SAP Client Copy – Complete Step-by-Step Guide 2025
Introduction
SAP Client Copy plays a pivotal role in enabling businesses to duplicate their SAP system’s data and configuration settings, thereby creating new clients. Enterprises, regardless of their size, rely on SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products), a widely embraced enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, to efficiently manage various facets of their daily operations, including finances, supply chain, and human resources.
As a business grows and evolves, it often needs to establish new SAP clients to effectively manage various aspects of the company. SAP client copy serves as an indispensable process for achieving this goal, empowering businesses to replicate their SAP system’s data and configuration settings when creating these new clients.
In this beginner’s guide, we’ll furnish you with all the essential information necessary to navigate the world of SAP client copy. We will walk you through the process of duplicating your SAP system’s data and settings to create new clients, ensuring that these clients function seamlessly. Whether you’re new to SAP or an experienced user, you can rest assured that we have you covered with all the information required to confidently manage your SAP clients.
Understanding SAP Client Copy
What is SAP Client?
In SAP landscape, a client functions as a self-contained or independent entity within a system, serving to segregate data and settings among various different business units or departments.
The client copy process involves copying data and settings from one client to another, and it holds a crucial role in SAP system administration. It enables businesses to generate new clients with settings and data mirroring those of existing clients, eliminating the need to begin from scratch. This streamlined process saves time, minimizes errors and ensures inconsistency.
Types of SAP Clients
Characteristics of SAP Data
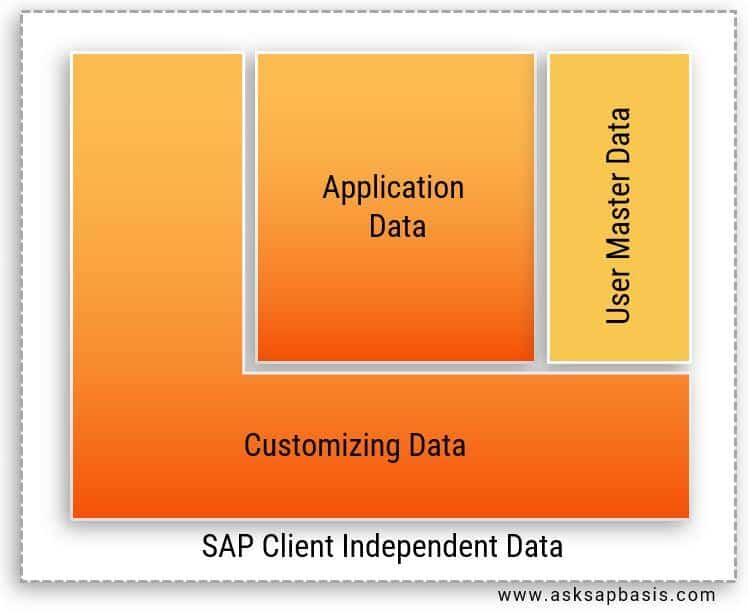
Data in SAP is categorized into two types:
1) Client Independent Data
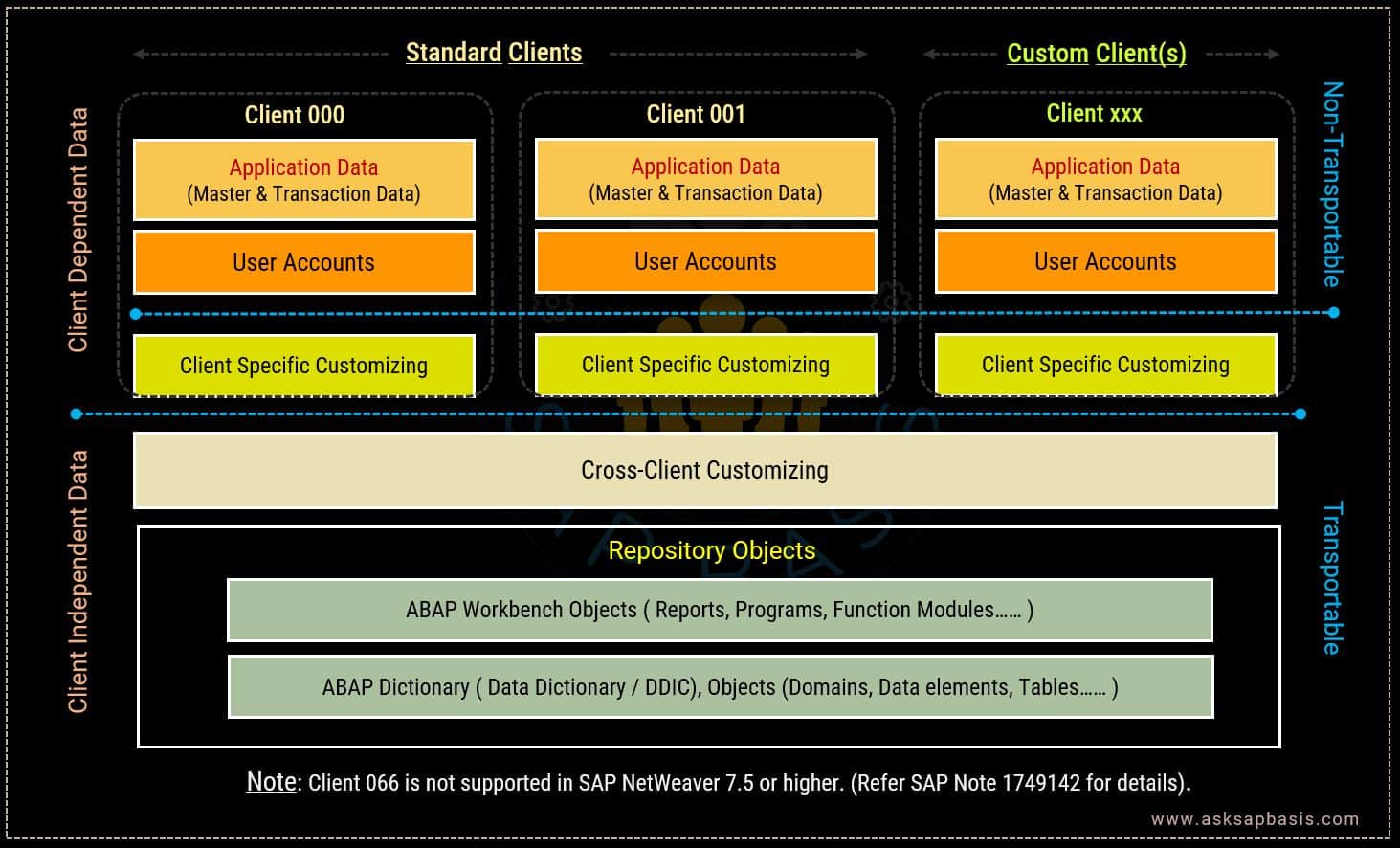
- Client independent data refers to cross-client objects, which are accessible across all SAP clients with the same system.
- Examples include: global or cross-client configuration settings, system-wide master data, user roles and authorizations, repository objects, data dictionary (system tables and structures) & workbench reports (reports, programs etc).
2) Client Dependent Data
- Client dependent data refers to objects specific to a particular SAP client within the SAP system. The data is stored and managed within the client and is not accessible from other clients within the same SAP system.
- Examples include: client-specific configuration settings, user accounts, user-specific data such as saved reports or preferences. parameters that control business processes.
- Client dependent data is categorized into
- Customizing data: it refers to objects like organization units, assignments, document types, etc.
- User master data: it refers to objects like users groups, authorizations parameters etc.
- Application data: it refers to objects like business transaction data, material master data etc. Its important to note that application data can only be copied along with the corresponding customizing data.
SAP Clients
Standard SAP Clients
In SAP, the system comes pre-loaded with three standard clients, each serving specific purposes: clients 000, 001, and 066.
- Client 000 functions as the SAP installation client, and stores standard system settings and data. SAP administrators primarily use this client for system maintenance and updates. It’s crucial to refrain using this client for any other purpose besides its designated role. SAP recommends to use this client 000 as “source” for client copy.
- Client 001 serves as the SAP reference client, containing sample data for each SAP module. Developers and consultants often use this client as a reference for designing and configuring new SAP systems. However, it’s is not advisable to use this client 001 for actual business transactions or testing.
- Client 066 is the SAP EarlyWatch client, and used to monitor the SAP system performance and usage. SAP support and maintenance teams rely on this client to identify and resolve system issues. [Note: Client 066 will no longer be available if you install SAP system based on SAP NetWeaver 7.5 or higher versions. For more information, refer to SAP Note 1749142.]
It’s important to note that these clients have specific purposes and should be used accordingly.
Custom SAP Clients
Creating new SAP clients specifically for certain purposes is advised to avoid any potential issues with the standard clients. Creating custom SAP clients is recommended to address specific business needs and avoid potential issues with standard clients. To create a custom client, define its purpose, configure client-specific settings, populate it with relevant data, test its functionality, and maintain thorough documentation.
Custom clients offers flexibility and tailored solutions within your SAP environment. You should managed them carefully to ensure alignment with your business objectives and to prevent conflicts with standard clients.
Here are common scenarios:
- Standard SAP Clients: In many cases, businesses choose to copy data from a standard SAP client like client 000 (SAP installation client) or client 001 (SAP reference client) as a starting point. This is a convenient option because these standard clients often contain baseline data and configurations that can be useful. However, you’ll need to customize the copied data to align with your specific needs.
- Existing Custom SAP Client: If you have already created custom SAP clients for similar purposes in the past, you can use an existing custom client as the source for copying. This is particularly helpful if your new custom client has similar requirements to a previous one, as it can save time and effort in configuration.
- Data Import or External Source: In cases where you require specific data sets or configurations that are not available in standard or existing custom clients, you may need to import data from an external source or another system. This could involve data migration from legacy systems, data uploads from spreadsheets, or integration with other applications.
- Development Systems: For development and testing purposes, you may have a separate development system where you create and refine custom client configurations. You can use this development system as the source for copying configurations and data to your production custom client when ready.
The choice of the source depends on your project’s requirements, the type of data and configurations needed, and the existing landscape of your SAP environment. It’s essential to carefully plan and document the copying process to ensure that the custom client aligns with your business objectives and functions as intended.
What is SAP Client Copy?
SAP client copy is the process of duplicating client data and configuration settings from an existing SAP client to create a new one. This new client serves various purposes such as testing, training, or for development purposes, all without impacting the production environment.
Purpose
SAP Client Copy is indispensable in SAP system management for several reasons:
- New Functionality and Testing: It allows for the creation of a new client dedicated to testing or developing new functionalities without risking disruptions in the production system.
- Data Refresh: When data in the current client becomes outdated or corrupted, SAP Client Copy can refresh it with data from another client.
- Data Migration and Consolidation: It facilitates the smooth migration and consolidation of data from one client to another, ensuring consistency and currency of data across all clients.
- Customizing Settings: You can efficiently copy customizing settings from one client to another.
- Data Replication: It supports data replication across multiple systems in a distributed environment.
By leveraging SAP client copy, organizations can ensure the smooth functioning of their SAP systems while minimizing disruptions and maximizing efficiency.
Benefits
SAP client copy is a vital process for companies that use the SAP system.
- Time-saving: It expedites the creation of new clients with identical data, settings, and configurations, reducing the need for manual configuration and saving valuable time.
- Error reduction: Manual configuration of new clients can introduce errors, potentially leading to data inconsistencies and other issues. SAP Client Copy minimizes this risk.
- Cost-effectiveness: Manual client creation can be resource-intensive. SAP client copy offers a cost-effective alternative for client creation and maintenance.
- Test environments: It facilitates the establishment of test environments for new features, updates, or changes, allowing thorough testing before deployment in the live environment.
- Data Segregation: SAP Client Copy aids in segregating data for various departments or subsidiaries, enhancing data organization and management.
In summary, SAP Client Copy provides businesses with several advantages, including time savings, error reduction, cost-effectiveness, and improved data organization and management.
SAP Client Strategy Checklist
Creating a comprehensive SAP client strategy checklist involves considering various aspects of the client’s needs, objectives, and resources. Here’s a generalized checklist that can be customized based on specific client requirements:
1) Assessment and Planning:
- Define the client’s business objectives and goals.
- Assess the current SAP landscape, including systems, modules, and integrations.
- Identify pain points, challenges, and areas for improvement.
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success.
2) Alignment with Business Processes:
- Analyze existing business processes and workflows.
- Identify opportunities for optimization and automation.
- Align SAP solutions with business requirements and industry best practices.
3) Infrastructure and Architecture:
- Evaluate the client’s IT infrastructure and architecture.
- Determine hardware and software requirements.
- Plan for scalability, reliability, and security.
4) System Integration:
- Assess integration needs with other systems and applications.
- Identify data sources and interfaces.
- Plan for data migration and legacy system decommissioning.
5) Solution Selection and Customization:
- Evaluate SAP solutions and modules based on client requirements.
- Determine the need for customization and development.
- Define scope, timelines, and budget for customization efforts.
6) Change Management and Training:
- Develop a change management strategy to ensure smooth adoption.
- Plan for user training and support.
- Communicate the benefits of the SAP solution to stakeholders.
7) Governance and Compliance:
- Establish governance policies and procedures.
- Ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards.
- Define roles and responsibilities for system administration and security.
8) Testing and Quality Assurance:
- Develop a testing strategy for functional, integration, and performance testing.
- Define test cases and scenarios.
- Conduct thorough testing to ensure the reliability and accuracy of the SAP solution.
9) Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support:
- Plan for the go-live phase, including data migration and system cutover.
- Provide post-implementation support and troubleshooting.
- Monitor system performance and address any issues that arise.
10) Continuous Improvement:
- Establish processes for ongoing system maintenance and optimization.
- Monitor KPIs and performance metrics.
- Implement feedback mechanisms for continuous improvement.
By following a structured checklist tailored to the client’s specific needs, organizations can effectively plan, implement, and optimize their SAP solutions to drive business success.
Performing SAP Client Copy
Types of SAP Client Copies
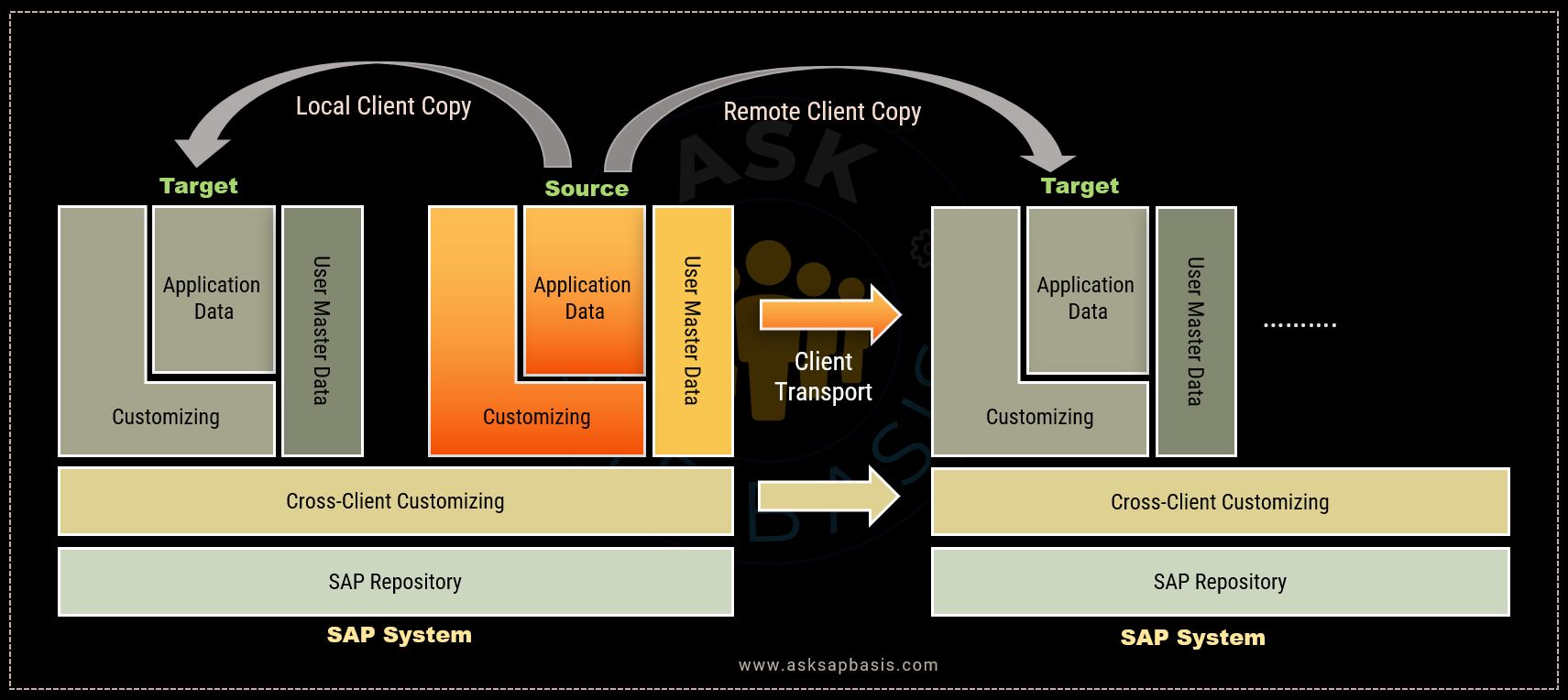
SAP provide three tools for copying data between clients:
- Local Client Copy: This tool copies data within the same SAP system. It is often used for training, testing, or creating a new client for specific purposes.
- Remote Client Copy: This tool copies data from one SAP system to another. It’s employed when you want to copy data from the production system to a test system.
- Client Export / Import: This tool copies data between different SAP systems using a transport request.
The key difference is that in remote client copy, data is directly copied between the two systems, whereas in client export/import, the data is first moved to a transport directory and then imported using the transport management system (TMS).
Pre-requisites
To ensure a successful SAP client copy, several factors need to be addressed proactively before starting the operation. Some important prerequisites include:
- Sufficient disk space: Ensure that the target system has ample disk space, preferably at least twice the size of the source client.
- RFC connections: Confirm that RFC connections are established between the source and target systems.
- User authorization: Verify that the user performing the client copy possesses the necessary authorizations in both the source and target systems.
- Database backup: Take a backup of the source client database before initiating the client copy to ensure data integrity.
- System status: The source and target systems should be on the same release and patch level, and client copy should not be performed during peak business hours.
- Background processing: Disable all background processing jobs during the client copy process to prevent data inconsistencies.
- Network connection: Ensure a stable and reliable network connection between the source and target systems to avoid interruptions during the client copy.
These are the main pre-requisites to meet before conducting an SAP client copy. Consulting the SAP documentation and seeking guidance from experienced consultants before such critical operations is always recommended.
SAP Profiles
In SAP, a profile is a pre-configured set of instructions that automates various functions within the system, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
In the context of SAP’s client copy process, a profile determines what specific data should be copied and how it should be managed during the process. This ensures precise and efficient data transfer, making profiles an essential component of the SAP client copy process. Profiles dictate whether to copy only customizing data, application data, how to handle authorization data, and whether to include specific objects like tables, views, or programs.
| Client Copy Profiles | Meaning |
| SAP_ALL | All client-specific data without change documents. |
| SAP_APPL | Customizing and application data without change documents. |
| SAP_APPX | SAP_APPL without authorization profiles and roles. |
| SAP_CUST | All client-specific customizing and authorization profile. |
| SAP_CUSV | All client-specific customizing and user variants. |
| SAP_CUSX | All client-specific customizing without authorization profiles and roles. |
| SAP_PROF | Only authorization profiles and roles |
| SAP_RECO | Recovery (only if Source Client = Target Client) |
| SAP_UCSV | Customizing, User master records, and user variants |
| SAP_UCUS | Customizing and User master records |
| SAP_UONL | User without authorization profiles and roles |
| SAP_USER | User master records and authorization profiles |
In addition to above profiles, below are some of the copy profiles available for client transports (SCC8)
| Client Copy Profile | Meaning |
| SAP_EXBC | SAP_UCSV with cross-client customizing |
| SAP_EXPA | SAP_ALL with cross-client customizing |
| SAP_EXPC | SAP_CUSV with cross-client customizing |
Below are some of the special profiles available for remote client copy (SCC9) and client transport (SCC8) ONLY.
| Client Copy Profile | Meaning |
| SAP_RECO | For recovering accidentally recovering client. It contains delivery class local tables (L and M), and the change documents, as well as SAP_ALL |
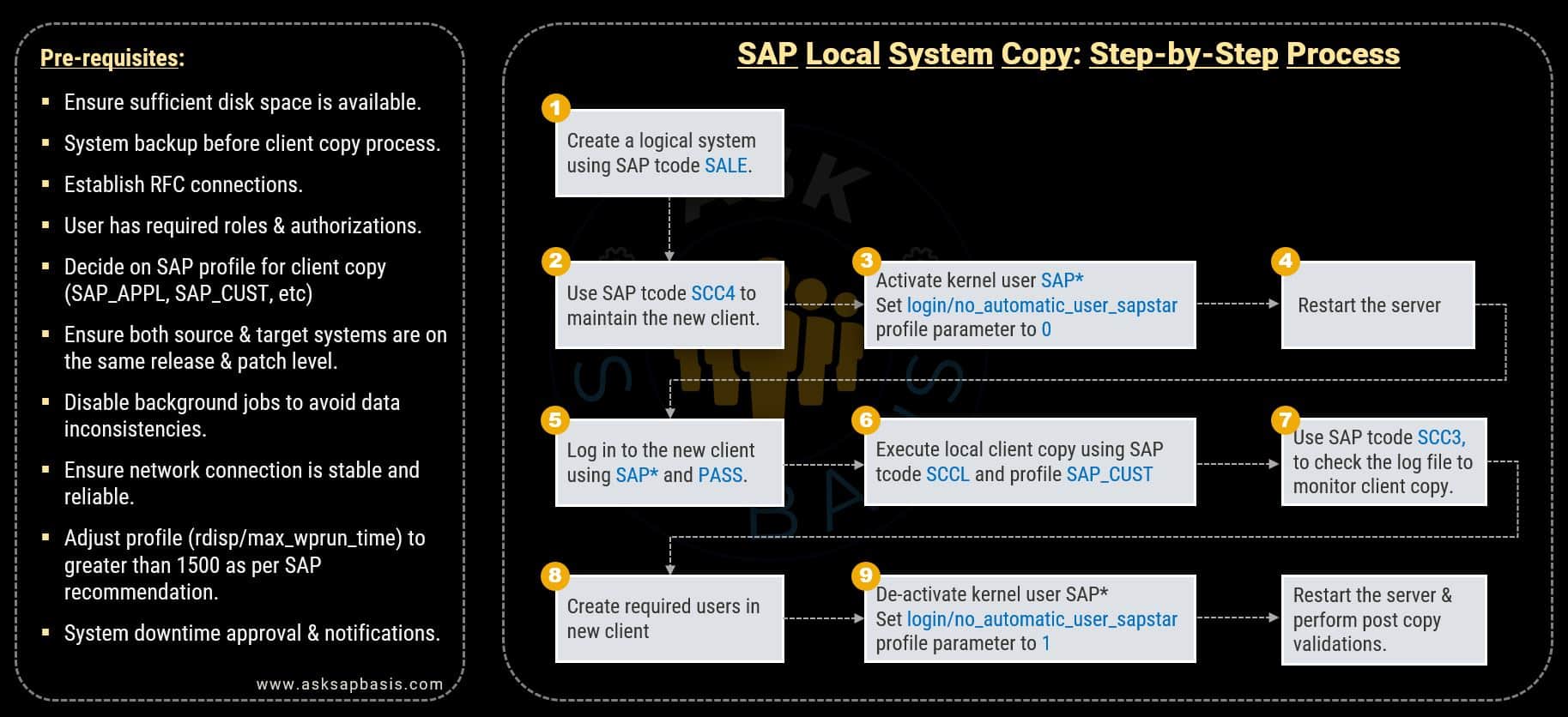
SAP Local Client Copy (SCCL): Step-by-Step Process
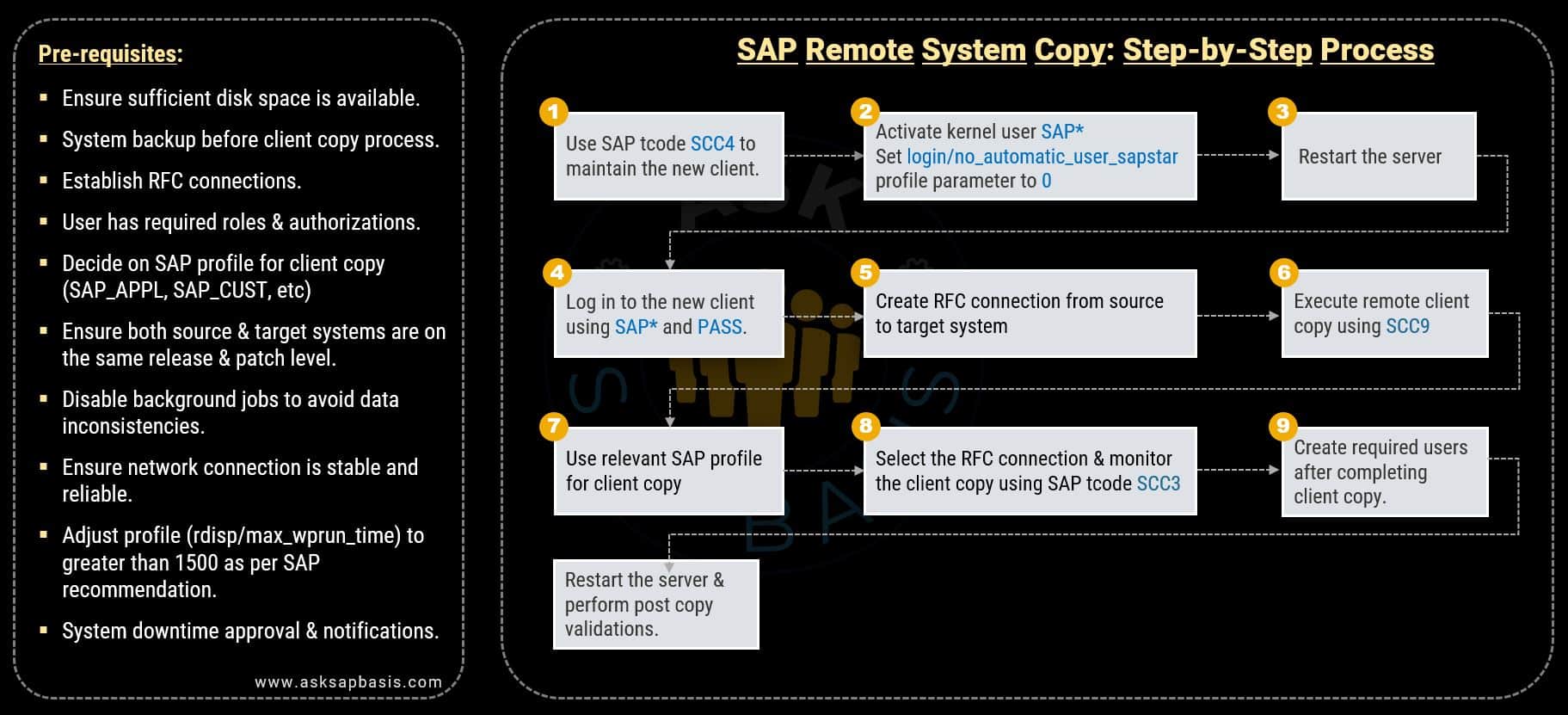
SAP Remote Client Copy (SCC9): Step-by-Step Process
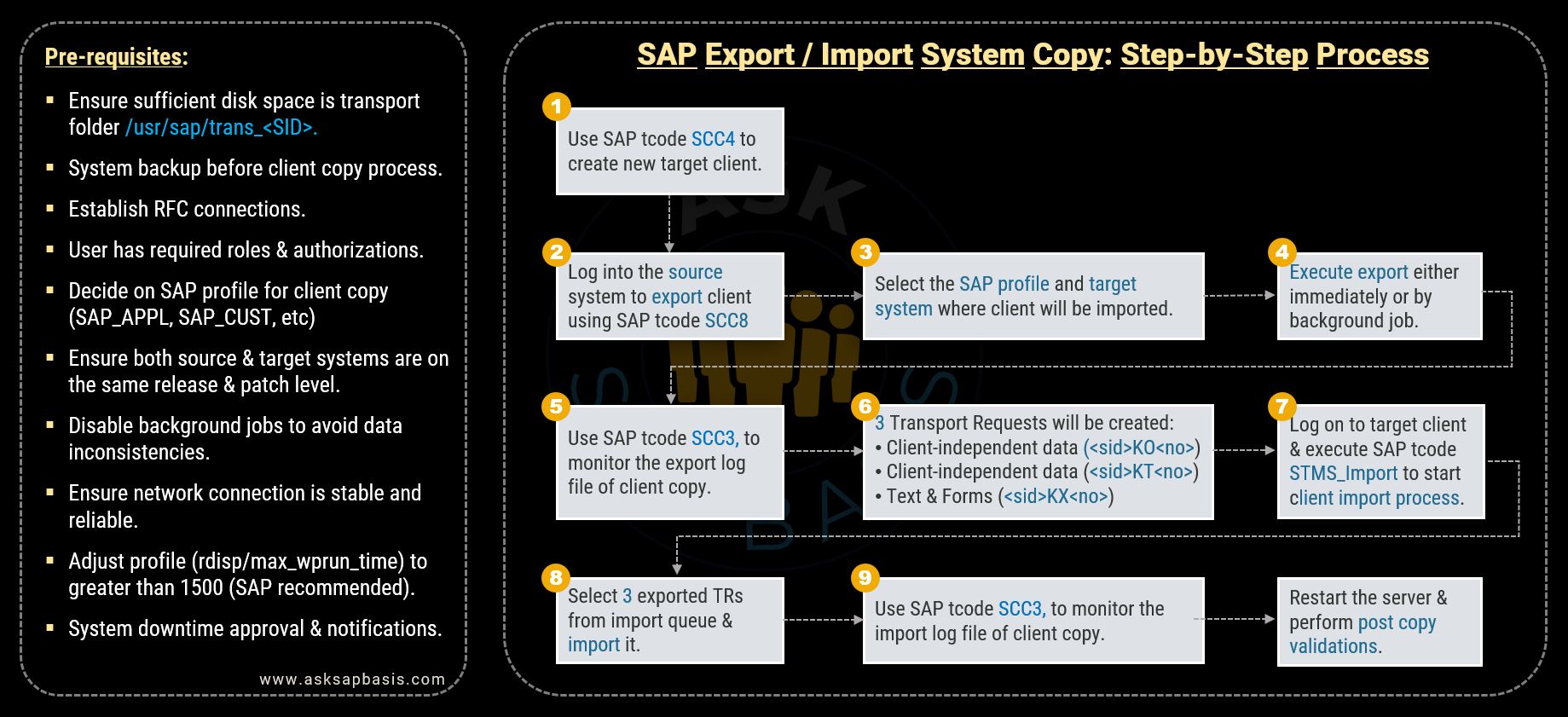
SAP Export / Import Copy (SCC8): Step-by-Step Process
Post Steps Of SAP Client Copy
After performing an SAP Client Copy, several post-copy steps should be carried out to ensure the new client functions correctly. These steps include:
- Verify Successful Client Copy: Ensure that the client copy completed without errors or warnings. Analyze the client logs for any observed problems or errors requiring remedial actions.
- Confirm Target System Settings: Check that the target system mirrors the source system in terms of configuration, data, and system settings.
- Testing The New Client: Conduct comprehensive testing on the new client to confirm the proper functioning of all operations, features, and transactions. Test a representative sample of transactions to validate their accurate copying.
- Adjust User and Authorization Settings: Verify the correctness of user and authorization settings, ensuring that users can access the correct transactions and functions. Review and modify user master records as needed.
- Configure System-Specific Settings: Configure any system-specific settings, such as printers, default views, or customizing settings, to align with the source system.
- Database Reorganization: Execute a database reorganization to optimize the performance of the new client. Utilize the SAP program RSDBAJOB to schedule and perform this crucial step.
- Implement Regular Maintenance: Establish a regular maintenance plan for the new client to maintain its proper functioning. This may involve routine backups, removal of outdated data, and continuous monitoring of system performance to ensure ongoing smooth operation.
Scheduling and Monitoring
Scheduling SAP Client Copy Process
To initiate the SAP client copy, follow these steps:
- Log into the SAP system as a user with sufficient permissions to perform client copies.
- Open the transaction code SCCL in the command field.
- Select the source client and the target client for the copy.
- Choose the “Background” option in the “Execution mode” field.
- Click the “Schedule Job” button.
- Enter the start date and time for the background job.
- Define any other job parameters such as maximum runtime, priority and spool parameters.
- Save the job and note the job name for record or future references.
Monitoring SAP Client Copy Process
To monitor the progress of an SAP Client Copy, use the SAP transaction code SCC3:
- Log in to the SAP system with sufficient permissions for client copies.
- Execute the SAP transaction code SCC3 in the command field.
- Select the client copy request that you want to monitor from the list of requests.
- Click on the “Display logs” button to view the logs for the selected client copy request.
- The logs provide information about the progress of the client copy, including the status of the various phases of the copy process, any errors or warnings that occurred, and the duration of the copy.
- Transaction codes SCC5 and SCCL can also be used to monitor and manage client copy background jobs.
By monitoring the progress using SCC3 and related transaction codes, you can stay informed about the copy’s status and address any issues promptly.
Choosing the Right Client Copy Strategy
| Scenario | Recommended Method | T-Code | Profile | Notes |
| New Sandbox client needed | Local Copy | SCCL | SAP_ALL | Use background processing |
| Copy client from QA to Dev | Remote Copy | SCC9 | SAP_CUST | Requires RFC config |
| Migrate config between systems | Export/Import | SCC8/SCC7 | SAP_CUST | Good for transportable copies |
| Refresh test client without user data | Local Copy | SCCL | SAP_CUST | Keeps customizing; skips master/transactional data |
| Test new customizing with standard master data | Local Copy | SCCL | SAP_APPL | Loads default SAP master data with customizing |
| Perform client copy with high transactional volume | Remote Copy | SCC9 | SAP_ALL / Z_CUSTOM | Use background with parallel processing |
| Copy only user master data | Local Copy | SCCL | SAP_USER | Only users; excludes roles unless extended |
| Rebuild client from scratch using SAP templates | Local Copy | SCCL | SAP_UCSV / SAP_CUST | Good for training/demo systems |
| Migrate client with manual import/export | Export/Import | SCC8/SCC7 | SAP_ALL | Requires STMS import; good for full config/migration |
| Copy only roles and authorizations | Local Copy | SCCL | SAP_ROLES | For authorization-specific testing |
Troubleshooting
Common SAP Client Copy Errors
Some of the common issues that are observed often causing the client copies to fail are:
- Network connectivity problems.
- Insufficient disk space on the target systems.
- Authorization and authentication issues.
- Locked objects in the source systems.
- Incompatible release or support pack levels.
- Performance discrepancies.
- Database-related issues.
It is crucial to monitor the client copy process and promptly troubleshoot any issues that arise to ensure a successful copy.
Troubleshooting SAP Client Copy Issues
Performing an SAP Client Copy can be a daunting task, requiring skill and experience. Despite taking all the proactive measures, there may be times when you may encounter issues or errors during the process.
Here are a few troubleshooting steps that you can take to remediate the issue:
- Check the logs: Utilize SAP t-codes like SM37 and SM21 to review job logs and system logs, respectively. These logs record every step and any errors or warnings encountered during the copy.
- Verify Source and Target Systems: Use SAP t-code STMS to check transport routes and system configurations. SAP t-code SPAM can validate installed software components.
- Database and Table Consistency Check: Utilize SAP t-codes DB02 and ST04 to inspect space issues, database logs and system tables. Search for any errors or inconsistencies that could affect the client copy process.
- Validate Authorizations: SAP t-code SU01 allows you to verify user authorizations and access rights; while SU53 helps identify authorization failures.
- Check System Locks: With SAP t-code SM12, Identify and release stale or deadlocks that may block copy jobs, especially common in interrupted background processes.
- Contact SAP support: If the above steps fail to resolve the issue and it still persists, prepare logs and contact SAP support. Make sure to include – job logs, system logs, dump analysis, any error codes.
Best Practices of SAP Client Copy
Executing a SAP client copy is complex. Ensure success by adhering to best practices for a smooth outcome.
Here are some general best practices to follow when performing a SAP client copy:
- Plan The Copy Strategically: Before proceeding, meticulously plan the process and right client copy strategy. Carefully define the scope, source and target clients, timeline, and ideal window (preferably during low activity).
- Decide the right copy profile: SAP offers various copy profiles, such as client-specific, cross-client, and client-independent data. Select the profile that aligns with your copy objective, system requirements and data type.
- Ensure adequate system resources: Verify that both source and target systems have enough disk space, memory, and CPU capacity to handle the data volume, especially for large client copies.
- Backup critical systems: Verify that both source and target systems have enough disk space, memory, and CPU capacity to handle the data volume, especially for large client copies. This safeguards against potential issues, allowing you to restore to the original state if needed.
- Select the appropriate copy method: Depending on the scenario, choose between local copy (SCCL), remote copy (SCC9), or export/import (SCC8/SCC7). The method should suit your system architecture and data migration need.
- Verify authorizations and roles: Confirm that the user executing the copy has sufficient authorizations (SAP_ALL or equivalent) and that missing roles or objects don’t cause the job to fail halfway through.
- Validate client-independent objects: Roles, profiles, and certain customizing settings are client-independent. Make sure these are aligned or migrated as needed, especially when copying to a clean target system.
- Monitor the copy process: Use SCC3, SM37, and system monitoring tools to keep track of background jobs, memory usage, and potential locks during execution. Address issues in real-time.
- Validate the copy results thoroughtly: After the process, review application logs and perform key tests to ensure the copied data is accurate, complete, and functional. Pay attention to user authorizations, config tables, and custom objects.
After completing the SAP client copy, double-check that all data has transferred flawlessly to the target client, free of errors or inconsistencies.