SAP and Cloud: A 2025 Optimization Guide
Overview
In the ever-evolving world of technology, the term “cloud” and internet are synonymous. By connecting to the internet, Our physical devices, such as computers, laptops, phones, and tablets, all come with inherent limitations. For instance, the storage capacity of hard drive is finite. Nevertheless, connecting to internet, allows us to leverage our devices for accessing virtually unlimited resources from a remote datacenter.
Gone are the days of building extravagant data centers and reserving excess computing resources. Step into the age of cloud computing, where hardware and software services seamlessly reside on the internet, fundamentally reshaping how we harness the power of technology. With the magic of cloud computing, you are no longer burdened by overprovisioning; you pay only for precisely what you need, exactly when you need. This journey leads us into the world of scalability and high availability, all without the heavy burden of on-premise infrastructure. Its time to ascend to new heights and bid farewell to the era of costly data centers.
The Versatility of Cloud Computing
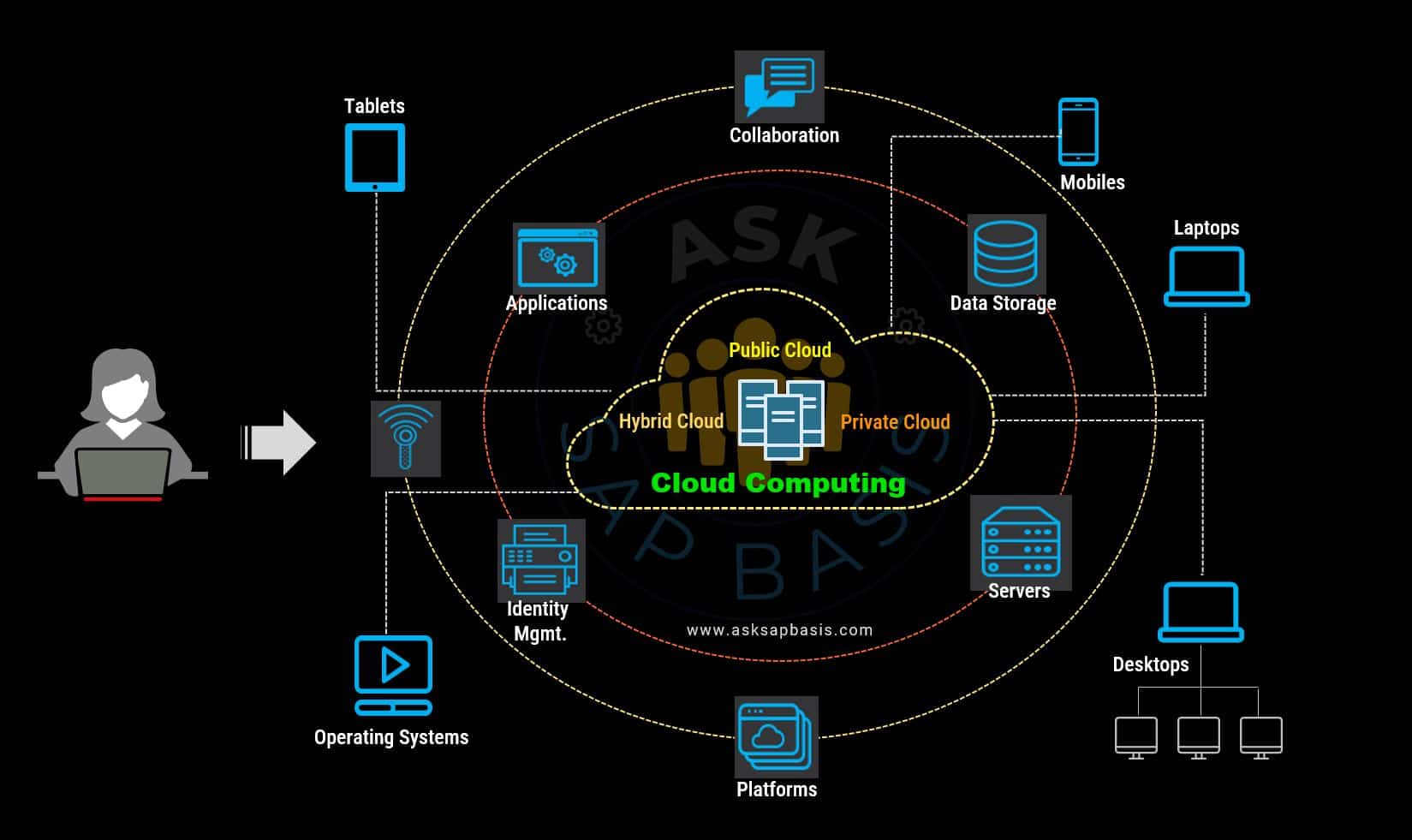
Cloud computing offers diverse deployments and service models, tailoring solutions to your unique requirements. Embrace a landscape that spans multiple regions, guaranteeing optimal availability and minimizing latency. Imagine a vast array of computing services right at your fingertips, including servers, storage, database, networking, software, analytics and intelligence.
Seamless Transition
Small and medium-sized businesses, can smoothly and straightforwardly transition to cloud. Enterprises, despite their complex infrastructures, can harness the cloud’s potential by adopting a phased approach, unlocking its transformative capabilities at their own pace.
Abundance of Choices
In a market brimming with cloud providers or vendors, the options are virtually boundless. Cloud providers offer an extensive array of cloud solutions, catering to wide range of every needs. Discover a world, where cost efficiency and agility reign supreme, revolutionizing the way businesses operate in the digital age.
Understanding Cloud Computing
Definition
At its core, Cloud computing is the delivery of applications, platforms, data storage, operating systems and other on-demand computing resources over the internet.
Instead of owning and maintaining the physical infrastructure, cloud computing allows users to access and utilize these resources on-demand from remote data-centers. This transformative shift brings several advantages, including cost efficiency, scalability, accessibility, reliability and security.
Concept
In the world of cloud computing, convenience and efficiency closely tied, ushering in a revolutionary way to access and utilize digital services.
Subscription Model
- The concept of cloud computing model, is similar to how subscription-based model works. In subscription-based model, you opt to pay a recurring fee to access and utilize certain services offered by the provider.
- Cloud computing model works identically to how you utilize your services in home such as water and electricity. You pay the utility provider on a subscription basis, and the provider is responsible for maintaining the infrastructure, such as water pipes and power lines used to deliver the services to you.
Traditional On-Premise Model
- The traditional on-premise model follows the CapEx and OpEx model approach.
- CapEx is the initial capital expenditure for purchasing and setting up the infrastructure such as servers, network, datacenters etc.
- OpEx is the operational expenditure incurred to maintain the operate the infrastructure including personnel salaries.
- Under the traditional on-premise model, the responsibility lies with the customer to procure and maintain the servers, the software’s, and all the necessary infrastructure resources, including personnel salaries.
Cloud’s Pay-As-You-Go Approach
- In contrast, cloud computing model offers customers the flexibility to subscribe to only the computing resources tailored to their needs and access them instantly and only pay for duration of their usage. This model is also called as “Pay-As-You-Go“. Customers can start with minimal resources and gradually scale-up as their needs grow. This offers low-risk approach to accessing and utilizing cloud resources.
- The benefits of using the cloud computing model include flexibility, scalability, cost efficiency, and elasticity, as users can easily adjust their resource allocation based on their needs.
- One of the key advantage of cloud computing is the ability to access digital services and data from anywhere with an internet connection. This mobility enables users to work remotely, collaborate with team members across different locations, and access their application and files on various devices.
By harnessing the power of cloud, organizations can streamline their operations, reduce costs and achieve greater agility and innovation. Cloud computing enables businesses to focus on their core activities while relying on the expertise of cloud service providers to manage and maintain the underlying infrastructure.
Benefits
Embrace the power of flexibility with cloud adoption, empowering your business to adapt and excel in ever-changing landscape. Its a journey of breaking free from limitations and soar to new heights. Cloud adoption opens the doors of flexibility, efficiency and strategic value. Experience the following benefits:
Cloud adoption unleashes the power of flexibility, enabling businesses to adapt and excel in an ever-changing landscape. It’s a journey marked by newfound efficiency and strategic value. Here’s a closer look at the key benefits:
a) Flexibility
- Scalability: It refers to system’s ability to handle increasing workload or accommodate a growing user base. Achieving scalability involves addition or removal of resources, such as servers or storage, to maintain performance and meet demands. It can be accomplished through horizontal scaling (adding more instances) or vertical scaling (increasing the resources of existing instances).
- Elasticity: It surpasses scalability by emphasizing the dynamic and automatic resource allocation. It pertains to the system’s or application’s ability to seamlessly adjust to fluctuating workloads or demand in real-time. Elasticity ensures the automatic scaling up and scaling down of resources based on current needs, guaranteeing optimal performance and cost efficiency. With elasticity, resources adapt effortlessly as demand patterns evolve, eliminating the needs for manual intervention.
- Global Independence: Access cloud services from any corner of the globe, breaking down the barriers imposed by physical location. Cloud services are accessible through standard protocols and API’s. Empower your team to work remotely, foster seamless connectivity across borders and drive global innovation and collaboration.
- Application Mobility: Effortlessly move applications and data between cloud environments, enabling workload portability and unmatched flexibility. Embrace the freedom to run applications on multiple cloud platforms or switch seamlessly between providers. Experience a new level of agility and adaptability in managing your applications in the cloud.
- Security: Safeguard your valuable data with robust security measures provided by cloud providers. Utilize your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to create an isolated and secure environment for your resources. Encrypt sensitive data both, at rest and in transit. Safeguard access with API keys for secure authentication and authorization.
b) Efficiency
Cloud computing opens the doors to unparalleled efficiency. Its a place where businesses can optimize costs, streamline operations and dynamically scale resources, accelerate time-to-market, ensure data resilience and propel business forward.
- Innovation: Enterprise users can get applications to market without worrying about underlying infrastructure costs or its maintenance. By leveraging the cloud’s agility and scalability to swiftly respond to market demands, gaining a competitive edge and capturing new opportunities.
- IT Excellence: Streamlines your IT operations with automated processes, centralized management, and self-service capabilities. Empower your team to focus on high-value tasks instead of manual and repetitive activities, increasing productivity and operational efficiency.
- Data Resiliency: Safeguard your valuable data and minimize the risk of data loss. Utilize networked backup solutions to ensure data integrity and resilience in the face of hardware failure. Benefit from redundant backups and distributed storage systems, ensuring the security of your data and seamless retrieval, thereby maintaining uninterrupted business continuity.
- Cost Optimization: Maximize your financial resources with pay-as-you-go model, eliminating the need for upfront infrastructure investment. This reduces capital expenditure, enabling strategic budget allocation and investment in other business priorities.
- Resource Optimization: Embrace the power of on-demand cloud services to ensure optimal resource utilization and minimize idle resources. Dynamically scale your resources according to your needs, eliminating wastage, maximizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Strategic Value
Businesses can redefine their strategies and seize new opportunities through cloud adoption. They can embrace agility, focus on core competencies, foster strategic partnerships, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
- Business Agility: Businesses can leverage the cloud’s agility and rapid innovations to seamlessly adapt to market changes. Stay one step ahead of the competition, by swiftly responding to emerging possibilities. Position your business for success in today’s dynamic and fast-paced landscape, by embracing change as an opportunity.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Delegate infrastructure management to reliable cloud providers, enabling organizations to prioritize core business activities. Allocate resources and talent towards innovation, enhancing customer experiences and delivering value-added services. Streamline operations to maximize organizational efficiency and effectively achieve strategic goals.
- Strategic Partnerships: Forge strategic partnerships with cloud vendors to leverage their expertise and access their extensive ecosystem. Accelerate your digital transformation, by collaborating closely with cloud providers. Tap into their industry knowledge, best practices, and cutting-edge technologies to gain a competitive edge by harnessing the collective power of your organization and cloud vendor expertise.
- Competitive Advantage: Leverage cloud services to gain a competitive advantage by utilizing advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and machine learning. Extract valuable insights, make data-driven decisions, and set your business apart from competitors. Enhance operational efficiency, and deliver exceptional customer experiences, to stay ahead of the curve.
Challenges
Cloud computing has brought about a significant transformation in the way businesses operate, offering a wide range of advantages, including scalability, cost-efficiency, and flexibility. However, adopting cloud technology isn’t without challenges. By implementing the right cloud adoption strategies, technologies, services and service providers, the challenges and risks can be mitigated.
Data Security and Privacy
- One of the foremost concerns when embracing cloud services is security. Organizations are understandably anxious about the safety and privacy of their data when it resides in a third-party cloud environment.
- Apprehensions arise due to potential data breaches, unauthorized access, and loss of control over sensitive information. To address these concerns, organizations should actively evaluate the security measures provided by cloud providers.
- This evaluation should encompass proper data encryption protocols and access controls. Additionally, establishing a comprehensive governance and compliance framework is crucial. This measures collectively work to not only address their concerns but also significantly mitigate the associated risks.
Data Governance and Sovereignty
- Data governance involves management of data within an organization by defining policies, processes, and controls to ensure availability, integrity and security of data. Its objective is to manage and protect data in alignment with organizational goals and compliance requirements.
- Sovereignty relates to the control and ownership of data, driven by legal and jurisdiction mandates. Organizations must comply with data residency, compliance, and legal requirements, to maintain sovereignty over their data.
- Its crucial that organizations must carefully review contractual agreements and assess providers’ adherence to data residency policies. They need to establish clear guidelines to maintain sovereignty over their data.
Legal, Regulatory, and Compliances
- Organization must navigate industry-specific regulations, compliances and data protection laws, when storing and processing data in the cloud.
- Understanding legal, regulatory, and jurisdictional compliances is vital to avoid potential legal issues and protect the reputational damage. Close collaboration with cloud service providers is essential in this regard.
Organizational Readiness and Skill Gap
- Adopting cloud computing often necessitates a cultural shift in organizations, along with change in processes and skills.
- To effectively work with cloud technologies and grasp the new cloud computing paradigm, some employees may require training or upskilling.
- Organizations must assess their current skill sets, identify any gaps, and invest in training and education programs.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
- Ensuring availability and resiliency of critical systems and data during disruptions or disasters is the key concerns during cloud adoption.
- Organization can address these concerns by proactively implementing robust plans. This includes designing backup and recovery strategies, establishing redundant systems, regular testing, and leveraging cloud based solutions.
- These measure minimize downtime, maintain operational resilience, enable swift recovery from disruptions in the cloud computing environment.
Partnering With Right Cloud Service Provider
- Selecting the right cloud service provider is a critical challenge when it comes to cloud adoption.
- Organizations require transparency from their cloud service partner regarding reliability, data handling practices, security measures, compliance certifications and incident response protocols. So evaluating the service provider’s transparency, commitment and accountability is crucial.
- Conducting in-depth assessments and due diligence are crucial. These enables organizations to make informed decisions, choosing cloud service providers that aligns with their unique requirements and objectives, ultimately maximizing the benefits of cloud adoption.
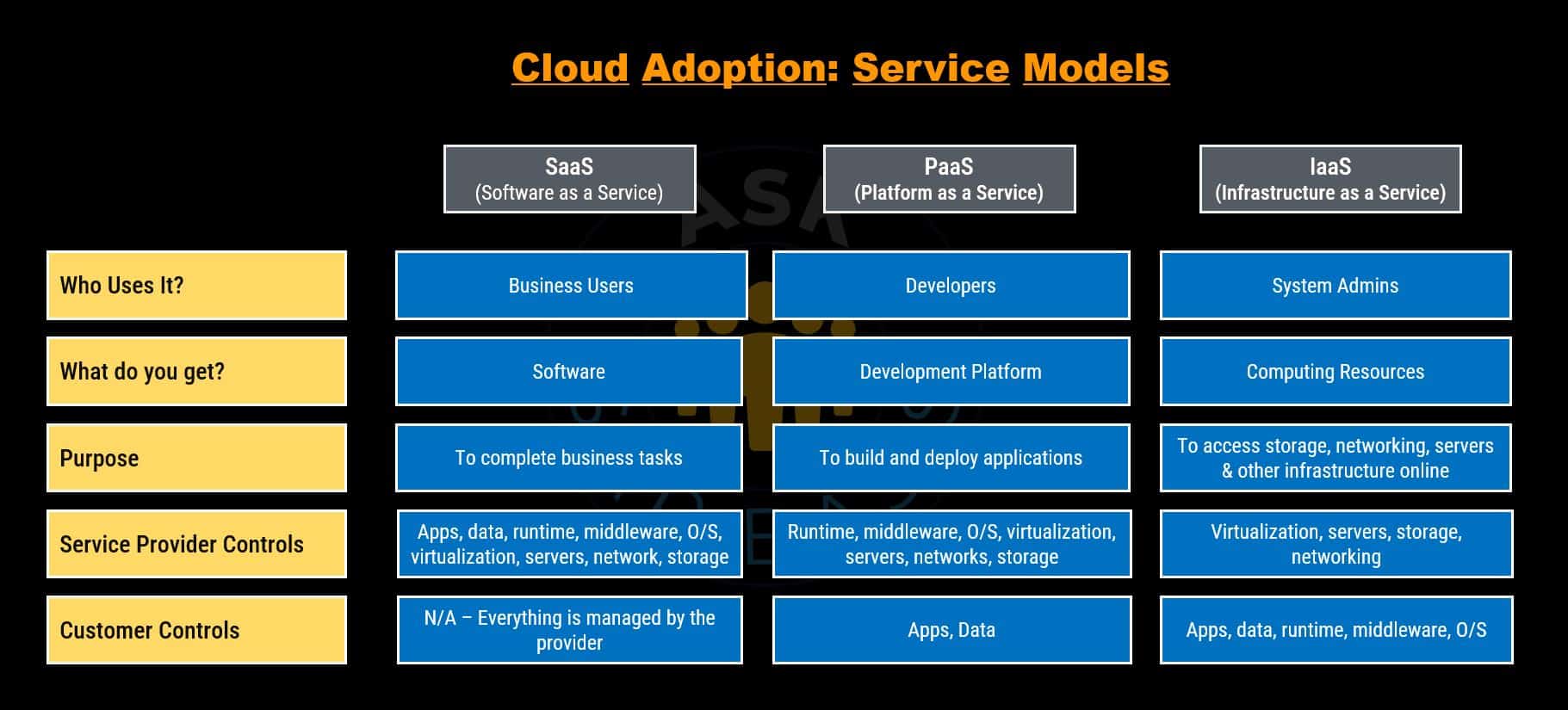
Cloud Service Models
The term “service model” in cloud computing refers to the way cloud resources and capabilities are delivered to users.
The service model concept emphasizes the idea that cloud computing is a service-oriented approach and is delivered as “as-a-Service“, where a consumer is billed on a subscription basis for what they use. This subscription based model is remarkably flexible and agile, allowing you to effortlessly adjust your scale of operations according to your requirements.
In context to cloud computing, three core service models have emerged, each catering to distinct needs:
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Applications are hosted by a third-party cloud provider, who makes them accessible to customers via the internet.
- Organizations can eliminate the expenses associated with hardware procurement, provisioning and maintenance. Additionally, they can avoid the costs of software licensing, installation and support.
- Consumers can easily access SaaS applications directly from browser, eliminating the need to purchase, install, maintain or update any software or hardware.
- The SaaS provider handles all the aspects, ensuring that customers always have access to the latest version of the application.
- Use cases for SaaS are:
- Reduce on-premises IT infrastructure and capital expenditure.
- Avoid on-going upgrades, maintenance and patching.
- Run applications with minimal input.
- Manage websites, marketing, sales, and operations.
- Gain resilience and business continuity of the cloud provider.
- A third-party provider actively hosts application development platforms and tools on their own infrastructure, making them accessible to customers over the internet.
- PaaS empowers developers with a comprehensive cloud platform and suite of tools, enabling them to effortlessly create and deploy cloud-based applications.
- PaaS simplify the job of developers in delivering elastically scalable and highly available cloud application by providing services and API’s.
- Users can access PaaS through web browser, eliminating the need to invest in and maintain the underlying software and hardware infrastructure.
- With PaaS, developers have the flexibility to select desired features on a subscription basis.
- Use cases for PaaS are:
- API development and management
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Business analytics/intelligence
- Business Process Management (BPM)
- Master Data Management
- IaaS is on-demand access to cloud-infrastructure, including physical and virtual servers, storage and networking – the underlying IT infrastructure for running applications and workloads in the cloud over the internet and on a “pay-as-you-go” model.
- IaaS provides you with highest level of scalability, flexibility and management control over IT resources.
- IaaS providers host the infrastructure and take care of tasks such as system maintenance and backups, relieving customers from the need to purchase hardware or employ in-house experts for its management.
- Use cases for IaaS are:
- Backup and recovery, storage, and managing storage need efficiently.
- Enables faster and cost-effective testing and development environments.
- Boosts computing power for big data companies.
- Scalability and high-performance for complex web projects, with dynamic traffic.
- Suitable for high-performance and productivity boosting programs.
- Accelerates cloud application deployment and simplifies infrastructure and storage management.
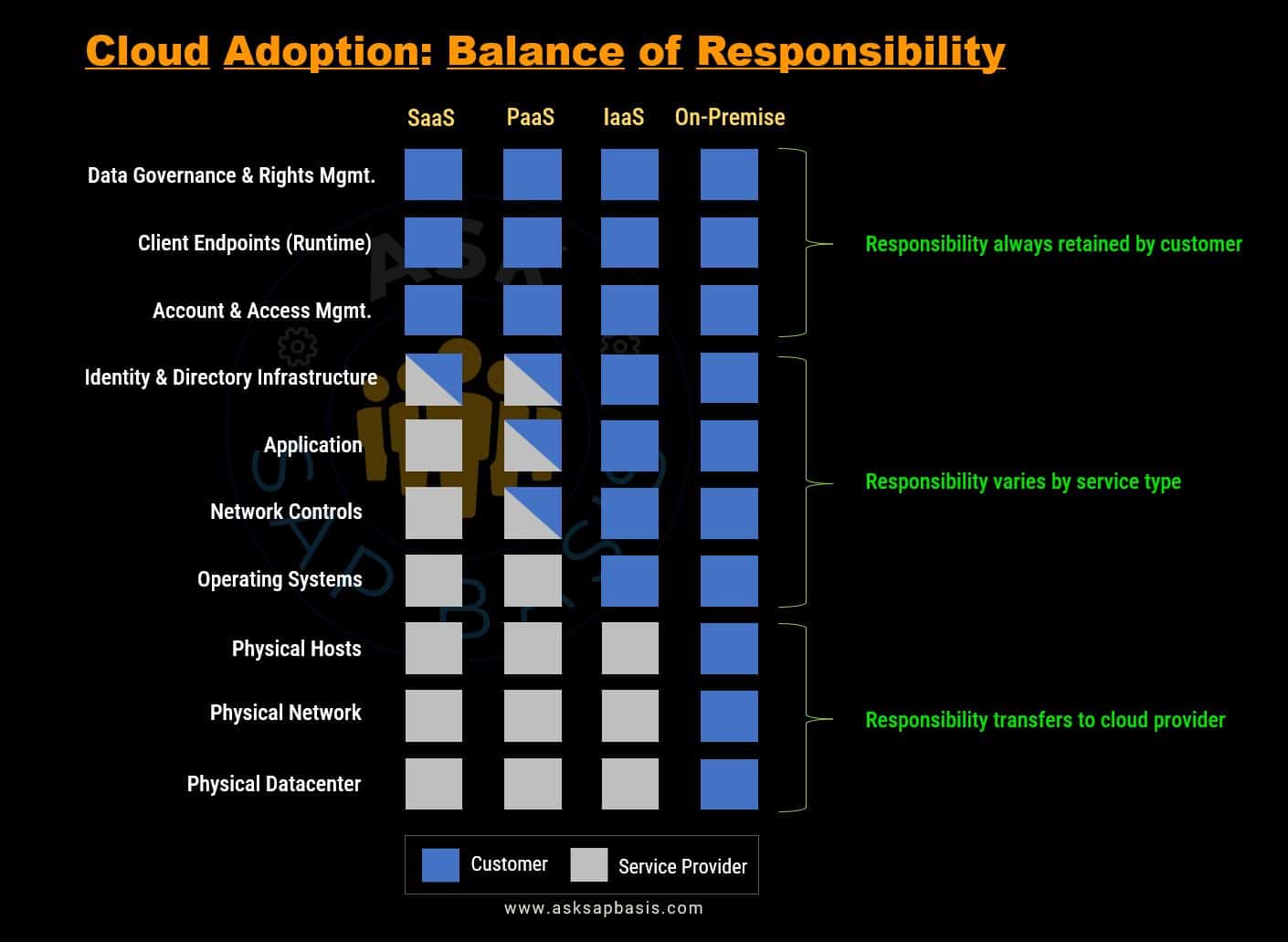
The above shared responsibility model actively illustrates how responsibilities are allocated among stakeholders, depending on the type of cloud service.
The ‘Customer‘ will always be responsible for:
- Safeguarding the information and data stored in the cloud.
- Controlling access to specific devices (such as cell phones, mobiles, laptop etc), that are allowed to connect to your cloud infrastructure.
- Managing and controlling the accounts and identities of services, individuals, and devices within your organization in cloud.
The ‘Cloud Service Provider‘ will always be responsible for:
- The physical data center (that contains infrastructure and equipment’s required to run the cloud service).
- The physical network (that connects various components and enables data transfer within the data center).
- The physical hosts (the actual servers and machines responsible for executing cloud services).
Your ‘Service Model‘ will decide the shared responsibility model and the areas you are responsible, such as:
- Operating Systems
- Network Controls
- Identity and Infrastructure
- Applications
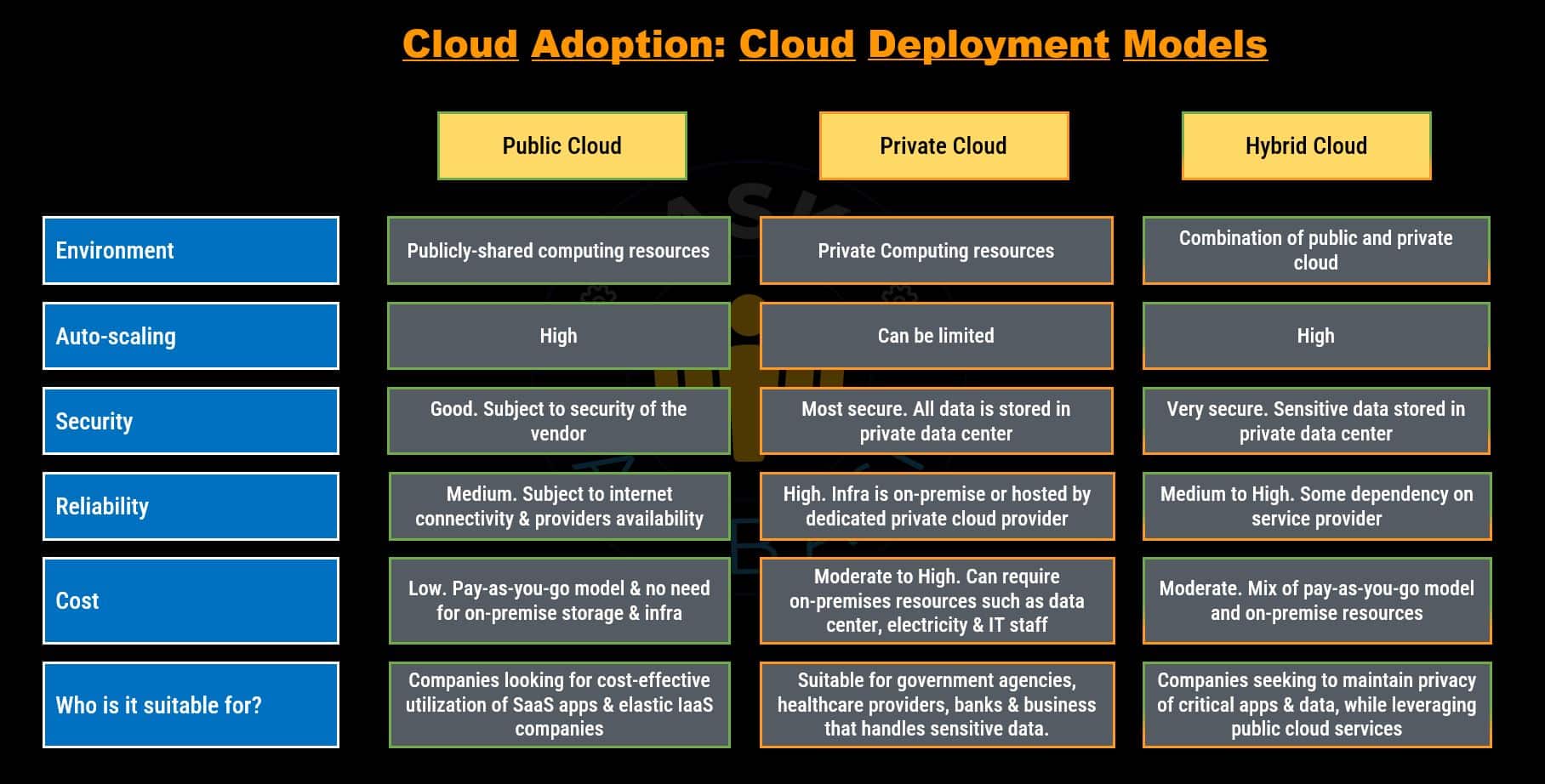
Cloud Deployment Models
Deployment models specify the location of the infrastructure, the entities responsible for ownership and management, and how cloud resources and services are made available to users.
In context to cloud adoption, there are distinguished into three categories:
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
- Public cloud is a cloud computing model, where cloud resources or services are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider. These providers make their infrastructure available to the general public over the internet.
- Public cloud typically operates on a multi-tenant server, where multiple customers and tenants share the same server resources.
- Public cloud is like an apartment building, where multiple tenants reside within a shared physical infrastructure and share certain resources. Each tenant in public cloud possesses their own unique key to a secure unit within the building. Rent of the tenant includes the cost of building and apartment unit maintenance, ensuring that their needs are promptly addressed when needed.
- Within the public cloud, customer data and applications remain isolated from one another, ensuring privacy. However, as customers share resources and the cloud provider handles maintenance, the public cloud emerges as a cost-effective and efficient solution.
- Public cloud offers several benefits, including scalability, elasticity, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to pay for resources on a “pay-as-you-go” model. Customers can access the services remotely, without having to worry about infrastructure maintenance or management.
- Some of the popular and trusted public cloud providers are: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud, Alibaba Cloud.
- Private cloud is a cloud computing model, where an enterprise owns an proprietary architecture and run cloud servers within its own data center and is responsible for its maintenance.
- Unlike public cloud where resources are shared among in multiple-users, a private cloud runs on a single-tenant server, and offers dedicated resources and infrastructure for each tenant. One of the key benefit is, it offers greater control over their resources and data, ensuring enhanced security and customization.
- With private cloud you can have infrastructure and security tailored to your needs. It is an appealing option for industries with strict compliance and regulations or those dealing with highly confidential and sensitive information.
- In private cloud, the infrastructure that is dedicated exclusively to a single organization, which consists of multiple consumers. The infrastructure can be located on-premises within the organizations own data center’s or it is hosted externally and owned, managed and operated by a third-party provider, exclusively for that organization. This is also referred as “Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)”.
- Hybrid cloud is a computing model, that combines elements of both public and private clouds. It allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both environments.
- Hybrid cloud offers a flexible and integrated solution for managing workloads and data across multiple cloud environments. This gives customers a diverse landscape consisting of a combination of different integrated solutions.
- With hybrid cloud, organizations have the ability to run certain applications or store specific data in private cloud, while utilizing the public cloud for other workloads. This flexibility enables them to optimize resource allocation, cost-efficiency, and performance based on their specific needs (such as data sensitivity, privacy, legal or compliance regulations) and requirements.
- Hybrid cloud architecture, also provides a level of redundancy and resilience. If one cloud environment experiences an outage or disruption, organizations can rely on the other environment to maintain business continuity and minimize downtime.
- The success of navigating through the intricacies, involved in managing a hybrid cloud, hinges on the effective implementation of orchestration and management tools, which allow organizations to monitor, control, and optimize the distribution of workloads and data across the different cloud environment.
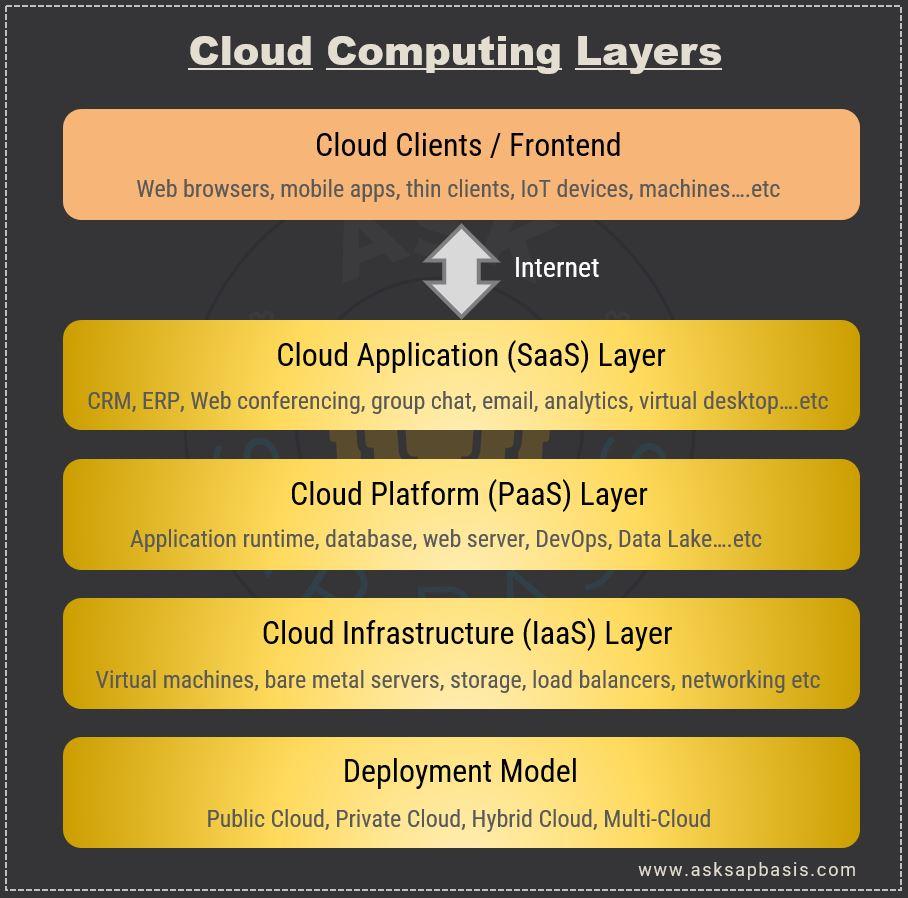
Cloud Computing Layers
Cloud computing architecture is organized into hierarchical layers, each fulfilling specific functions within the cloud ecosystem. These layers represent different levels of abstraction and functionality, organizing the components of the cloud infrastructure based on their roles and responsibilities.
- The deployment model, defines how cloud services are implemented and delivered to users. The primary deployment models include – public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud and multi-cloud. These models offer varying levels of control, security, and scalability, allowing organizations to choose the most suitable approach for their needs.
- The infrastructure layer (IaaS), often referred as the foundation layer, encompasses the physical resources that constitute the backbone of the cloud infrastructure. These layer manages servers, storage devices, and networking equipment’s focusing on the hardware and virtualization technologies that enable efficient allocation and utilization of resources.
- The platform layer (PaaS), also known as the middle layer, offers a development platform and environment for developers to create, deploy, and manage applications in the cloud. It provides an array of tools, frameworks, and services that streamline the development process, enabling developers to concentrate on building innovative software solutions.
- The application layer (SaaS), is where end-users interact with cloud environment. It contains ready-to-use software solutions accessible via the internet. Users can leverage these applications without the hassles of installation or maintenance, benefitting from the convenience, scalability, and flexibility that cloud computing offers.
- The cloud client or front-end layer serves as the interface through which users interact with cloud services and applications. It encompasses the devices, software, and user interfaces that enable seamless access to and utilization of cloud resources.
By comprehending these layers of cloud computing architecture, organizations gain a deeper understanding of how each component contributes to the overall cloud ecosystem. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions when implementing cloud solutions and optimizing their cloud infrastructure for enhanced efficiency and functionality.
FAQs on Cloud Computing
How do I choose a cloud service provider?
When selecting a cloud service provider, consider key factors such as reliability, security, scalability, pricing, compliance requirements and available services. It also essential to evaluate provider’s reputation or track record, service level agreements, data protection measures and customer support.
What is virtualization in cloud computing?
Virtualization is a fundamental technology in cloud computing that enables to create multiple virtual machines (VM’s) or virtualized resources on a single physical server. It plays a crucial role in optimizing resource utilization and isolating workloads, leading to improved scalability and flexibility in cloud environments.
By abstracting the underlying hardware, virtualization allows efficient allocation of computing power, memory, and storage to meet the dynamic demands of cloud-based applications. This capability enhances the overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness of cloud computing solutions.
What is the difference between public cloud and private cloud?
Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party providers, making resources accessible to multiple organizations or users. Private clouds, on the other hand, are dedicated to a single organization and can be managed internally or by a service provider. Private clouds offer greater control and customization but require additional maintenance and infrastructure investment.
What are potential challenges of cloud computing?
Cloud computing presents both benefits and challenges. Some common challenges include data security and privacy concerns, reliance on internet connectivity, the possibility of vendor lock-in, compliance and regulatory issues, and effective management of cloud costs. It is crucial to understand these challenges and address them appropriately to ensure successful adoption of cloud computing.
What is serverless architecture in cloud?
Serverless architecture, also referred to as Function-as-a-service (FaaS), empowers developers to build and execute applications without the need to manage servers or infrastructure. In this model, developers write functions that are triggered by events or specific triggers. The cloud provider handles the underlying infrastructure, automatically scaling resources to meet the application needs. This approach ensures optimal resource utilization and allows developers to focus solely on writing code and delivering functionality.