SAP Journey: From SAP to S/4HANA Explained
Introduction
SAP, stands for Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing, a global leader in the enterprise software industry, providing integrated business software solutions to organizations across multitude of sectors.
Founders and their Enterprise Vision
SAP’s journey began on April 1, 1972. It was initiated by a visionary group of five former IBM employees in Germany – Dietmar Hopp, Hasso Plattner, Claus Wellenreuther, Klaus Tschira, and Hans-Werner Hector. They recognized the vast business potential presented by technology. Fueled by their unwavering belief in the technology’s transformative power to reshape business processes and innovation, they founded the SAP. And they embarked on a path that would shape the future of enterprise software.
At the core of company’s vision was to create a standard enterprise software that integrated all business processes and enabled data processing in real time. And this software would not only seamlessly connect but also automate critical business functions, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and facilitating data-driven decision making.
Diversification and Innovation
Over the years, SAP has broadened its product offerings, diversifying into various areas of enterprise software. Today, SAP’s solutions encompass a wide spectrum of business functions, including finance, sales, supply chain management, human resources, and more. The company’s unwavering dedication to continuous improvement and innovation has been instrumental in its meteoric rise, making SAP a trusted partner for businesses worldwide.
A Journey Through SAP’s History
This blog aims to embark on a captivating journey through SAP’s rich history, tracking from its humble beginnings and groundbreaking contributions to the world of ERP and database technologies. By delving deep into SAP’s journey, we can gain a deeper understanding of its evolution and enduring impact on the enterprise software landscape. We’ll witness SAP’s remarkable transformation, from its visionary founders’ pioneering steps to cutting-edge advancements in ERP and database technologies, and its unyielding commitment to propelling business success.
SAP ERP History
Let’s delve into the remarkable journey of SAP ERP as we explore its key milestones. From its humble beginnings to its global dominance, witness the pivotal moments that shaped one of the most influential ERP systems in the business world.
Join us on a captivating voyage through time as we unveil the innovations, breakthroughs, and strategic shifts that propelled SAP ERP to revolutionize the way enterprises operate and thrive.
Key Milestones
The history of SAP’s Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solution is a testament to continuous innovation, shaping the way businesses operate and achieve success. By examining the key milestones in SAP ERP’s evolution, we gain valuable insights into its profound impact on the global business landscape.
In this exploration, we’ll delve into the pivotal moments that have shaped the SAP ERP’s journey. We analyze how these milestones represent groundbreaking advancements in technology and functionality. We’ll discover how ERP has transformed core business processes, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. We’ll gain a deeper understanding of how these developments have empowered businesses to achieve their strategic objectives.
SAP ERP has evolved over the years, and several versions have been released with significant improvements, new features and digital innovation. Let’s visit those era’s.
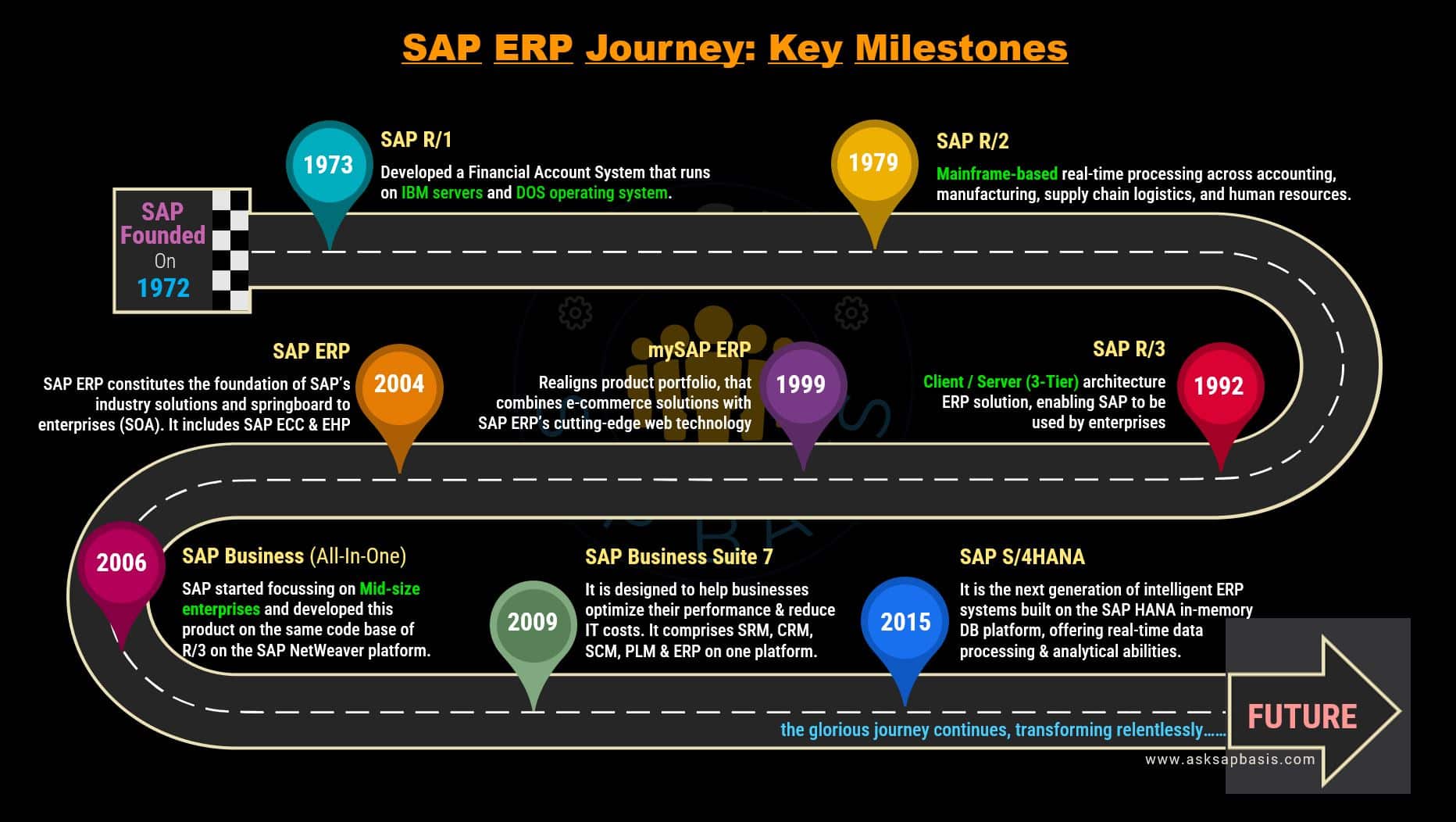
1972-1986: The Early Years (From R/1 to R2)
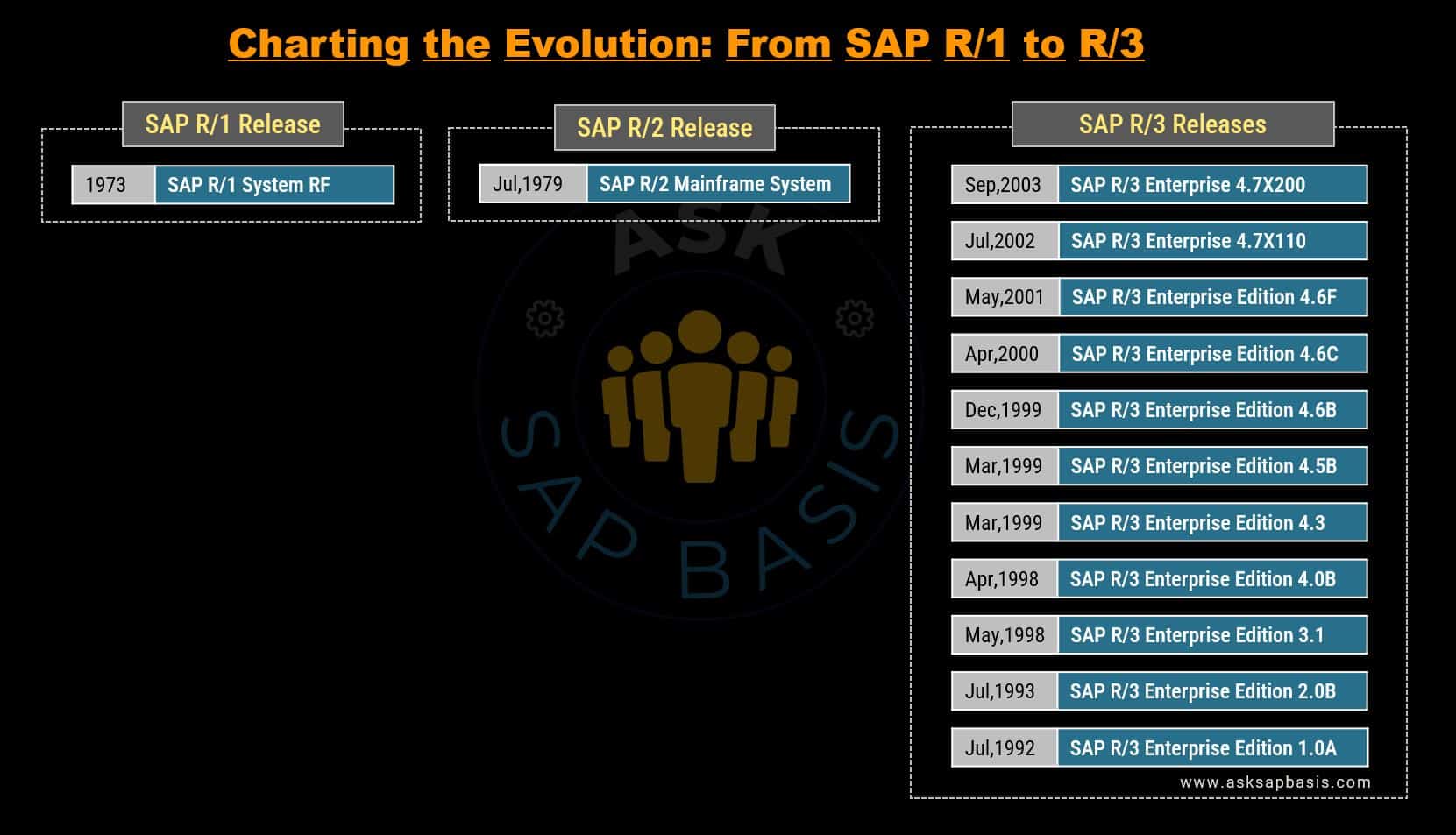
SAP R/1
The groundbreaking era of SAP R/1 started from 1972 to 1980. This phase materialized the vision of real-time computing into a tangible reality, eliminating the need for overnight batch processing. This monumental innovation triggered a paradigm shift in business operations, furnishing instantaneous insights that revolutionized decision-making for organizations.
On 1st April 1972, five former IBM employees started the company, System Analysis and Program (SAP) Development. Driven by visionary concept, their mission was to forge a revolutionary enterprise software solution that seamlessly integrated every facet of business operations, all while empowering real-time data processing.
In 1973, company introduced its first financial accounting system with RF (Real-Time Financials). This became the foundational building block, later known as “SAP R/1“, an all-encompassing suite of comprehensive solutions that transformed the way businesses manage their financial processes with real-time capabilities.
In 1975, their relentless innovation led to the development of transformative applications. They introduced RF for financial accounting, along with invoice verification and inventory management solution called RM (Real-Time Management). This cutting-edge solution, fundamentally reshaped how businesses managed their finances, verified invoices and controlled inventory.
Here are some of the notable features of SAP R/1, that laid foundation for subsequent versions:
1) Financial Accounting
- SAP R/1 focused on financial accounting functionalities, offering essential capabilities for managing ledger, accounts payable and accounts receivables.
- This feature formed the cornerstone of SAP ERP’s financial management capabilities.
2) Data Processing
- SAP R/1 enabled real-time data processing, empowering businesses to access and process financial information promptly.
- By merging real-time and batch-processing, it delivered up-to-the-minute insights into their financial transactions, fostering informed decision-making.
3) Modularity
- SAP R/1 pioneered a modular system approach. Initially focused on financial accounting, it offered the flexibility to expand and integrate additional modules for various business functions.
- This modular architecture became a hallmark of SAP ERP’s design.
4) Centralized Data Management
- SAP R/1 introduced a centralized data management system, enabling businesses to store and retrieve financial data from a single source.
- This feature ensured data consistency and accuracy, reducing errors and redundancy.
5) Reporting and Analytics
- SAP R/1 provided basic reporting capabilities, facilitating businesses to generate financial reports and gain insights into their financial performance.
- This feature supported financial analysis, budgeting, and forecasting.
6) User-Friendly Interface
- SAP R/1 introduced a user-friendly graphical user interface (GUI), allowing users to interact with the system more intuitively.
- This GUI enhanced usability and accessibility for a broader range of users.
SAP R/2
In the era of SAP R/2 from 1981 to 1990, businesses experienced profound transformation driven by real-time data processing capabilities it brought forth. Powered by SAP’s packaged mainframe software, it enabled seamless integration of entire spectrum of business functions.
In 1979, SAP shifted its focus to developing second generation software known as SAP R/2, built on mainframe system. The features of this ground-breaking release were:
1) Client Server Architecture
- SAP R/2 introduced a cutting-edge two-tier client-server architecture.
- This architectural shift marked a distributed computing model, where the central server took charge of data management and processing, while the user terminals served as the interface for users to access and interact with the system.
- This streamlined operations and enhanced efficiency.
2) Batch Processing
- In 1979, SAP R/2 facilitated robust batch processing functionality, automating repetitive tasks for timely execution, eliminating the need for overnight batch processing.
- This innovation automated repetitive tasks, ensuring timely execution of critical functions such as data uploads, report generation, and data backups. Operational efficiency received a significant boost as a result.
3) Extended Functional Scope
- With R/2, SAP extended its functional scope beyond financial accounting.
- New modules were introduced, including: Sales and Distribution (SD) in 1978, Production Planning (PP) in 1981, and Human resources (HR) in 1986, Materials Management (MM) in 1990.
- These modules offered a comprehensive unified solution support essential business processes across different departments, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
4) Integration with External Systems
- Around 1983-84, SAP R/2, started developing interfaces and connectors, to facilitate seamless communication and data exchange, between R/2 and external applications or systems.
- This initiative, aimed to establish a seamless information flow across the entire enterprise, enhancing data coherence and accessibility.
5) Multi-Lingual and Multi-Currency Support
- Around 1984-85, SAP R/2 addressed the need of global businesses by incorporating multi-lingual and multi-currency support capabilities.
- This featured allowed the users to work with different languages and currencies, simplifying international business operations and fostering global operations.
6) Hierarchical Data Structure
- In 1989, SAP launched a user-friendly interface ABAP/4 programming environment for R/2 and new tools. These tools utilized a hierarchical data structure, for organized and consistent data storage.
- This structure facilitated easy data retrieval and laid a foundation for data integrity and consistency.
7) Customization and Extension
- SAP R/2 was designed to be adaptable to the specific needs of organizations.
- This could be achieved by configuring settings, defining custom reports, and implementing user exits and enhancements. This flexibility ensured that SAP R/2 was not just a one-size-fits-all solution but a tool that could evolve with the changing demands of businesses.
1987-2010: From SAP R/3 To Global Player
From 1991 to 2000, SAP R/3 established its dominance by evolving from its SAP R/2 era into a global player in the realm of enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions.
SAP R/3
In 1992, SAP R/3 made its debut in the marking, heralding an era of unparalleled growth and technological advancement. This pivotal release brought with it a host of ground-breaking features that revolutionized the way businesses operated, becoming the driving force behind globalization.
Here are some of the noteworthy features and innovations of SAP R/3:
1) Client Server Architecture
- SAP R/3 adopted a 3-tier client-server architecture, comprising of presentation, application and database layer.
- This architectural shift brought about significant improvements in performance, scalability, availability, flexibility and maintenance. It laid the foundation for a more robust and efficient system.
2) Integrated Business Processes
- SAP R/3 seamlessly integrated core financial accounting, sales, materials management, production planning, and human resources.
- This integration fostered efficient data flow and promoted cross-functional collaboration within organizations, streamlining operations and enhancing productivity.
3) Advanced Workflow Management
- SAP R/3 introduced a comprehensive workflow management system, that empowered businesses to define, automate, and monitor organizational processes.
- This innovation led to improved efficiency and transparency in workflows, driving productivity and accountability.
4) Advanced Reporting and Analytics
- SAP R/3 delivered robust reporting and analytics capabilities.
- Users could generate complex reports, conduct in-depth data analysis, and create meaningful visualizations.
- This functionality supported better decision-making and strategic planning within organizations.
5) Embracing Internet
- In 1996, SAP R/3 embraced the power of internet, paving the way to online connectivity.
- This breakthrough allowed customers to conveniently access SAP systems through user-friendly web interfaces, fostering collaboration and enabling remote access.
- Then in 1999, SAP introduced an innovation strategy, in mySAP.com, and realigned its product portfolio.
- This strategic shift focused on seamlessly integrating e-commerce solutions with SAP’s robust ERP application, cutting-edge web technology to propel into digital age.
- A decade later, SAP expanded into three future markets: mobile technology, database technology and cloud.
6) Globalization and Localization
- SAP R/3 expanded its globalization capabilities to facilitate global operations while ensuring compliance with local regulations.
- It supported multiple languages, currencies, and legal requirements, enabling businesses to operate seamlessly in diverse international environments.
7) Industry-Specific Solutions
- In year 1994, SAP intensified its efforts to introduce industry-specific solutions for SAP R/3.
- These solutions were tailored to sectors such as manufacturing, retail, healthcare, utilities, and more, providing pre-configured functionalities and best practices to each industry’s needs.
8) Enhancements In User Experience
- SAP R/3 prioritized user experience by introducing a more intuitive interface, featuring drop-down menus, graphical icons, and customizable screens.
- These enhancements made navigation and interaction more user-friendly.
9) Scalability and Flexibility
- SAP R/3 offered scalability to accommodate expanding system resources and provided flexibility through customizable business processes and configurations.
- This adaptability allowed organizations to tailor the system to their unique requirements.
SAP mySAP.com
In 1994, SAP embarked on a series of strategic collaborations and technological advancements that would reshape the landscape of enterprise resource planning (ERP) and pave the way for the revolutionary mySAP.com platform.
1) Collaboration with Microsoft
- In 1994, SAP partnered with Microsoft to port SAP R/3 to Windows NT.
- This collaboration was instrumental in expanding the reach of SAP’s ERP solutions and making them more accessible to a wider range of users.
- Windows NT compatibility opened new doors for SAP in terms of operating system support.
2) IXOS Project Involvement
- SAP joined the IXOS project, focusing on electronic document archiving.
- This involvement showcased SAP’s commitment to staying at the forefront of document management technology, a crucial aspect of modern ERP systems.
3) Compatibility with SUN Hardware
- Achieving compatibility with SUN hardware was a significant milestone.
- It meant that SAP R/3 could run on SUN systems, further broadening its compatibility and accessibility, catering to diverse set of hardware platforms.
In 1999, SAP introduced mySAP.com, a transformative strategy that merged ERP applications with web technology and e-commerce solutions, revolutionizing enterprise software.
mySAP.com was more than a software; it was a comprehensive suite of business applications to support various business functions and processes. Some of its key components included:
- ERP Backbone (SAP R/3): SAP R/3 formed the core of the suite, serving as a backbone for the mySAP.com, ensuring robust and efficient enterprise resource planning.
- Business Intelligence Solutions: mySAP.com featured a range of business intelligence (BI) solutions, including Business Information Warehouse (BW), Knowledge Warehouse Management, Strategic Enterprise Management (SEM) and Corporate Finance Management (CFM). These tools empowered organizations with data-driven decision-making capabilities.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) Solutions: The suite encompassed solutions like SAP Advance planner and optimizer (APO), Logistics Execution System (LES), Business-to-Business Procurement (BBP), Environment, Health & Safety (EHS). These offerings enabled businesses to streamline their supply chain operations for greater efficiency.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): mySAP.com included CRM solutions such as Employee Self Service (ESS), Internet Sales Services (ISS), facilitating better customer relationship management and enhanced user experiences.
- Product LifeCycle Management (PLM) Solutions: PLM solutions within mySAP.com covered various aspects, including Product Data Management (PDM), Computer Aided Design (CAD) Integration, Document Management System (DMS), Quality Management (QM), Environment Compliance (EC) etc. These tools ensured better management of products through their lifecycle.
- Supplier Relationship Management (SRM): The platform offered a range of SRM solutions, including Supplier Management, Sourcing and Contracting Management, Supplier Collaboration, Purchase Requisition and Order Management, Catalog management, Self-Service Procurement, Invoice and Payment Management etc. These tools ensured better management of products throughout their lifecycle.
- Clustered Industry Solutions: mySAP.com included 21 clustered Industry Solutions, catering to specific sectors like Retail, Manufacturing, Healthcare, Utilities, Automotive, and Public Sector, among others. These specialized solutions provided pre-configured functionalities and best practices tailored to each industry’s unique needs.
In essence, mySAP.com represented a paradigm shift in enterprise software, offering a holistic approach to business process management and automation. It empowered organizations to operate more efficiently, make data-driven decisions, and enhance their relationships with customers and suppliers. This bold step by SAP set the stage for the digital transformation era, and its impact continues to resonate in the business world today.
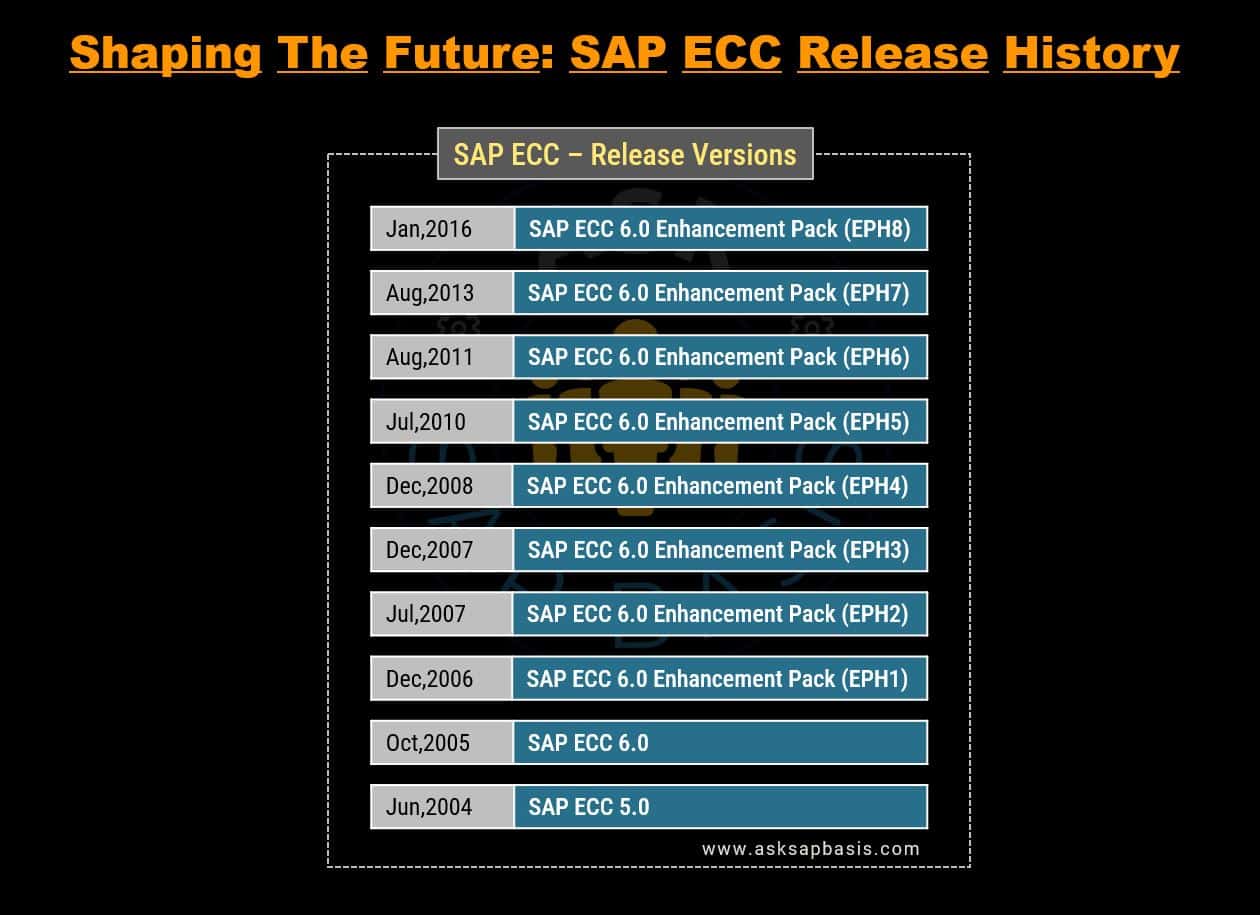
SAP ERP
In 2004, SAP embarked on an significant architectural transformation with the introduction of SAP ERP. This marked a significant shift as SAP R/3 was replaced by ERP Central Component (ECC), bringing substantial changes and improvements in the SAP ecosystem.
SAP ECC represented a major leap forward by consolidating several key components into a unified instance, streamlining operations for users. The notable advancements included:
1) Integration of Key Modules
- SAP ECC seamlessly merged critical components such as SAP Business Warehouse (BW), SAP Strategic Enterprise Management (SEM), and Internet Transaction Server (ITS), into a unified instance, simplifying operations for users.
- This integration enhanced cohesion and efficiency within the SAP ERP systems.
2) SAP Netweaver
- In 2003, the Web application server (WAS) was encapsulated into SAP Netweaver.
- This cutting-edge solution provided a powerful foundation for the ERP system, facilitating improved performance and adaptability.
3) Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA)
- SAP recognized the importance of embracing SOA, as a part of its architectural changes.
- SOA allowed businesses to design and integrate software services in a modular and flexible manner.
- It promoted the creation of reusable, loosely coupled services, enabling the construction of complex applications with enhanced flexibility and interoperability.
The Evolution of SAP ERP
The release of SAP ERP 6.0 in 2006 marked the latest version of the software. Since then, SAP ERP 6.0 has undergone updates through SAP enhancement packs (EHP). The latest update is EHP8, released in 2016.
SAP enhancement package are updates that provides additional features, improvement and functionalities to the existing SAP ERP software. They serve as a means for businesses to stay current with latest advancements in SAP technology and benefit from the enhanced functionalities.
EHPs allow organizations to tailor their ERP systems to meet evolving business needs, ensuring that they remain competitive and efficient in a rapidly changing landscape.
In conclusion, the introduction of SAP ERP and the subsequent evolution through enhancement packages represented a pivotal moment in the world of enterprise resource planning. These architectural changes not only simplified operations but also positioned SAP as a leader in embracing service-oriented architecture, fostering flexibility, and enabling businesses to adapt and thrive in an ever-changing business environment.
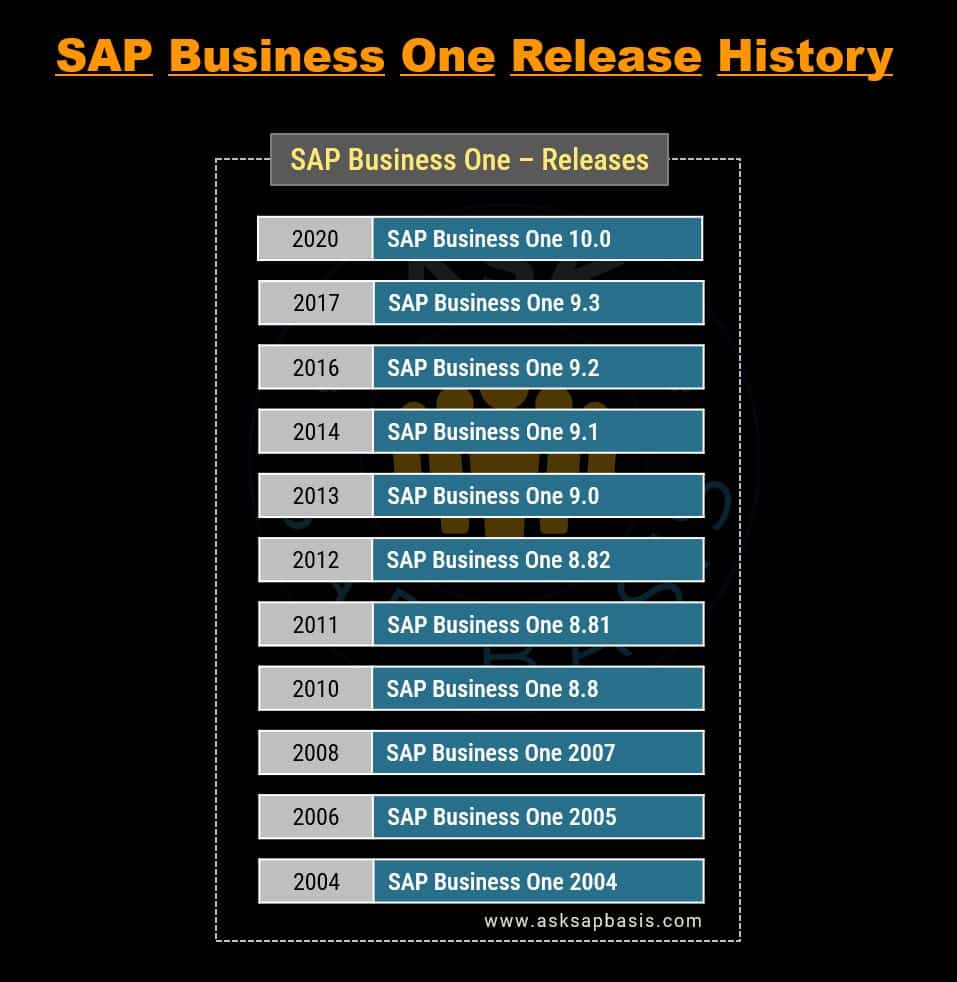
SAP Business One (All-In-One)
In 2006, SAP introduced SAP Business One, an customized ERP solution crafted for small and mid-sized enterprises (SME’s). This robust solution automates the essential functions in finance, operations and human resources.
By embracing SAP business one, SME’s can effortlessly streamline their operations, boost efficiency, and pave way for sustainable growth and success.
Key Features:
The latest version of SAP Business One 10.0, was released in 2020. Some of the notable features are:
- Web Client Enhancements: With these enhancements, based on SAP Fiori, the web client now offers a modernized and user-friendly interface, ensuring a seamless user experience.
- Document Printing & Approval: Improved document processing simplifies workflows, saving time and resources.
- Gantt Chart: The addition of a Gantt Chart greatly aids in project management, enhancing project visibility and control.
- Microsoft Office 365 Integration: This seamless integration with Microsoft Office 365 enhances productivity and collaboration.
- New UK (Brexit) Localization: Ensuring compliance with the ever-evolving regional requirements, this feature allows SMEs to operate confidently in the UK market.
- Platform Enhancements: Comprehensive enhancements across the platform have been made to further improve performance and functionality.
- Service Layer Configuration UI (HANA only): For HANA users, a user-friendly interface simplifies service layer configuration, streamlining operations.
- Support for SLES 15 (HANA): With expanded compatibility, SMEs can benefit from the latest technologies and security enhancements.
These updates empower SMEs to operate more efficiently, make data-driven decisions, and stay aligned with the ever-evolving business landscape. SAP Business One continues to be a vital asset for smaller enterprises seeking to thrive in today’s competitive markets.
SAP Business Suite 7
In 2009, took a significant step forward by introducing SAP Business Suite, a comprehensive and integrated suite of end-to-end business applications that revolutionized the way businesses managed their data, processes, collaboration and functions (such as finance, HR, as well as industry-specific (IS) features).
This SAP Business Suite, built on SAP’s technology platform called Netweaver, introduced in 2003, brought together various essential components to empower organizations across industries.
Key Components
There are 5 components that make up the SAP Business Suite 7:
- SAP ERP 6.0: At its core, SAP Business Suite 7 featured SAP ERP 6.0, offering a comprehensive solution for managing a wide range of business operations, from finance to human resources, and industry-specific functionalities.
- SAP CRM 7.0: Focusing on sales and marketing, SAP CRM 7.0 enabled organizations to enhance their customer relationships and drive sales growth through tailored customer-centric approaches.
- SAP SRM 7.0: Covering procure-to-pay and collaborative service procurement, SAP SRM 7.0 facilitated seamless interactions with suppliers, optimizing procurement processes.
- SAP SCM 7.0: With a focus on business planning, logistics, and order fulfillment, SAP SCM 7.0 helped organizations streamline their supply chain operations for greater efficiency and responsiveness.
- SAP PLM 7.0: SAP PLM 7.0 assisted companies in managing their product lifecycle needs, ensuring efficient product development, documentation, and compliance.
Key Features:
- Enhancement Packages: One of the most notable features of SAP Business Suite 7 was the introduction of enhancement packages. This modular approach allowed customers to selectively activate and implement new features and functionalities without undergoing a full system upgrade. This provided flexibility and minimized disruptions during system updates.
- User Interface: The suite introduced the SAP Netweaver Business Client, offering a unified and intuitive user interface for accessing various SAP applications. This interface was personalized and role-based, enhancing productivity and the overall user experience.
- Industry-Specific Solution: SAP Business Suite 7 included Industry Value Networks (IVNs), offering pre-configured business processes tailored to specific industries, such as manufacturing, retail, utilities, and more. These solutions helped organizations streamline their operations and align with industry best practices.
- Business Process Platform: Leveraging the SAP Netweaver technology stack, SAP Business Suite 7 transformed into a robust business process platform. This allowed organizations to integrate existing applications, develop custom applications, and extend standard business processes using open standards and service-oriented architecture (SOA).
- Analytical Capabilities: The suite incorporated advanced analytical capabilities through SAP BusinessObjects solutions. This empowered users to gain real-time insights, perform ad-hoc analysis, create interactive dashboards, and generate reports to support data-driven decision-making across teams.
- Mobile and Collaboration: SAP Business Suite 7 recognized mobile and collaboration trends. It provided mobile applications for accessing critical business data on-the-go. Additionally, it introduced tools like SAP StreamWork, facilitating effective collaboration and decision-making.
- Enhanced Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC): The suite enhanced GRC capabilities. It aided risk management, compliance and strong governance practices. It included features like audit management, and access control to protect sensitive data and ensure regulatory compliance.
During this period, SAP also expanded its product portfolio through strategic acquisitions, enhancing its offerings to cater to evolving business needs and trends in e-commerce.
Listed here some of the key competitors it acquired during this e-commerce era (1987 to 2010):
- 1991: Steeb
- 1994: Dacos
- 1997: Kiefer & Veittinger
- 1998: OFEK-Tech, AMC Development
- 1999: Campbell Software
- 2000: In-Q-My Technologies GmbH, Prescient Consulting
- 2001: Toptier, Infinite Data Structures, COPA GmbH, Paynet International AG, IMHC
- 2002: Topmanage, Expression, Guimachine
- 2003: DCW Software, SPM Technologies
- 2004: A2i
- 2005: ilytix, TomorrowNow, DCS Quantum, Lighthammer, Triversity, Khimetrics, Callixa
- 2006: Virsa Systems, Frictionless Commerce, Praxis Software Solutions, Factory Logic
- 2007: Pilot Software, Outlooksoft, MaXware, Wicom, Yasu Technologies, BusinessObjects
- 2008: Visiprise
- 2009: Highdeal, SAF
- 2010: Sybase, Cundus
The evolution of SAP from its SAP R/3 era to becoming a global player marked a remarkable journey of innovation and growth. As SAP expanded its offerings and reach, it solidified its position as a key player in its global enterprise software market, shaping the future of technology-driven business solutions.
2011-2023: Into The Cloud With SAP HANA
In 2015, SAP unveiled S/4HANA, a cutting-edge ERP suite built on the advanced SAP HANA in-memory platform. It shattered past constraints and ushered in a new era of limitless possibilities.
Today, SAP has transformed into a powerful platform provider, redefining collaboration within business networks, setting the stage for even greater possibilities in the future.
- In 2011, SAP introduced its flagship SAP HANA, an in-memory computing database platform, revolutionizing the speed and efficiency of data processing and analysis. It has the capability of swiftly analyzing the data in seconds, instead of days or weeks.
- In 2013, the entire SAP Business Suite transitions to SAP HANA. This strategic move unlocked a plethora of opportunities for the SAP, enabling them to harness the power of in-memory computing. This transition not only solidified SAP’s position as an industry leader, but also fueled their growth by offering customers a game-changing platform to accelerate innovation, streamline operations, and make data-driven decisions.
- Adoption of SAP HANA became a cornerstone to SAP’s success, propelling them to the forefront of the digital transformation revolution and driving their continued growth in the competitive enterprise software market.
- The convergence of cloud computing, mobile devices and in-memory technology has ushered a new era of possibilities for accessing real-time data, no matter where or when. SAP, driven by strategic acquisitions and cutting-edge innovations, has harnessed this transformative power to fuel its growth.
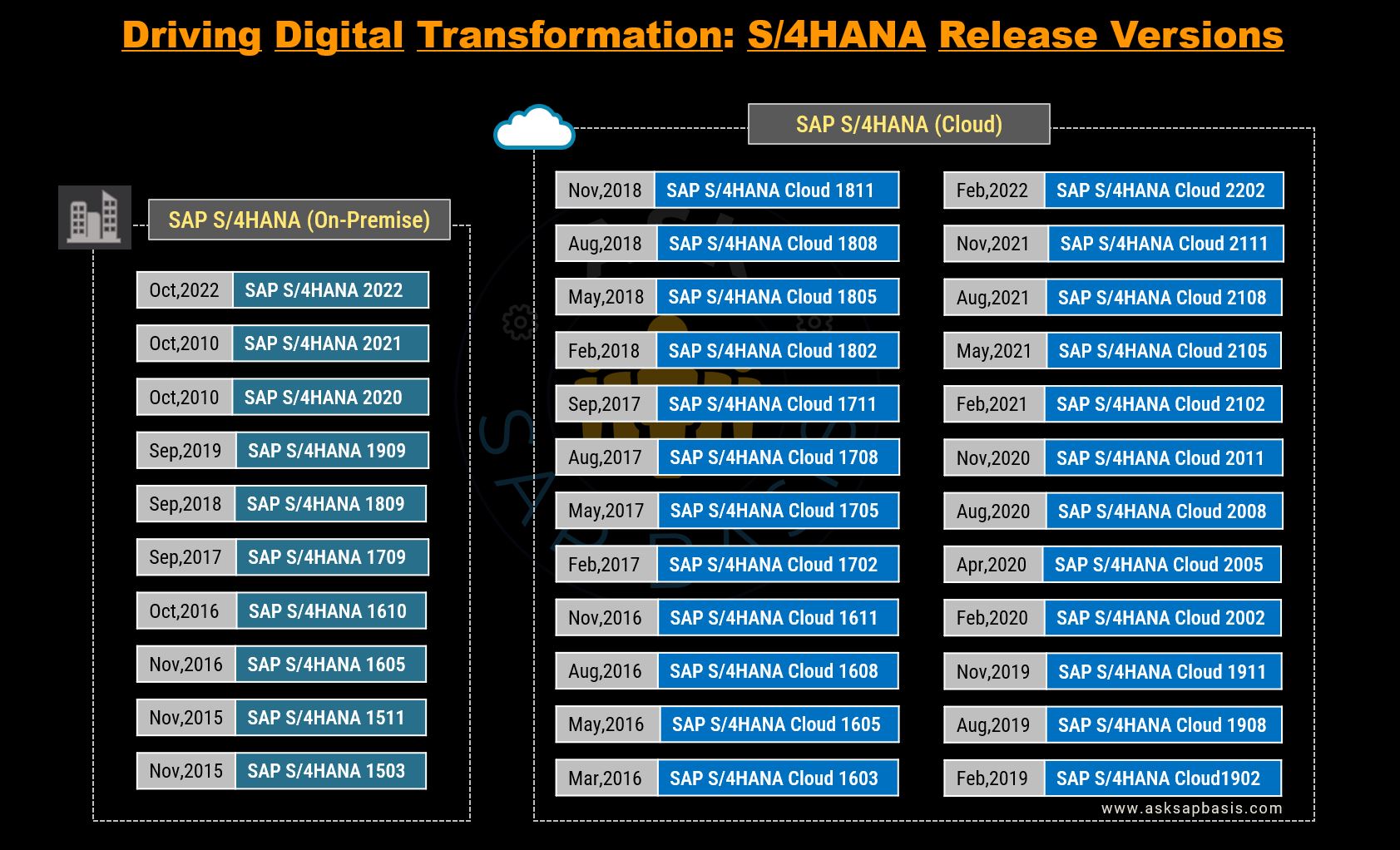
SAP S/4HANA
- In 2015, SAP unveils the 4th generation of ERP software with a new business suite, known as S/4HANA, offering unprecedented IT flexibility and fueled business innovation.
- SAP S/4HANA is crafted exclusively on the SAP HANA advanced in-memory platform, shattering the constraints of the past, and forging a new era of limitless possibilities.
- It embraces the latest design principles, it introduces SAP FIORI user experience (UX) for mobile devices. This sleek and intuitive interface redefines how users interact with enterprise software.
- Recognizing the diverse hybrid need of the businesses, SAP in 2015 soon launched cloud edition of S/4HANA. This innovative offering allows customers to choose a hybrid model, combining on-premise and cloud solutions. This resulted in offering unprecedented IT flexibility and the ability to recognize business innovation.
- SAP’s introduction of SAP S/4HANA marks a significant leap forward, embracing the future of enterprise software. This suit lays the foundation for digital transformation, to stay ahead in rapidly evolving business landscape.
- SAP S/4HANA launch redefines success in the enterprise software market. This also solidifies SAP’s position as an industry leader and a catalyst for innovation and growth.
- Let’s delve into the impressive rooster of acquisitions that fueled SAP’s evolution during this transformative digital era (2011 to 2023) are:
- 2011: Secude, Crossgate, SuccessFactors
- 2012: Datango, Syclo, Ariba
- 2013: Ticket-Web, SmartOps, Camilion, Hybris, KXEN
- 2014: Fieldglass, SeeWhy, Concur Technologies
- 2016: MeLLmo Inc.(Roambi), Fedem Technology, Altiscale, Plat.One, Abakus
- 2017: Gigya
- 2018: Recast.ai, Callidus Cloud, Coresystems, Contextor, Qualtrics
- 2020: Emarsys
- 2021: Signavio, AppGyver
- 2022: Taulia
SAP’s S/4HANA marked a significant leap into the future of enterprise software, laying the foundation for digital transformation in a rapidly evolving business landscape. This launch solidified SAP’s position as an industry leader, driving innovation and growth. Alongside, a series of strategic acquisitions from 2011 to 2022 enriched SAP’s portfolio, reinforcing its commitment to evolving in the digital era.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SAP’s journey through the evolution of ERP software has left an indelible mark in history. From its modest beginnings to its groundbreaking innovations, SAP has constantly adapted and expanded to meet the ever-changing needs of businesses.
With its transition to the cloud and integration of cutting-edge technologies, SAP has solidified its position as a leader in the industry. Through strategic acquisitions and a customer-centric approach, SAP has streamlined operations, empowered decision-making, and driven innovation across sectors.
As SAP continues to shape the future of enterprise software, its remarkable history serves as a testament to its unwavering commitment to innovation and customer success.