downtime and improving overall productivity.
- Built-in Disaster Recovery: Cloud platforms often include built-in disaster recovery options, simplifying the process of data backup and restoration in case of unforeseen events.
- Global Reach: Cloud data centers are strategically located worldwide, reducing latency and ensuring consistent performance for users across different geographic regions.
5) Elevated Security and Compliance
When you host SAP on Cloud, it can bring about the added advantage of boosting security and compliance measures. By utilizing cloud platform, you can benefit from advanced security features, such as data encryption and identity management, that can provide protection to your SAP data against potential cyber threats. In addition, Cloud’s compliance with various industry standards and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001, makes it easy for you to meet your compliance obligations with minimal effort and hassle.
- Advanced Security Measures: Hosting SAP on the cloud bolsters your security posture. Cloud providers offer advanced security features like robust data encryption and identity management, fortifying your SAP data against potential cyber threats. This enhances the protection of your SAP data and applications.
- Compliance Assurance: Cloud platforms adhere to a myriad of industry standards and regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. This simplifies compliance obligations, allowing organizations to meet stringent regulatory requirements with ease.
Essential Factors for SAP Cloud Sizing
Sizing your SAP system on cloud hosting platforms is a critical endeavor that demands careful consideration of several key factors. To ensure your SAP deployment runs seamlessly, let’s break down these essential aspects:
1) Understanding You SAP Workload
The first step in sizing your SAP system on cloud is to understand your system’s workload and performance requirements, based on which the appropriate virtual machine configuration can be explored. You need to understand your system’s usage patterns, data storage requirements, and performance metrics. Additionally, you should consider any future growth or changes to your SAP system.
The first step in effectively sizing your SAP system for the cloud is gaining a profound understanding of your system’s workload and performance requirements. This knowledge forms the foundation upon which the appropriate virtual machine (VM) configuration can be crafted. To achieve this, delve into the following:
- Usage Patterns: Analyze historical and projected transaction volumes. Scrutinize your system’s usage patterns to identify peak loads and typical operational demands. Understanding transaction patterns is key to resource allocation.
- Concurrent Users: Consider the number of users accessing your SAP system simultaneously. Different modules and tasks may have varying user demands, so segment your analysis accordingly.
- Data Storage Needs: Assess the volume of data your SAP system generates and stores. Understanding your data storage requirements is crucial for resource allocation.
- Data Processing Requirements: Examine the intricacies of data processing. Are there resource-intensive batch jobs or real-time data streaming? This level of granularity ensures your system is tuned for optimum performance.
- Performance Metrics: Establish clear performance metrics to gauge your system’s responsiveness and efficiency.
- Future Considerations: Anticipate future growth or changes in your SAP system to ensure scalability.
Remember, precise performance data forms the bedrock of effective sizing. The more accurately you analyze your SAP workloads, the better equipped you’ll be to make informed decisions.
2) Choosing appropriate VM Size
Before we delve into sizing your SAP system, it is imperative to understand the fundamentals of cloud virtual machines (VMs). They come in variety of sizes, each offering a distinct combination of CPU cores, memory, and disk space. These size options range from small, low-cost options to robust, resources-rich alternatives.
Next step is to determine the perfect blend of virtual machines needed to host your SAP system. When sizing your SAP system, precision is key. Selecting the right VM size hinges on aligning it with your system’s workload and performance prerequisites. Notably, not all cloud VM types are compatible with SAP applications. SAP mandates specific CPU-to-memory ratios, and there exists a specialized set of VMs tailored precisely for SAP hosting.
Its not just about the number of VMs, its about ensuring each one is finely tuned with the required specifications, such as:
- CPU Allocation: Calculate CPU requirements based on your performance analysis. Consider factors like number of cores, clock speed, and hyper-threading capabilities.
- RAM Configuration: Determine the optimal RAM size for each VM. SAP workloads often demand significant memory resources, so striking the right balance is critical.
- Disk Space: Don’t overlook storage performance. Consider not only the size of disks but also their type (SSD or HDD) to ensure smooth, responsive operations. The number of data disks you can attach to a virtual machine and the type of storage you can use to host these disks are determined by the virtual machine’s size.
3) Networking Resources
Your network infrastructure is the lifeline of your SAP ecosystem. SAP workloads require high network bandwidth to ensure fast and reliable communication between servers and clients. It must be robust enough to effortlessly handle SAP’s intricate web of communications:
- Bandwidth: Ensure your network provides ample bandwidth for SAP communication. High data transfer rates are vital for a responsive system.
- Latency: Keep latency to a minimum. Low-latency networks enhance the user experience and support real-time data processing.
- Redundancy: Implement redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure network reliability. A network outage can disrupt your entire SAP environment, so plan for resilience.
4) Storage Requirements
The heart of your SAP workloads lies in data, and so estimating your storage needs is paramount. SAP systems generate a large amount of data and you need to ensure that your VM’s have sufficient storage to handle data. Also, you need to consider the appropriate storage type you need, either standard HDD or SSD. To avoid bottlenecks and data access delays, consider:
- Database Size: Calculate the size of your SAP database. Account for both current data and future growth projections.
- Application Binaries: Don’t forget about the space required for SAP application binaries and libraries. These files play a vital role in system performance.
- Log Files: Ensure you allocate ample space for transaction logs and other system logs. Neglecting log storage can lead to unexpected issues.
Choosing the right storage type, whether it’s the speed of SSDs or the capacity of HDDs, is a strategic move for top-notch performance. Each storage choice comes with its own set of benefits and considerations, so make an informed decision based on your specific needs.
5) Security
SAP systems contain sensitive data, underscoring the critical importance of robust data security measures. protection is one of the key aspect that need to be protected. Also, you need to consider other security factors during sizing, such as identity and access management (to control access to SAP system), network security, compliance (with relevant regulations and industry standards), monitoring and auditing (security incidents or potential threats).
In the realm of sizing, security considerations extend to:
- Identity and Access Management: Implement stringent controls to govern access to your SAP system, safeguarding it against unauthorized entry.
- Network Security: Fortify your network’s defenses to repel potential threats and breaches.
- Compliance: Ensure that your SAP system adheres to relevant industry standards and regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001).
- Monitoring and Auditing: Implement robust monitoring and auditing procedures to promptly detect and respond to security incidents or potential threats.
6) Availability and Disaster Recovery
Your SAP system is the lifeblood of your business, and its continuous availability is non-negotiable. In this context, cloud hosting offers critical features such as availability sets and site recovery capabilities. These features are instrumental in ensuring the high availability and disaster recovery preparedness of your SAP system.
Plan for the unexpected by building in high availability and redundancy to minimize downtime and ensure data integrity.
- Load Balancing: Distribute incoming traffic evenly across multiple servers to prevent overloading and ensure consistent performance.
- Failover Mechanisms: Implement automated failover systems that seamlessly switch to backup resources in case of hardware or software failures.
- Redundancy Planning: Incorporate redundancy in critical components of your SAP system to eliminate single points of failure. Redundancy is a critical aspect of SAP sizing on the cloud.
- Disaster Recovery Testing: Regularly test your disaster recovery plan to ensure it functions as expected during real-world scenarios, an integral part of SAP sizing to maintain performance and availability.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up your SAP data to protect against data loss and facilitate rapid recovery in case of disasters.
- Scheduled Backups: Set up automated, regular backups of your SAP system data to ensure you have up-to-date copies, aligning your backup strategy with SAP sizing principles.
- Offsite Storage: Store backup copies in an offsite location to safeguard against on-premises disasters, an essential consideration in SAP sizing.
With these elements in your arsenal, you’re well on your way to mastering SAP sizing on the cloud, unlocking peak performance, and ensuring that your SAP workloads thrive in the digital realm.
Understanding SAP Cloud Sizing
Sizing Approaches: Traditional Vs Cloud Sizing
Sizing SAP in the cloud has significant differences from traditional on-premises or hosted solutions. In the past, system administrators and consultants had to buy hardware infrastructure that was intended to serve for the next 3 to 5 years. But now with the advent of the cloud, the ability and flexibility to dynamically resize on demand are one of the distinguishing characteristics of cloud sizing and traditional on-premise sizing.
Challenges of Traditional Approaches:
- Static Hardware Investments: Historically, IT administrators were tasked with purchasing hardware infrastructure meant to endure 3 to 5 years. However, this static approach often clashed with the dynamic nature of the business needs, making it difficult to accurately forecast future needs.
- Virtualization Constraints: Virtualization technology offered the ability to modify hardware resources available within a virtual machine, including doing so dynamically in real-time. However, it remained constrained by the underlying hardware limitations. Without extensive infrastructure (virtualization farms were deployed at a hyper-scale), this flexibility often when underutilized.
- Ad-hoc Demands: Unplanned requests from the business teams for system copies to test new functionalities frequently strained resources, leading to delays and inefficiencies.
- Excessive Buffering: Traditional hardware procurement typically included a substantial buffer to account for uncertainties and risks tied to static resource allocation. This often resulted in over-provisioning and inefficient resource use during the initial stages. However with cloud deployments, there is no need for such a large buffer.
Advantages of Cloud Deployments:
- Dynamic Scalability: Unlike traditional hardware investments, cloud solutions offer unprecedented flexibility. Organizations can seamlessly adjust resources in response to evolving business needs, eliminating the problem of over-provisioning and ensuring optimal resource allocation. This dynamic scalability directly addresses the challenge of static hardware investments.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Cloud deployments break free from the constraints of physical hardware. They allow organizations to allocate and de-allocate virtualized resources on-demand, maximizing resource utilization. This efficiency counteracts the limitations of traditional virtualization technology, which often bound resource adjustments by physical hardware limitations.
- Rapid Response to Ad-hoc Demands: In the cloud, organizations can easily accommodate unplanned requests for system copies. The scalability and availability of resources enable swift provisioning of virtual machines and storage, effectively meeting unplanned demands. This capability directly addresses the challenge of resource scarcity during spontaneous business requests.
- Precise Resource Allocation: Traditional hardware procurement often involved excessive buffering to mitigate uncertainties, leading to resource underutilization in the initial stages. In contrast, cloud deployments introduce precise resource allocation and billing models, allowing organizations to allocate resources with precision. This fine-grained allocation aligns resources more closely with actual requirements, eliminating the need for excessive buffering.
In summary, cloud deployments offer a strategic advantage by not only mitigating the challenges posed by traditional approaches but also providing a dynamic, efficient, and cost-effective solution. Embracing cloud-based SAP sizing empowers organizations to adapt swiftly to changing business landscapes, optimize resource utilization, and gain a granular understanding of infrastructure costs, fostering a more agile and efficient business environment.
Cloud Sizing Methodology
Historically, when sizing or purchasing infrastructure for SAP on-premises, you have to try and predict not only what you need today, but also what you might need for the next 3 to 5 years. However, sizing on the cloud offers you greater flexibility to scale up and scale down as and when required. This distinction between traditional on-premises sizing and cloud-based sizing is a game-changer.
Now, let’s delve into the crucial aspect of ensuring you have the right amount of computing power and storage when migrating your SAP applications to the cloud. This is where SAP’s right-sizing and tight-sizing methodologies come into play, providing you with invaluable guidance to achieve optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
The objective of these two approaches is to ensure optimal performance while avoiding overprovisioning, which can lead to unnecessary costs.
Understanding SAP Right Sizing
SAP’s ‘right sizing’ approach revolves around provisioning precisely the resources your SAP applications require in the cloud environment. This includes a comprehensive evaluation of various factors, including user activity, system complexity, and a performance analysis of your SAP workloads. The ultimate goal? Identifying the ideal balance of CPU, memory, and storage to support your SAP application effectively.
In simpler words, in the cloud, the right approach is to size what you need today and then scale up or scale down as business requirement evolve. This approach is referred to as “right sizing“.
Right sizing eliminates the risk of under provisioning, which can result in performance bottlenecks, as well as the peril of overprovisioning, which unnecessarily inflates costs. It’s a dynamic approach that aligns your resources precisely with your current demands.
Exploring SAP Tight Sizing
On the other hand, SAP’s ‘tight-sizing’ approach takes resource optimization to the next level for your SAP applications in the cloud. This involves fine-tuning various factors, such as memory utilization, CPU efficiency, and disk space allocation.
In other words, “tight sizing” involves looking for opportunities to further fine tune the system sizing. It is driven by the unique nature of your business and how your SAP systems are utilized.
Tight sizing guarantees that your SAP applications operate at peak efficiency without squandering valuable resources or compromising on performance. By optimizing resource utilization, you can achieve substantial cost savings while enhancing overall performance.
In summary, SAP’s ‘right-sizing‘ ensures that you have precisely the resources you need for today, with the flexibility to adapt to future changes. Meanwhile, ‘tight-sizing‘ fine-tunes these resources to maximize efficiency. Both methodologies are your keys to achieving the perfect balance between performance and cost-effectiveness in your cloud-based SAP environment.
| Right Sizing | Tight Sizing |
| Right sizing lowers the upfront cost. | Tight sizing for close relation of system sizes with service demands. |
| Use Quick sizer or reference sizing to determine initial system size. | Most system demands are predictable (quarter end, year end, business events etc). |
| Shorten your sizing horizon - size for 6 months instead of multiple years. | Ongoing cost monitoring and controlling. |
| Rationalize the simple lift and shift, instead rationalize system and system sizes. Azure allows flexible quick upsizing later. | Azure allows flexible quick upsizing. |
| IT cultural shift toward infra on-demand mentality. | IT cultural shift. |
Cloud Sizing Strategy
SAP sizing strategy on the cloud involves determining the appropriate cloud resources and infrastructure requirements for implementing an SAP system in a cloud environment.
Cloud-based SAP systems require a different approach to sizing compared to
traditional on-premises systems because the cloud offers dynamic scalability & flexible pricing models.
Key Considerations for Cloud-Based SAP Sizing
When embarking on the journey of SAP implementation in the cloud, optimal performance and cost-effective operation are paramount. To achieve this, the sizing process must take into account several critical factors, such as the number of users, volume of data, desired level of availability, and expected growth in usage over time.
A meticulously planned sizing strategy for cloud-based SAP systems plays a pivotal role in steering clear of common pitfalls. These pitfalls include the dreaded scenarios of over-provisioning, leading to unnecessary costs, or under-provisioning, resulting in suboptimal system performance.
An effective sizing strategy is not just about preventing resource misallocation; its about optimizing the entire system performance and cost structure. Such a strategy equips organizations with a scalable and cost-efficient solution that grows in tandem with their evolving needs.
Both on-premise physical and virtual machines, as well as cloud environments, can benefit from two widely used sizing strategies for SAP system are:
1) SAP Quick Sizer (Greenfield Sizing)
If you are venturing into the cloud for the first time and haven’t yet embarked on deploying any systems or workloads, its recommended to begin with SAP Quick Sizer.
SAP Quick Sizer stands as a vital tool for capacity planning and budgeting, especially when sizing up your SAP system. It comes equipped with two distinctive approaches to sizing:
- User-Based Sizing: In this approach, SAP Quick Sizer considers the number of users who will interact with your SAP system. It then recommends the necessary resources based on this user count. The CPU sizing results are determined against an average CPU utilization of 33.3% to ensure predictable server performance.
- Throughput-Based Sizing: Conversely, this approach centers around the throughput or processing requirements of your SAP system. Quick Sizer provides a recommended number of SAPS (SAP Application Performance Standards) for each processing requirement. These SAPS serve as a benchmark for selecting the appropriate server. An average CPU utilization of 65% is factored in for throughput-based sizing to guarantee consistent server performance.
It’s noteworthy that the CPU utilization figures (33.3% for user-based and 65% for throughput-based) are already accounted for in SAP Quick Sizer. This negates the need for further complex calculations.
Leveraging SAP Quick Sizer for Informed Sizing Decisions
- SAP Quick Sizer simplifies SAP system sizing by providing SAPS recommendation. For instance, if your database server needs 80,000 SAPS, Quick Sizer guides you to select a server with precisely that capacity. Every cloud provider (Azure, AWS, GCP, etc.) offers SAPS data for virtual machines.
- SAP Quick Sizer accounts CPU utilization (65%), sparing you from complex calculations. So now you have two choices:
- Scale Up: Choose more SAPS if you need extra processing power.
- Scale Down: Pick fewer SAPS if your system exceeds expectations.
SAP Quick Sizer empowers data-driven sizing decisions, ensuring optimal performance and budget alignment for your SAP system in the cloud.
2) SAP Reference Sizing (Brownfield Sizing)
In your cloud journey, once you’ve deployed one or two systems, SAP reference sizing, steps in as the recommended method.
Leveraging Real-World Data for Precision
- The brownfield approach, involves a careful examination of the performance of SAP system you’ve already deployed or migrated to cloud, particularly those similar to the ones you plan to migrate or using other real-time productive customer performance data and hardware setup. By making this comparison, you can get a reasonably accurate estimate of your sizing needs.
- Example: Suppose you have an on-premises system that you wish to migrate to cloud, and it is three times larger than a system you have already deployed in cloud. In this scenario, you can adjust the sizing requirements based on the systems you have already deployed in cloud and then proceed to deploy the new system.
Flexibility and Agility in the Cloud
- What sets the cloud apart from on-premise hosting is the ease and speed with which you can adjust CPU and memory resources. This is made possible by selecting different virtual machine sizes, allowing for agile resource management.
- In contrast, the traditional on-premises approach involves assessing current infrastructure, adding a buffer, and accounting for expected workload growth over several years.
- However, its crucial to highlight that a simple 1:1 mapping of current on-premise CPU and RAM against cloud VM types is not recommended. Doing so often results in significantly oversized systems. This happens because on-premise are sized with a three-year future horizon in mind, while the cloud offers the flexibility to scale up and scale down as needed.
Insightful Sizing and Iterative Process
- For on-premise reference sizing, having a clear understanding of current SAP CPU resource utilization is crucial. This data can be provided by tools like the Early Watch Report (EWA), offering detailed insights that aid in accurate sizing.
- Sizing SAP systems is typically an iterative process. The accuracy of your sizing is heavily influenced by the quality and quantity of information available during the sizing process. Moreover, it hinges on where a customer stands in their SAP project lifecycle.
- Reference sizing, or brownfield sizing, allows organizations to harness real-world data and cloud flexibility to arrive at precise sizing decisions. It’s a pivotal step in ensuring that SAP systems in the cloud perform optimally without unnecessary resource allocation.
If a customer is just beginning their SAP journey, SAP Quick Sizer is the tool of choice. However, if SAP is already implemented for production, a combination of expert sizing with Quick Sizer or reference-based sizing comes into play.
Cloud Sizing Approach
To successfully deploy an SAP system on a cloud service provider’s infrastructure, a strategic cloud sizing approach is indispensable. This approach ensures seamless compatibility between your on-premises SAP system(s) and the cloud service provider’s Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) support matrix for SAP.
The foundation of this approach lies in verifying the harmonious coexistence of your operating system, database, and SAP applications with the resources and availability service level agreements (SLAs) offered by the cloud service provider.
- As a first step, customers need to validate below items:
- Supported VM types, provided by cloud service providers that are certified for hosting SAP systems
- SAP supported products and releases on cloud IaaS.
- Supported OS and DB combinations for specific SAP products in cloud.
- SAPS throughput and storage types provided by different Azure SKU’s.
- You can find answers to these questions in relevant cloud service providers SAP Notes.
- As a second step, you need to validate the cloud IaaS resource and bandwidth limitations, against the actual resource consumption of on-premises systems.
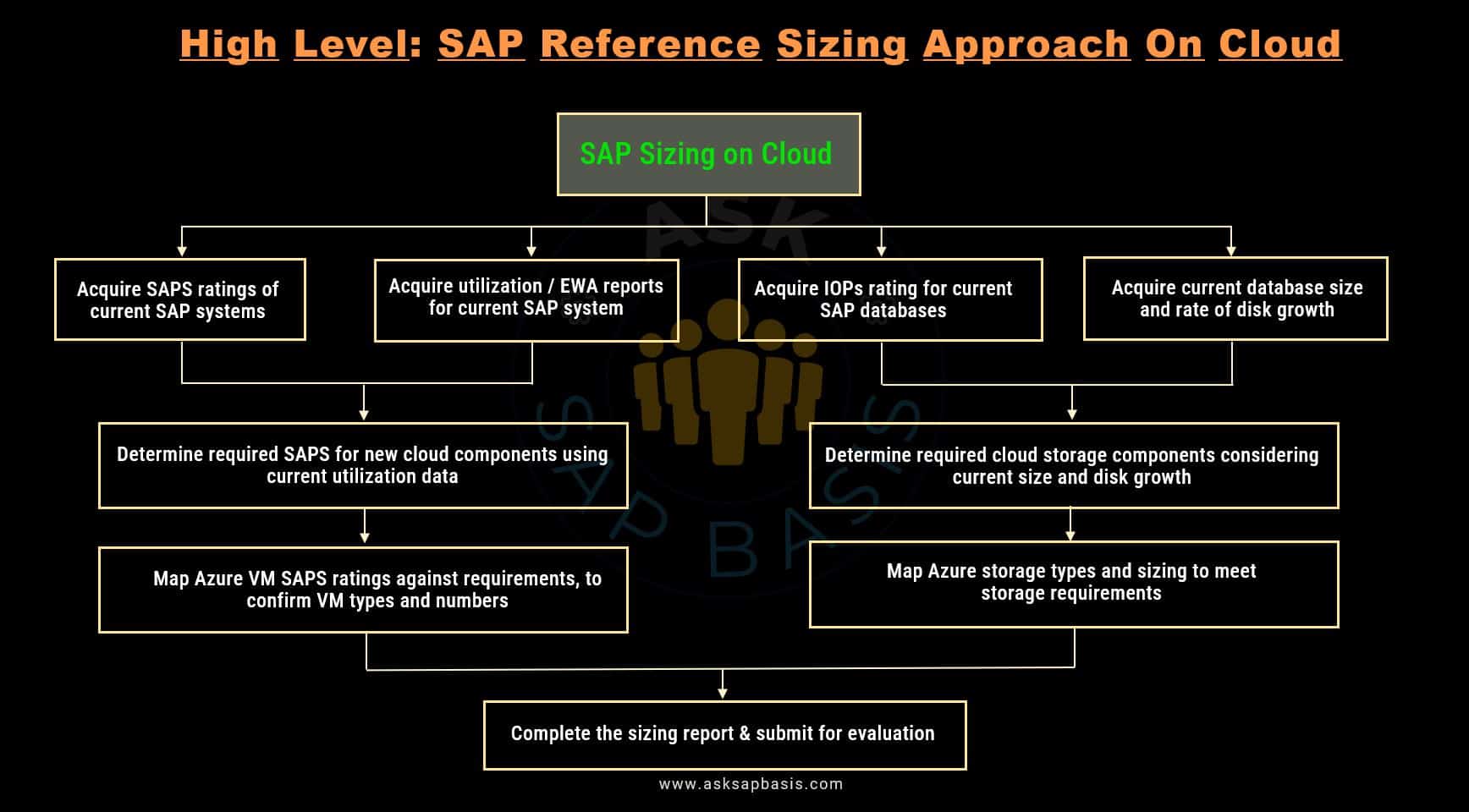
- Determine the SAPS requirement for a given SAP system (SAPS requirement for both App & DB layer needs to be separately considered).
- Obtain SAPS for current SAP system based on current CPU resource utilization and SAPS rating, based on which relevant cloud VM requirement can be derived.
- Obtain IOPS for current SAP database, based on current DB size & growth, based on which relevant could storage requirements can be derived.
- Map the derived SAPS & IOPS requirements against the relevant cloud service provider SAP Notes, for determining SAP supported cloud VM types & storage requirements.
- Explore different capabilities of cloud VM types supported with SAP in the areas of:
- Consider CPU and memory resources of different VM types,
- IOPS bandwidth of different VM types.
- Network capabilities of different VM types.
- As a last step, evaluate availability requirements. Some cloud supported geographical regions of cloud service provider, may not offer all VM SKU’s and not all types of cloud VMs can support SAP applications. You can find answers to relevant VM SKUs availability provided by various SAP cloud service providers here.
Cloud Sizing Best Practices
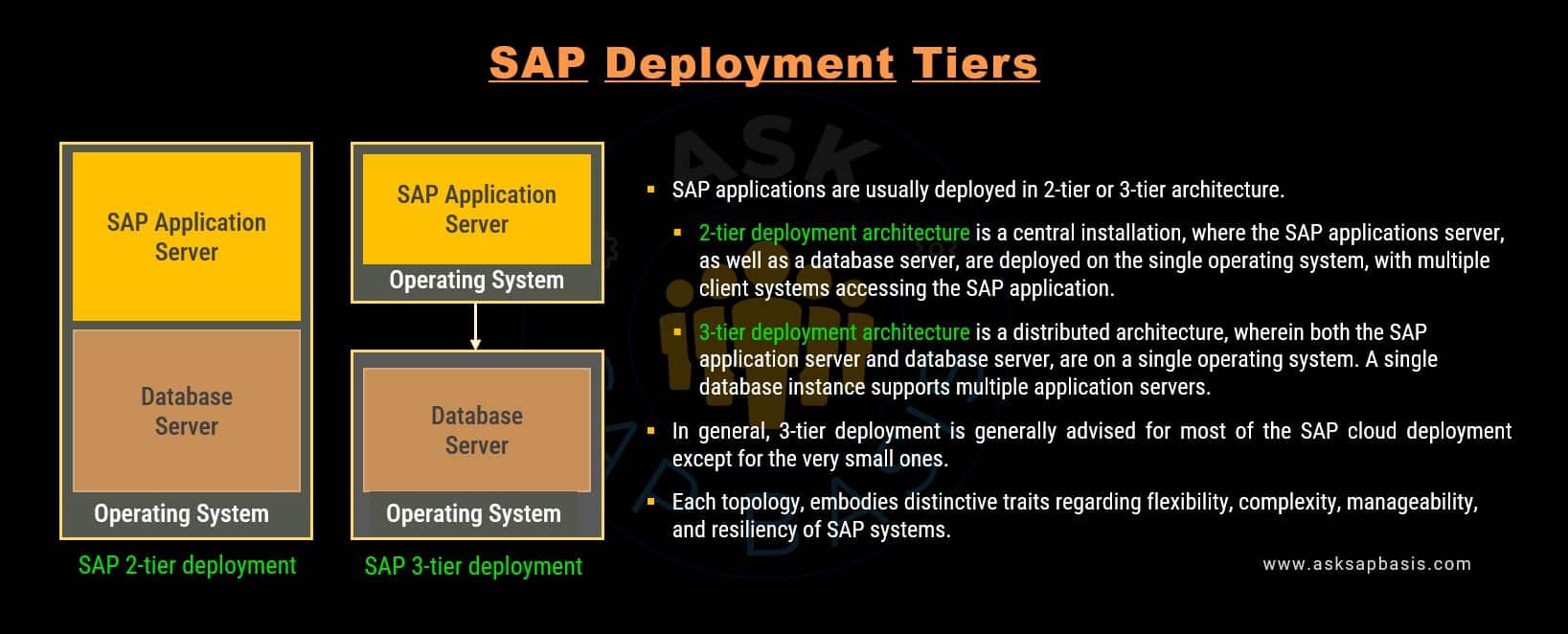
SAP Deployment Tiers
Before diving into the intricacies of cloud sizing for SAP infrastructure, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamentals, starting with understanding the different SAP deployment tiers.
SAP sizing on the cloud revolves around two primary categories of virtual machines: application / ASCS servers and DB servers.
Guidelines for SAPS Allocation
Once we are equipped with SAPS number, below guidelines are commonly leveraged to split the SAPS between the DB and application servers.
- For OLTP systems: Allocate 60% SAPS to the DB server, and 40% for the App server(s)
- For OLAP systems: Allocate 33% of SAPS to the DB server, and 66% for the App server(s)
These guidelines offer as a starting point but may require adjustments based on specific SAP systems and workload types. However, its crucial to consider SAPS requirement for the DB server as a bare minimum. Typically, OLTP systems typically require approximately 0.6 times the DB SAPS for IOPS, while OLAP systems require about 0.9 times the DB SAPS.
Sizing Application Servers/ASCS Servers
Application servers are responsible for executing business logic and processing user requests, while ASCS servers provide central services like lock management and enqueue handling.
Key Considerations:
- User Load: The number of users accessing the system at any given time can significantly impact server performance. You need to determine the expected number of concurrent users and ensure that each application server can handle the expected load.
- Transaction Volume: You need to determine the peak transaction volume and ensure that the servers can handle the load without experiencing performance issues.
- System Complexity: The complexity of your SAP system, including the number of modules and customizations, can impact server performance. A more complex system will require more server resources to function optimally.
- Hardware Configuration: Once the server type is selected, it is essential to choose the right hardware. The hardware should be capable of handling the SAP workload. The hardware should have sufficient memory, CPU, and storage capacity. The hardware should also have redundant components to ensure high availability.
- Plan For Future Growth: When sizing SAP application servers and ASCS servers, it is essential to plan for future growth. The SAP system should be scalable, and the server should be capable of handling future workload demands. Therefore, it is recommended to size the server for future growth and add additional resources when required.
Key Parameters Affecting SAP ABAP Application Servers:
- CPU Performance per Thread: Individual performance of a single processor.
- Physical RAM for SAP Buffers: Memory available for SAP buffers, including PXA, table, nametab and extended memory.
Most performance constraints in SAP systems are determined by these two parameters, with network throughput to the database VM playing a lesser role.
Most of the infrastructure related performance constraints on most of SAP systems are largely determined by above two parameters. While network throughput to the database VM is also a contributing factor but it is not as significant as the above two parameters.
Sizing Database (DBMS) Servers
Key Factors:
- Disk I/O Performance: Latency and volume throughput of disk I/O.
- Network Performance: Volume throughput and latency of network performance.
- RAM for Data Buffers: Available RAM for data buffers or caches.
- CPU Performance: Total combined CPU (aggregate) performance of all processors.
Optimizing these factors significantly enhances DBMS performance. It’s important to note that DB SAPS and overall SAPS are not the same, with a general conversion rule estimating DB SAPS at roughly 0.3 times the total SAPS.
For HANA systems, there’s a distinct sizing approach that focuses on memory.
Sizing for HANA Systems
SAP recommends the “50/50” rule for HANA VMs, where VMs should have twice the memory of the net HANA DB size. However, practical considerations often lead to deviations from this rule, especially for cost-effectiveness.
In addition, Azure VMs come in t-shirt sizes, which can sometimes force you to size up significantly. For example, if you have an 8TB HANA ERP system, you may need to select a 12TB VM unless you can reduce the size of the DB by archiving or relegating some of the data to cool/cold storage.
Sizing for HA/DR Solutions
If you’re implementing high availability (HA) or disaster recovery (DR) solutions for your SAP infrastructure on cloud, you may need to add specific VMs such as jump boxes. These VMs are typically smaller than the application and DB servers, and the sizing will depend on the specific requirements of your HA/DR solution.
These best practices form the foundation for a well-informed SAP sizing strategy in the cloud, ensuring optimal performance, scalability, and resource allocation for your SAP infrastructure.
Pre-requisites For Running SAP In Cloud
If you’re planning to run your licensed SAP software on an Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) platform, there are essential prerequisites and requirements to consider. These ensure a successful deployment of SAP software on an IaaS infrastructure.
1) Resource Requirements
The first and foremost prerequisite is understanding the resource requirements of your SAP application in the cloud. This information is derived from SAP system sizing, enabling you to select the appropriate instance types provided by the IaaS provider, which are approved for SAP software.
2) SAP Platform Availability Matrix (PAM)
The SAP Platform Availability Matrix (PAM) is a vital online tool. It offers information about the availability of SAP software products, software maintenance status, supported OS, databases, browsers, patch level info, and more. Ensure your IaaS provider supports the SAP software releases listed in the PAM.
3) Private Cloud Infrastructure
For private infrastructures, the hardware releases in combination with Linux are documented on the SAP Community website, while Windows systems are documented on the SAP website. Virtualization solutions can only be used on certified hardware, which is documented in below SAP Note:
4) Public IaaS Environment
In a public IaaS environment, support is guaranteed only if one provider manages the entire infrastructure, including compute, network, and data store. This is essential due to the close coupling between runtime components. Verify that the SAP product is explicitly approved for use with the relevant infrastructure components in the provider’s environment.
5) SAP Certified Providers
SAP offers certification programs for operating service providers, including business process outsourcing, application management, and classic hosting. These providers have demonstrated their ability to operate SAP applications in released IaaS environments while meeting the support requirements. A list of SAP-certified providers for the operation of SAP software can be found in the below links:
- SAP on Linux – Supported Platforms
- Certified Hardware for SAP Solutions on Microsoft Windows
- Certified and Supported SAP HANA Hardware
6) Network Connectivity
To ensure a seamless experience, test and understand the quality of the network connection, including bandwidth, latency, and packet loss, between infrastructure components. This encompasses connectivity from on-premise locations to the data center regions of your IaaS provider and the connectivity between these regions.
7) Operating System Compatibility
Before selecting an IaaS provider, it’s crucial to determine which operating systems are supported in combination with SAP software. This is because certain IaaS providers may not support the specific operating systems required by SAP.
8) SAP MaxAttention Support Service
For specialized support, consider SAP’s MaxAttention support service. Ensure that your chosen IaaS provider supports the specific operating systems required by SAP. For MaxAttention services refer to SAP Notes 9501193 and 9503815.
9) Technical Expertise
Configuring an SAP system correctly on the IaaS platform demands technical expertise. Individuals or businesses must be proficient in dealing with fully or partially virtualized infrastructures. Alternatively, you can choose to have your SAP system managed by a hosting-certified or cloud-certified service provider.
To summarize, running SAP software on an IaaS platform can provide many benefits, but it’s important to ensure that the above prerequisites are met to ensure a smooth transition and continued support from SAP.
SAP Certified Public Cloud Service Provider
The table below presents a comprehensive list of IaaS platforms that are certified and released by SAP for public use. To ensure compatibility and optimal performance, refer to the relevant SAP Notes that outline the platform-specific support requirements and specify the SAP products that can be used in combination with the supported infrastructure and machine types.
SAP recommends to disregard any other sources other than the ones listed in below table that may contain conflicting information. You need SAP OSS User ID to access the relevant SAP Notes in below table.
Useful Resources
- SAP Note 1612283: Hardware Configuration Standards and Guidance
- SAP Note 1100926: FAQ: Network performance
- SAP Note 500235: Network Diagnosis with NIPING